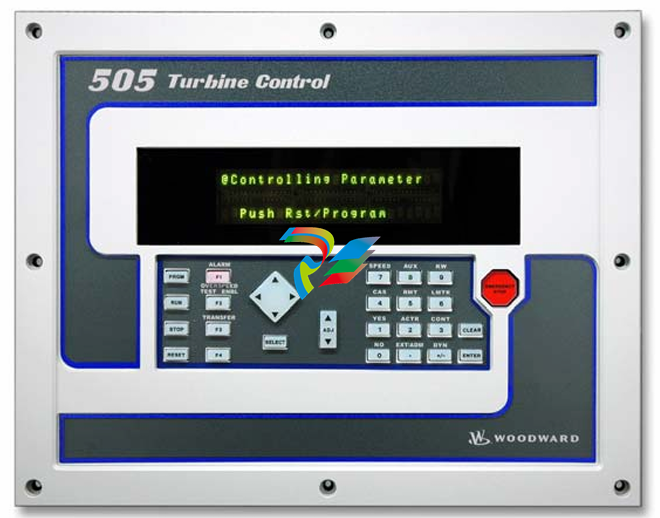
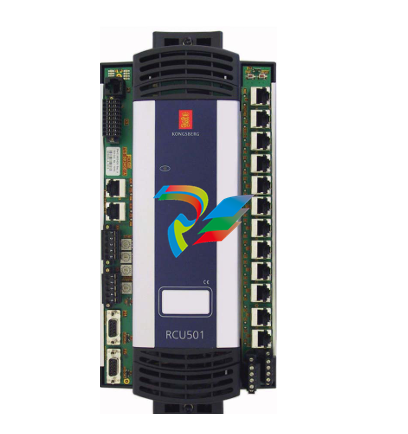
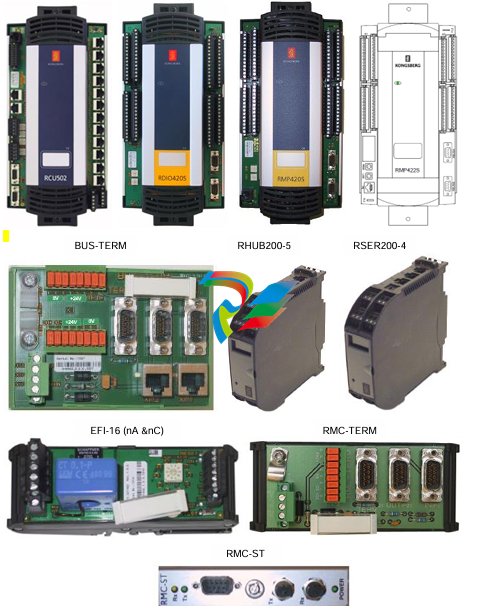
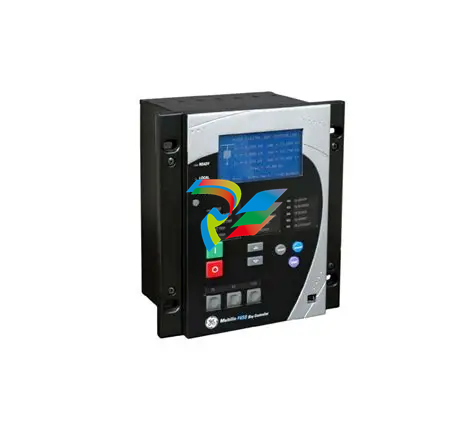
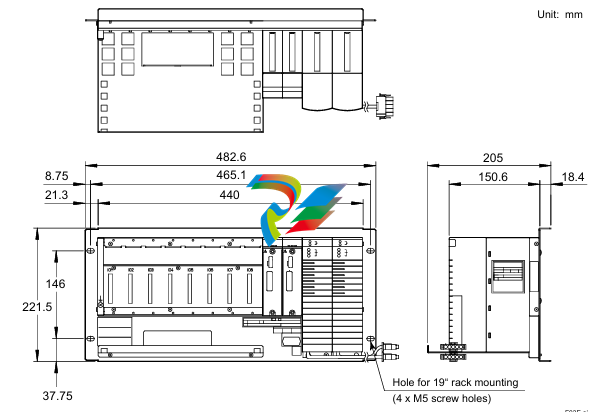
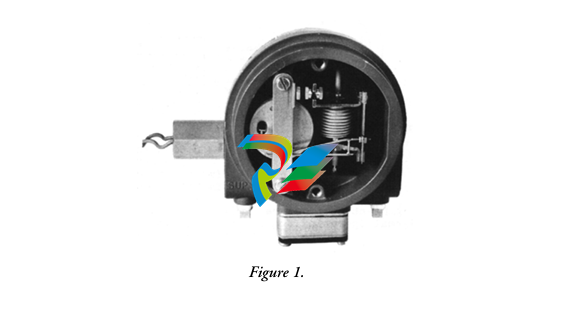
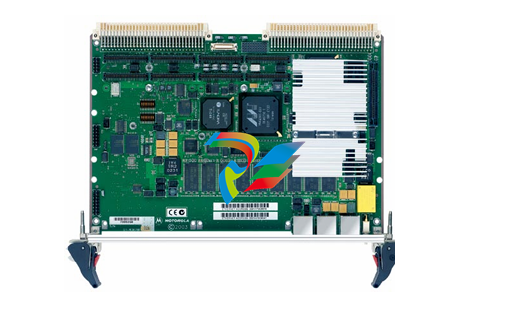
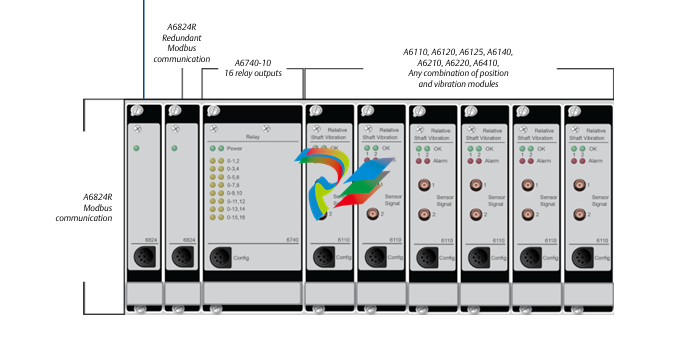
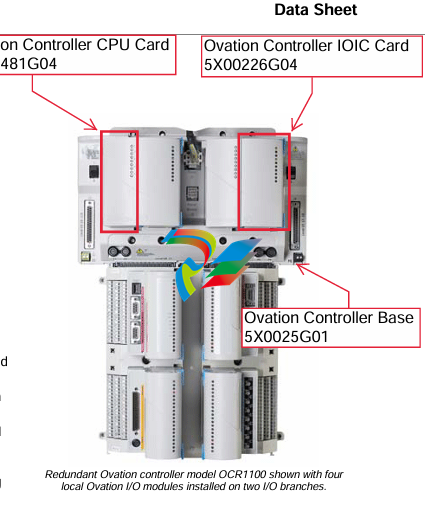
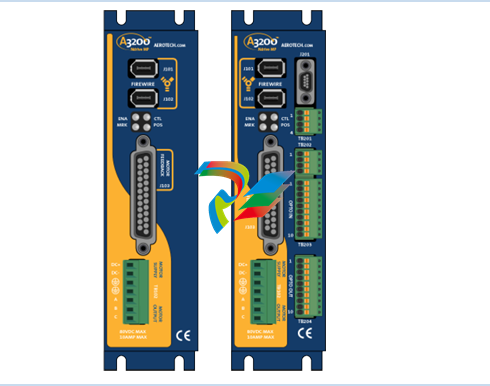
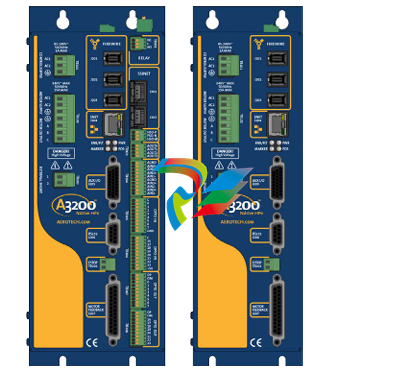
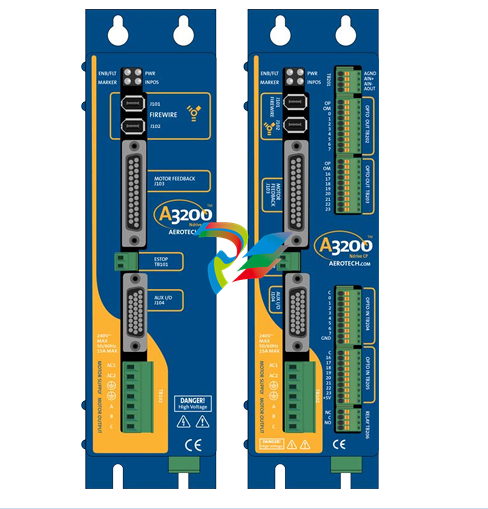
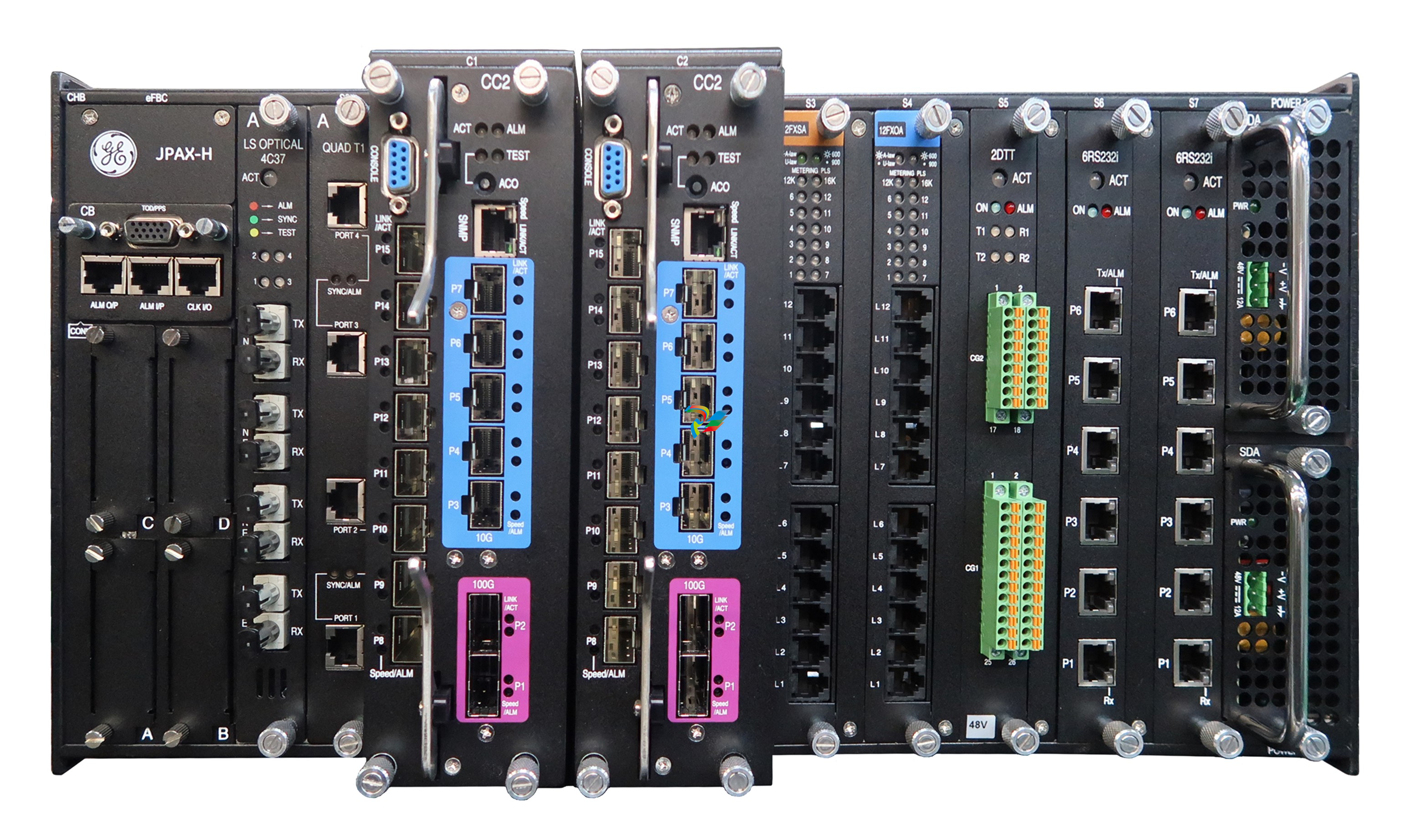
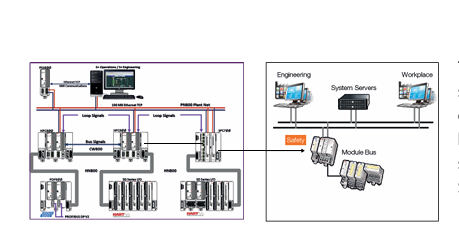
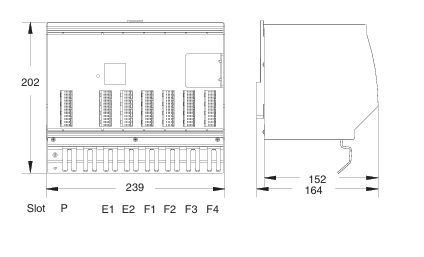
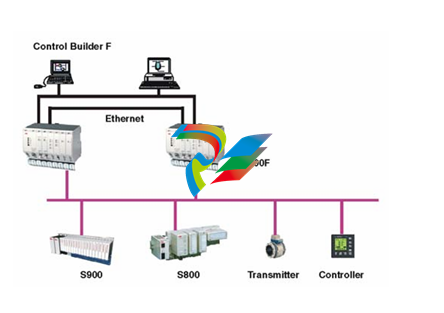
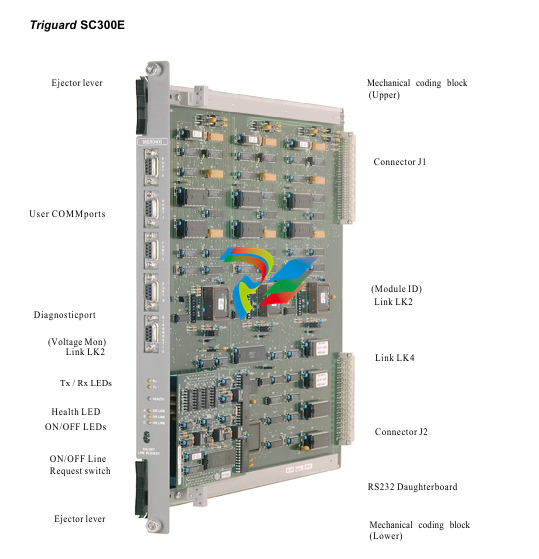
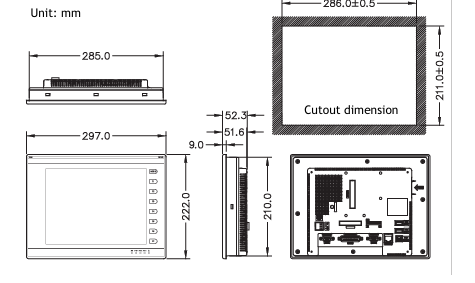
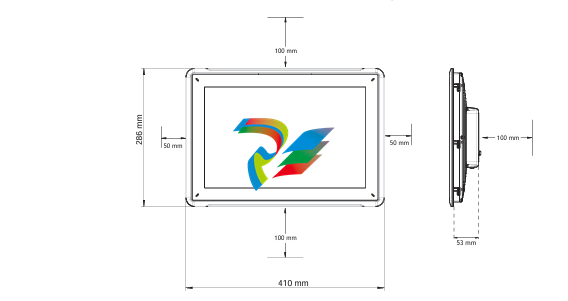
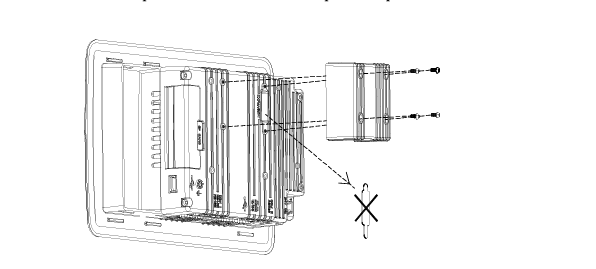
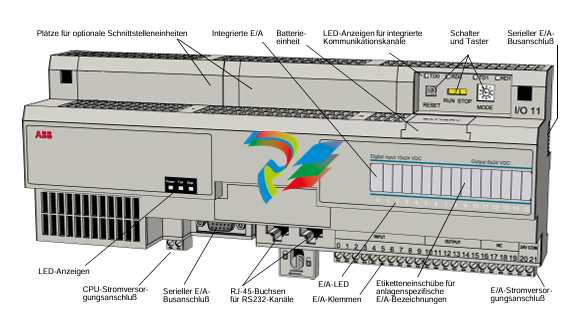
### Precautions for Products #### Installation Precautions 1. **Read the Instructions Carefully** Before installing any product, thoroughly read the installation manual provided by the manufacturer. It contains crucial information about the correct installation sequence, required tools, and any specific environmental conditions the product needs. For example, for some electronic equipment, it might specify that the installation area should be free from excessive dust and humidity to ensure proper functioning. 2. **Check Compatibility** Verify that the product is compatible with other components or systems it will be integrated with. This includes checking aspects like electrical voltage and current ratings, signal types (analog or digital), and communication protocols. For instance, when installing a new sensor in an industrial automation system, make sure its output signal can be correctly received and processed by the existing control unit. 3. **Proper Mounting and Alignment** Ensure that the product is mounted securely and in the correct position. In the case of mechanical products like motors or pumps, proper alignment is essential to avoid excessive vibration, premature wear, and reduced efficiency. For example, when installing a motor, it should be precisely aligned with the driven shaft to prevent misalignment-related issues. #### Operation Precautions 1. **Operator Training** All operators who will use the product should receive proper training. They need to understand the basic functions, operation buttons or interfaces, and how to interpret the displayed information (such as error messages or status indicators). For example, for a complex industrial control panel, operators must know how to set parameters, start and stop processes, and respond to alarms. 2. **Follow Operating Parameters** Adhere to the specified operating parameters provided by the manufacturer. Do not exceed the rated values for factors like temperature, pressure, speed, or load. For instance, if a machine tool has a maximum cutting speed specified, operating it beyond that speed can lead to tool breakage and damage to the workpiece. 3. **Regular Monitoring** During operation, continuously monitor the product's performance. Check for any abnormal noises, vibrations, or changes in output values. Regularly review the status indicators or diagnostic data (if available) to detect potential problems early. For example, in a power generator, monitoring the voltage and current output regularly can help identify issues with the generator's internal components before a major breakdown occurs. Maintenance Precautions 1. **Scheduled Maintenance** Follow the recommended maintenance schedule provided by the manufacturer. This may include tasks like cleaning, lubrication, calibration, and replacement of consumable parts at regular intervals. For example, for a printing press, regular cleaning of the ink rollers and calibration of the print heads are necessary to maintain print quality. 2. **Use of Genuine Parts** When replacing parts during maintenance, always use genuine parts from the manufacturer or authorized suppliers. Using counterfeit or unauthorized parts can lead to compatibility issues, reduced performance, and even safety risks. For example, using a non-genuine filter in an air conditioning system may not effectively remove dust and pollutants, affecting the system's efficiency and lifespan. 3. **Proper Storage** If the product needs to be stored for a period of time, ensure that it is stored in a suitable environment. Protect it from extreme temperatures, moisture, and dust. For some products like batteries, proper storage conditions are crucial to maintain their charge and overall performance. ### Safety Aspects #### Electrical Safety 1. **Proper Grounding** All electrical products should be properly grounded to prevent electrical shock hazards. Ensure that the grounding connection is intact and complies with relevant electrical safety standards. For example, in a household electrical appliance, faulty grounding can put users at risk of electric shock when they touch the appliance's metal casing. 2. **Overload Protection** Install appropriate overload protection devices such as fuses or circuit breakers to protect the product from excessive current flow. If there is a power surge or a short circuit, these devices will cut off the power supply to prevent damage to the product's electrical components and reduce the risk of fire. 3. **Safe Handling of Cords and Plugs** When plugging in or unplugging electrical products, hold the plug firmly and do not pull on the cord. Make sure that the cords are in good condition, without any visible damage like fraying or exposed wires, which could lead to electrical accidents. #### Mechanical Safety 1. **Guards and Protective Covers** For products with moving parts such as machinery or tools, ensure that all guards and protective covers are in place and properly secured during operation. These prevent users from accidentally coming into contact with the moving parts and getting injured. For example, on a lathe machine, the chuck guard should be closed when the machine is running to protect the operator's hands from being caught by the rotating chuck. 2. **Lockout/Tagout Procedures** When performing maintenance or repair work on mechanical products that involve stored energy (such as springs or pressurized systems), follow proper lockout/tagout procedures. This ensures that the energy source is isolated and the product cannot be accidentally started or activated, protecting the safety of maintenance personnel. 3. **Proper Lifting and Handling** For heavy or bulky products, use appropriate lifting equipment and follow proper handling techniques to avoid physical injuries to workers. For example, when moving a large industrial compressor, use a forklift or a crane with the correct load capacity and follow the correct lifting and positioning instructions. #### Chemical Safety 1. **Label Reading** If the product involves chemicals (such as cleaning agents, lubricants, or chemical reagents), carefully read the labels to understand the chemical composition, hazards, and proper handling instructions. For example, some strong acids or alkalis may require specific personal protective equipment when being handled. 2. **Ventilation and Storage** When using or storing chemical-containing products, ensure that the area has proper ventilation to prevent the accumulation of harmful fumes. Store chemicals in accordance with their specific storage requirements, such as separating incompatible chemicals to avoid chemical reactions that could pose a hazard. 3. **Personal Protective Equipment** When working with chemical products, wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) including gloves, goggles, and protective clothing as required by the nature of the chemicals. For example, when handling a flammable solvent, wearing fire-resistant gloves and safety goggles is essential to protect against burns and eye injuries. ### Application Industries #### Manufacturing Industry - The manufacturing industry widely uses various products. In automotive manufacturing, precision machine tools are used for cutting, shaping, and assembling vehicle components. Industrial robots are employed for tasks like welding, painting, and material handling to improve production efficiency and quality. In the electronics manufacturing sector, automated assembly lines use products like pick-and-place machines, soldering equipment, and testing devices to produce electronic components and devices. #### Energy Industry - In the power generation sector, turbines, generators, and control systems are essential products. For thermal power plants, boilers and steam turbines work together to convert heat energy into electrical energy. In the renewable energy field, solar panels, wind turbines, and their associated inverters and control systems are used to harness and convert solar and wind energy into electricity. In the oil and gas industry, drilling equipment, pumps, and pipeline monitoring systems are crucial for exploration, production, and transportation of oil and gas resources. #### Healthcare Industry - Medical devices are key products in this industry. Diagnostic equipment like X-ray machines, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners, and ultrasound devices help doctors detect diseases and assess patients' health conditions. Treatment devices such as infusion pumps, surgical instruments, and radiotherapy equipment are used for medical procedures. Additionally, in hospitals, patient monitoring systems that track vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation are constantly in use. #### Food and Beverage Industry - In food processing plants, products like food mixers, ovens, and packaging machines are used for preparing, cooking, and packaging food products. In the beverage industry, bottling lines with filling machines, capping machines, and labeling machines are essential for producing and packaging beverages. Hygiene monitoring products are also used to ensure food safety and quality by checking parameters like temperature, humidity, and cleanliness levels in production areas. #### Construction Industry - Construction machinery and tools are widely applied. Excavators, bulldozers, and cranes are used for earthmoving and lifting heavy materials during building construction. Concrete mixers and pumps are essential for pouring concrete. Power tools like drills, saws, and grinders are used for cutting, shaping, and finishing building materials. In addition, building materials testing products are used to assess the quality of materials like cement, steel, and bricks before and during construction.
| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|