
Industrial Robot Automation
### Title: Industrial Robot Automation: Transforming Manufacturing and Beyond In the modern manufacturing landscape, industrial robot automation has emerged as a powerful force that is reshaping industries and driving significant advancements in productivity, quality, and efficiency. Industrial robots are no longer a novelty but an integral part of factories and production lines around the world. #### 1. Introduction to Industrial Robot Automation Industrial robot automation involves the use of robotic systems to perform a wide variety of tasks in industrial settings, replacing or augmenting human labor. These robots are designed with precision engineering and are equipped with advanced sensors, actuators, and control systems that enable them to carry out repetitive, complex, and often physically demanding tasks with high accuracy and speed. Robots used in industrial automation can be categorized into different types based on their structure and functionality. For example, articulated robots have multiple joints that mimic the movement of a human arm, allowing them to reach various positions and orientations in a workspace. Cartesian robots, on the other hand, operate along three linear axes, making them ideal for tasks that require precise positioning in a rectangular coordinate system. SCARA robots (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm) are known for their fast and precise movements in a horizontal plane and are commonly used in assembly operations.
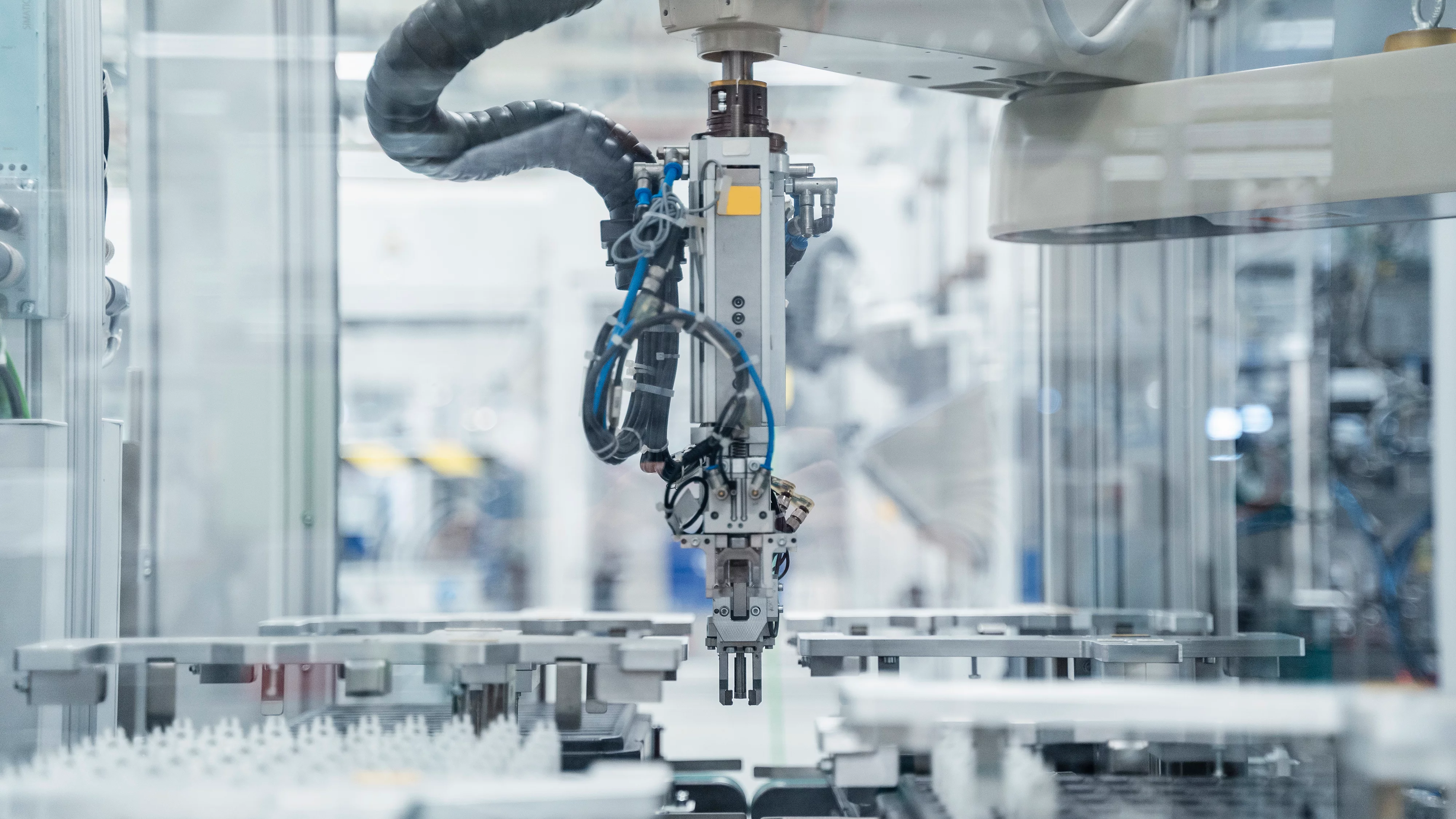

The control systems of industrial robots are highly sophisticated. They are programmed using specialized software that allows operators to define the robot's movements, sequences of operations, and responses to different stimuli. The programming can range from simple point-to-point movements for basic pick-and-place tasks to complex path planning and motion control algorithms for tasks like welding, painting, or intricate assembly work. #### 2. Applications in Different Industrial Sectors - **Automotive Industry**: - Industrial robots have been widely adopted in the automotive industry for decades. They play a crucial role in tasks such as welding car bodies, where precise and consistent welds are essential for structural integrity. Robots can perform hundreds of welds in a short time, ensuring uniformity and high quality. - Assembly operations also heavily rely on robots. They can accurately install components like engines, transmissions, and interior parts with speed and precision. For example, robots can precisely position and fasten bolts, reducing the risk of errors and improving the overall assembly efficiency. - Painting is another area where robots excel. They can apply paint evenly across the surfaces of vehicles, achieving a smooth and consistent finish while minimizing paint waste and exposure of workers to harmful chemicals. - **Electronics Industry**: - In the electronics manufacturing process, robots are used for tasks like component placement on printed circuit boards (PCBs). They can handle tiny electronic components with extreme precision, placing them in the correct positions at a rapid pace. This is vital for the mass production of smartphones, laptops, and other electronic devices. - Testing and inspection of electronic products are also automated using robots. They can check for electrical connectivity, detect defects in components or soldering joints, and ensure that the final products meet quality standards. This helps to improve the overall reliability of electronic goods and reduce the number of faulty items reaching the market. - **Food and Beverage Industry**: - Robots are increasingly being used in food packaging tasks. They can pick up and place food items into containers, seal packages, and label products with speed and hygiene. For example, in a bakery, robots can handle freshly baked loaves of bread and package them neatly, maintaining cleanliness and reducing the risk of contamination. - In beverage production, robots can assist in tasks like palletizing cases of drinks, loading them onto trucks or storage racks. They can handle heavy loads and work continuously, improving the efficiency of the distribution process. #### 3. Benefits of Industrial Robot Automation - **Enhanced Productivity**: Industrial robots can work continuously without breaks, fatigue, or distractions. They can perform tasks at a much faster pace than humans, resulting in increased production output. For example, in a manufacturing plant, a robot can complete dozens of assembly operations in the time it would take a human worker to complete just a few, thereby significantly boosting productivity. - **Improved Quality**: With their high precision and repeatability, robots ensure consistent quality in the products they produce. They can maintain extremely tight tolerances in tasks like machining or welding, reducing the occurrence of defects and variations. This leads to higher-quality finished products that meet or exceed industry standards. - **Increased Workplace Safety**: Many industrial tasks involve working in hazardous environments, handling heavy loads, or being exposed to harmful substances. By automating these tasks with robots, the risk to human workers is greatly reduced. For instance, in a foundry where molten metal is involved, robots can perform pouring and casting operations, protecting workers from burns and other accidents. - **Cost Savings**: Although the initial investment in purchasing and installing industrial robots can be significant, in the long run, they can lead to cost savings. Robots can reduce labor costs as they replace human workers in repetitive tasks. They also minimize material waste due to their precise operations and can lower maintenance costs through predictive maintenance enabled by built-in sensors and data analytics. #### 4. Challenges and Future Trends - **Initial Investment and Return on Investment (ROI)**: The high cost of purchasing, installing, and programming industrial robots can be a deterrent for some small and medium-sized enterprises. Calculating the ROI accurately requires considering factors such as production volume, labor savings, and the lifespan of the robot. However, as the technology advances and prices gradually decline, more companies are finding it feasible to invest in robot automation. - **Workforce Adaptation**: The increasing use of industrial robots may lead to concerns about job displacement. However, it also creates new job opportunities in areas such as robot programming, maintenance, and supervision. There is a need for workforce training and upskilling programs to ensure that employees can transition into these new roles and work effectively alongside robots. - **Complexity of Programming and Integration**: Programming industrial robots to perform complex tasks can be a challenging and time-consuming process. Additionally, integrating robots with existing production systems, such as conveyor belts, automated storage and retrieval systems, and other machinery, requires careful planning and technical expertise. The development of more user-friendly programming interfaces and standardized integration protocols will be crucial to overcome these challenges. - **Advances in Technology**: The future of industrial robot automation will see continued advancements in areas such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT). AI and ML can enable robots to adapt to changing conditions, learn from past experiences, and make more intelligent decisions during operations. IoT connectivity will allow robots to communicate with other devices in the factory, enabling better coordination and optimization of the entire production process. In conclusion, industrial robot automation is transforming the industrial landscape by offering numerous benefits in terms of productivity, quality, safety, and cost savings. Despite the challenges it presents, the continued evolution of this technology will undoubtedly have a profound impact on manufacturing and other industries in the years to come, opening up new possibilities for innovation and growth.




.jpg)






























































.jpg)
.jpg)





.jpg)



.png)
.jpg)

.jpg)
_lVjBYb.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)







.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)






