
Top 13 Innovative Technology in Construction for 2024
In 2023, the market size of the U.S. construction sector was valued at around $2.3 trillion. Though business is booming, the industry faces several challenges relating to materials costs, labor shortages, and operational inefficiencies.
The implementation of new construction technology is serving to alleviate these strains. Far from replacing traditional construction methods, these tools are augmenting the role of human workers and vastly improving outputs on job sites. For example, it’s projected that using robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) could reduce building costs by up to 20%.
Here’s a rundown of 13 innovative technologies that are taking the construction industry by storm.
1. Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality

Yuganov Konstantin / Shutterstock.com
Typically powered using mobile applications, headsets, and other smart devices, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) rose to prominence in the gaming industry, but they have numerous applications in construction.
While AR superimposes images generated by a computer onto its user’s view of the physical world, VR is an entirely computer-generated, immersive environment with which a user can interact in seemingly real or physical ways.
Both technologies are being used to enhance collaboration, improve on-site safety, train new hires, and drive project efficiencies. Key stakeholders benefit from virtual building tours, enabling them to remotely monitor their teams’ progress.
AR goggles scan labels and tags to provide workers with critical information — such as instructions for handling certain machinery or hazard information — which improves on-site safety.
VR and AR are used during employee onboarding, providing new recruits with a safe and engaging means to familiarize themselves with their new surroundings.
Increasingly, construction companies are implementing mixed reality (MR). This combines VR and AR to provide the best of both worlds: a truly immersive and engaging experience that allows users to stay in touch with their surroundings.
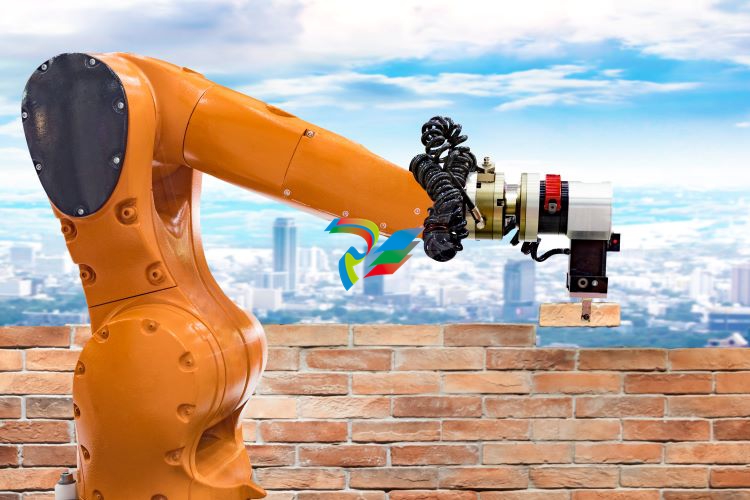
2. Construction Robots

Engineer studio / Shutterstock.com
Construction robots are used on building sites to increase accuracy, improve productivity, reduce accidents, and save costs.
The most common are demolition robots, which currently comprise 90% of the construction robot market. However, thanks to rapid advancements in AI and machine learning (ML), on-site robots are becoming more autonomous and more highly skilled.
Today, these machines are used for excavating and lifting heavy objects, bricklaying, welding, plastering, drilling, assembling, and 3D printing. A combination of increasingly affordable hardware and worker shortages is fuelling the growing demand for robots in construction.
Get more insights in our article “5 Ways Robots Are Assisting Construction Workers.”
3. Digital Twin
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical object, such as a machine or building, or a system, such as computer software.
The device integrates real-world data and other technologies, such as IoT and AI, to run simulations predicting how a product or system will perform. Often used for individual products, such as vehicles or machinery, digital twins can also be applied on a larger scale. For example, digital twin cities enable local governments to plan and manage public services.
In construction, digital twins are typically deployed to support asset management and space optimization, including who will use the space, how, when, and what assets will live there. In addition, the technology can test safety procedures and emergency action plans. For example, it would be possible to simulate a building evacuation to determine if additional exit routes are required.
A digital twin continues to be useful following a project’s culmination by supporting building management teams.
4. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are proving invaluable throughout the entire construction process.
For starters, these technologies help construction firms design spaces that are optimized for human end-users and identify mistakes in a project plan that could lead to long-term problems. This drives operational efficiencies and lowers overall project costs.
When construction begins, AI and ML solutions are implemented to supervise daily operations, which ensures the safety of construction workers and enables project managers to monitor progress in real-time. In addition, AI- or ML-powered robots perform some of the most monotonous and labor-intensive on-site tasks, such as bricklaying and welding. This enables skilled professionals to focus on value-adding activities.
Construction companies leverage the data collected and analyzed by AI and ML solutions to continually enhance their operations. For example, an analysis of on-site video footage might highlight worker non-compliance or safety hazards. These tools also review historic building systems data to inform the design of future projects, enabling companies to optimize various performance metrics, such as energy efficiency and air quality.


.jpg)
















































.jpg)
.jpg)





.jpg)



.png)
.jpg)

.jpg)
_lVjBYb.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)







.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)











.jpg)




.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)








