GEMARK* VIE CONTROL PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
• Automatic reconfiguration
• Accuracy is specified over full operating temperature
• Internal temperature sensor
• LEDs:
- Power status and attention
- Ethernet link-connected and
communication-active
- Application-specific
• 28 V dc power
• Internal solid-state circuit breaker and soft start
A power supply provides a regulated 28 V dc power feed to each I/O pack.
The negative side of the 28 V dc is grounded through the I/O pack metal
enclosure and its mounting base. The positive side has solid-state circuit
protection built into the I/O pack with a nominal 2 A trip point. Online repair
is possible by removing the 28 V dc connector, replacing the I/O pack, and
re-inserting the power connector. I/O packs are automatically reconfigured
if the Auto-Reconfiguration feature is enabled.
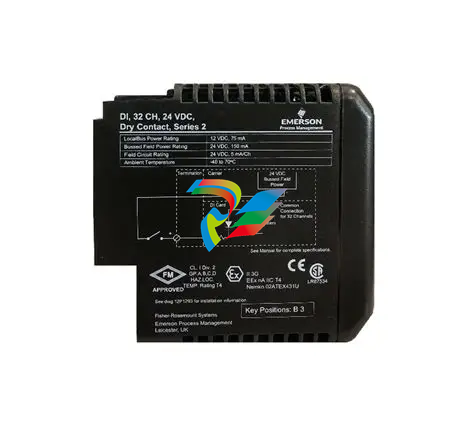
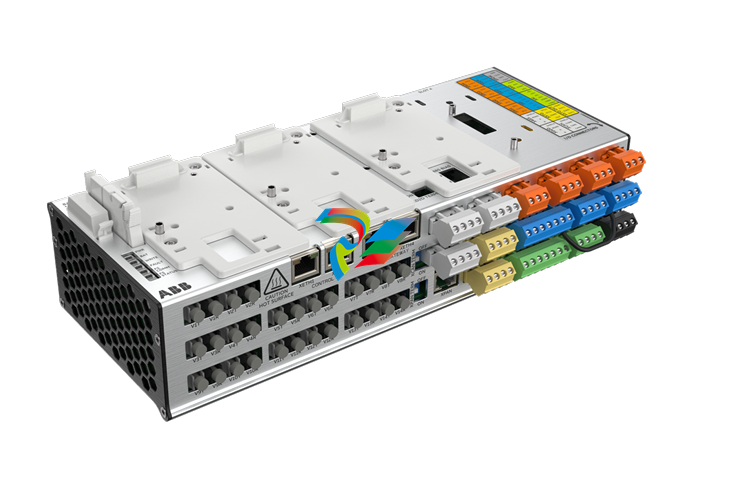
TERMINAL BLOCKS
Signal flow begins with a sensor connected to a terminal block on an I/O
module. The terminal board mounts to the cabinet and is available in two
basic types: T-type and S-type modules.
T-type modules typically fan the inputs to three separate I/O packs.
They contain two removable 24-point, barrier-type terminal blocks. Each
point can accept two 3.0 mm2 (#12,AWG) wires with 300 V insulation per
point and spade or ring-type lugs. Captive clamps are also provided for
terminating bare wires. Screw spacing is 9.53 mm (0.375 in) minimum,
center-to-center. T-type modules are normally surface mounted, but may
also be DIN-rail mounted.
A shield strip is provided next to each block, which is actually the left-hand
side of the metal base where the module is mounted. Wide and narrow
modules are arranged in vertical columns of high and low-level wiring that
can be accessed from top and/or bottom cable entrances. An example of a
wide module is a module containing magnetic relays with fused circuits for
solenoid drivers.
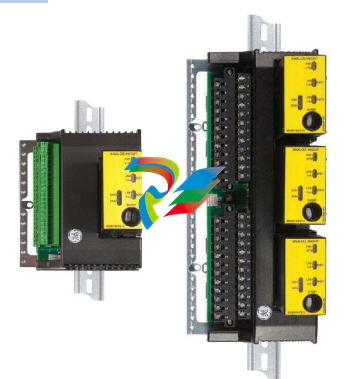
Box-type and Barrier-type Terminal Blocks in Simplex and Triple Redundant Configuration
S-type modules provide a single set of screws for each I/O point and allows
a single I/O pack to condition and digitize the signal. This board is used
for simplex, dual, and dedicated triple modular redundant (TMR) inputs by
using one, two, or three boards. They are half the size of T-type modules
and are DIN-rail or surface mounted. Two versions of the S-type modules
are available: fixed terminal blocks and removable terminal blocks.
Fixed box-type terminal blocks accept one 3.0 mm2 (#12 AWG) wire or two
2.0 mm2 (#14 AWG) wires with 300 V insulation per point. Screw spacing is
5.08 mm (0.2 in) minimum, center-to-center. Removable box terminals may
be replaced with spring-cage-clamp, insulation displacement, or crimpand-stab terminals. A shield strip is provided on each terminal block and is
tied to functional ground.
TEMPERATURE RATINGS
Mark VIe electronics are packaged in different locations world-wide and
customized for a variety of protection classifications with and without
ventilation and cooling. Controllers, I/O modules, power supplies, etc. are
rated for -30 to 65°C (-22 to 149°F) at the electronics. To compliment the
Mark VIe Control’s native I/O modules, a variety of fieldbus solutions are
available with master communication gateways on the I/O network. These
modules have slightly reduced operating temperature ratings:
• PROFIBUS® Master Gateway: -20 to 55°C (-4 to 131°F)
• CANopen® Master Gateway: -20 to 55°C (-4 to 131°F)
• FOUNDATION Fieldbus™ Linking Device: 0 to 55°C (32 to 131°F)
Modules with reduced operating temperatures should be mounted lower
in the cabinet to avoid the natural temperature gradient from the bottom
to the top of the enclosure. Control room equipment such as operator
stations has an operating temperature range of 20 to 30°C (68 to 86°F).
For shipping and storage, the controllers, I/O modules, power supplies, etc.
are rated -40 to 85°C (-40 to 185°F), and control room equipment is rated
0 to 30°C (32 to 86°F).
I/O MODULES
I/O modules can be categorized as generic and application-specific.
As an example, discrete inputs (contact inputs) are used in virtually all
applications and differ primarily in their voltage rating. Other considerations
in selecting a module are its redundancy, isolation (group or point), terminal
block type, availability for safety applications (IEC 61508), and approval for
hazardous locations.
A typical application-specific module is a servo module that is used for
fast closed-loop control of a turbine’s servo valve actuator or a complete
emergency over-speed trip system for a turbine. These unique modules
will not be described in the following tables. However, some applicationspecific modules such as a vibration module is commonly applied in
monitoring radial and axial shaft displacement of rotating machinery in
plant distributed control systems and will be described in a separate table.
Analog Input (AI) and Analog Output (AO) Modules
• V/I designates a voltage / current input