NIOPERATING INSTRUCTIONS AND SPECIFICATIONS NI 9505
installed on power supply inputs near power entries to
modules and controllers. Power supply and module cables
must be separated on opposite sides of the enclosure and
must enter and exit through opposing enclosure walls.
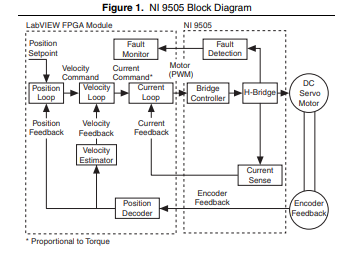
NI 9505 Hardware Overview
The NI 9505 provides unique flexibility and customization. The
NI 9505 works together with the LabVIEW FPGA Module to
create a highly customizable motor drive or actuator amplifier.
Figure 1 illustrates the functionality of the NI 9505 working in
conjunction with the LabVIEW FPGA Module in a typical motion
control application. Figures 2 and 3 show more detailed versions
of the position, velocity, and current loops implemented in the
LabVIEW FPGA Module. A typical application contains a
position loop, velocity loop, and current loop, implemented in
the LabVIEW FPGA Module block diagram. Depending on the
application, you may not need to use all three loops. The examples
installed in the labviewexamplesCompactRIOModule
SpecificNI 9505 directory illustrate methods for implementing
each of these loops.
The NI 9505 returns the motor or actuator current data to the
LabVIEW FPGA Module for use in a current loop or for
monitoring. The NI 9505 also returns status information such as
drive fault status, VSUP presence, and emergency stop status to the
LabVIEW FPGA Module for use in system monitoring. Refer
to the NI 9505 Reference Help book in the LabVIEW Help,
available by selecting Help»Search the LabVIEW Help, for
more information about the available status information.
The LabVIEW FPGA Module generates a PWM signal and sends
the signal to the NI 9505. The PWM signal is proportional to the
desired current or torque you want to provide to the motor or
actuator. Increasing the PWM duty cycle results in increased
current and thus increased torque.
Quadrature encoder signals pass through the NI 9505 and are
processed in the LabVIEW FPGA Module for use in the position
Hot-Swap Behavior
The NI 9505 is always disabled when it is inserted in the chassis,
regardless of whether VSUP is present or not. You can enable the
drive using the Enable Drive method in software. Refer to the
NI 9505 Reference Help book in the LabVIEW Help, available
by selecting Help»Search the LabVIEW Help, for more
information about enabling the drive.
When the NI 9505 is removed from the chassis while it is enabled,
the power to the motor is removed and the motor decelerates to a
stop based on its own friction.
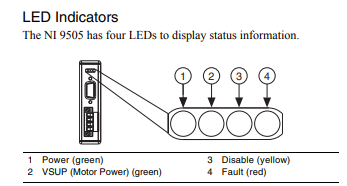
Power
The Power LED (green) illuminates when the NI 9505 is properly
inserted into a powered chassis.
Note The Power LED does not illuminate when the
chassis is in sleep mode.
VSUP
The VSUP LED (green) illuminates when the motor DC power
supply is properly connected and powering the drive.
Disable
The Disable LED (yellow) illuminates when the drive is disabled.
The drive is disabled by default at power-on. You can enable the
drive using the Enable Drive method in software. Refer to the
NI 9505 Reference Help book in the LabVIEW Help, available
by selecting Help»Search the LabVIEW Help, for more
information about this method.
Fault
Caution If the Fault LED is lit, determine the cause of the
fault and correct it before enabling the drive.
The Fault LED (red) illuminates when a fault occurs. A fault
disables the drive. Causes for fault are the following:
Caution VSUP greater than 40 V will result in damage to
the NI 9505.
• Overvoltage
• Undervoltage
• Motor terminal (MOTOR±) short to VSUP
• Motor terminal (MOTOR±) short to COM
• Module temperature exceeds 115 ºC
• Sending commands to the motor before enabling the drive
Note Do not command motor movement until the drive is
enabled with the Enable Drive method. Attempting to
control the motor before it is enabled will result in a fault.
• Violating PWM minimum pulse width requirements. Refer to
the Specifications section for more information about PWM.
Sleep Mode
This module supports a low-power sleep mode. Support for sleep
mode at the system level depends on the chassis that the module is
plugged into. Refer to the chassis manual for information about
support for sleep mode. If the chassis supports sleep mode, refer
to the software help for information about enabling sleep mode.
Visit ni.com/info and enter cseriesdoc for information about
C Series documentation.
Typically, when a system is in sleep mode, you cannot
communicate with the modules. In sleep mode, the system
consumes minimal power and may dissipate less heat than it does
in normal mode. Refer to the Specifications section for more
information about power consumption and thermal dissipation.
Wiring the NI 9505
The NI 9505 has a 9-pin female DSUB connector that provides
connections for the encoder inputs, a +5 V connection for encoder
power, a connection for an emergency stop input, and a connection
to COM. Refer to Table 1 for the pin assignments.