ABBDCS800 Hardware Manual DCS800 Drives (20 to 5200 A)
maintenance see chapter Dimensions and weights.
Cabinet installation
The required distance between parallel units is five millimetres (0.2 in.) in
installations without the front cover. The cooling air entering the unit must not exceed
+40 °C (+104 °F).
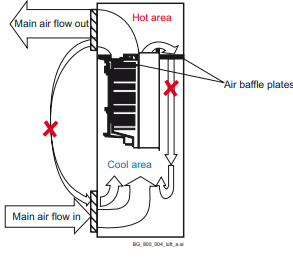
Preventing cooling air recirculation Unit above another
Prevent air recirculation inside and outside the cabinet.
Terminal cover according to VBG 4 regulations
For converter modules size D1 - D4 shrouds for protection against contact are
provided.
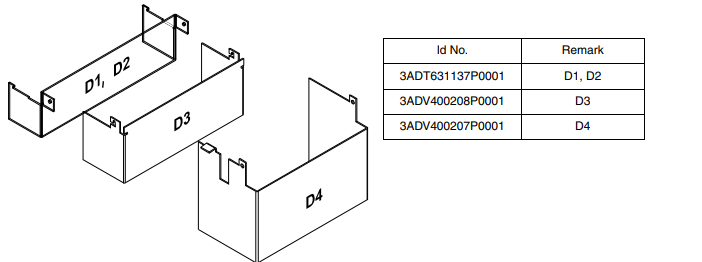
Mount the D1, D2 cover using the existing lateral pins and than swing it down to snap it into the terminal
row. D3 and D4 mounting is the same, without the snap-in mechanism.
Mounting the converter module D4+ inside an enclosure
Cooling air inlet
The cooling fan blows the air out of the front, right and left side of the converter
module. View from
View from: right side front side left side:
Free space around the converter module
In mm:
Planning the electrical installation
Chapter overview
This chapter contains the instructions that must be followed when selecting the
motor, cables, protections, cable routing and way of operation for the drive system.
Always follow local regulations. This chapter applies to all DCS800 converter
modules.
Attention:
If the recommendations given by ABB are not followed, the drive may experience
problems that the warranty does not cover. See also Technical Guide.
Options
Line reactors (L1)
For armature and field supply.
When thyristor converters operate, the line voltage is short-circuited during
commutation from one thyristor to the next. This operation causes voltage dips in the
mains PCC (point of common coupling). For the connection of a power converter
system to the mains, one of the following configurations applies:
Configuration A
When using a converter, a minimum of impedance is required to
ensure proper performance of the snubber circuit. Use a line reactor
to meet this minimum impedance requirement. The value must
therefore not drop below 1 % uk (relative impedance voltage). It
should not exceed 10 % uk, due to considerable voltage drops at the
converters outputs.
Configuration B
If special requirements have to be met at the PCC (standards like EN
61 800-3, DC and AC drives at the same line, etc), different criteria
must be applied for selecting a line reactor. These requirements are
often defined as a voltage dip in percent of the nominal supply
voltage. The combined impedance of ZLine and ZL1 constitute the total
series impedance of the installation. The ratio between the line
impedance and the line reactor impedance determines the voltage dip
at the PCC. In such cases, line chokes with an impedance around 4 %
are often used.
Example calculation with ukLine = 1 % and ukL1 = 4 %:
Voltage dip = ZLine / (ZLine + ZL1) = 20 %. Detailed calculations see