ABBAC 800M PROFIBUS DP Configuration
the project. The conversion is done with the GSD Import Tool.
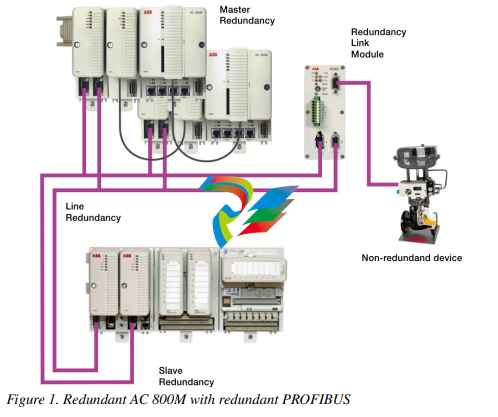
The following figure shows the redundant PROFIBUS connected to the redundant
AC 800M controller
Section 2 Functional Description
PROFIBUS Basics
Basic Functions DP-V0
Cyclic Data Communication
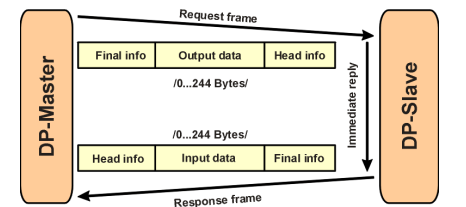
The data communication between the DPM1 (DP Master Class 1) and its assigned
slaves is automatically handled by the DPM1 in a defined, recurring sequence. With
each user data transfer, the master can write up to 244 bytes of output data to the
slave and read up to 244 bytes of input data from the slave. The Data is read and
written synchronously in one procedure
The assignment of the slaves to the DPM1, CI854/CI854A in this case, is done via
the HW configuration in Control Builder M.
The data communication between the DPM1 and the slaves is divided into three
phases: parameterization, configuration and data transfer. Before the master
includes a DP slave in the data transfer phase, a check is run during the
parameterization and configuration phase to ensure that the configured setpoint
configuration matches the actual device configuration. During this check, the device
type, format and length information and the number of inputs and outputs must also
correspond. This provides you with reliable protection against parameterization
errors.
Diagnostics
In addition to the cyclic data the PROFIBUS slave unit provides diagnostic data.
With this diagnostic data the slave can indicate errors or warnings on the slave unit,
the I/O-units or the I/O-channels. Some diagnostic data is generic and defined by the
PNO. But most of the diagnostic data is manufacturer specific.
The following errors/warnings are examples for PROFIBUS diagnostics:
Channel related:
– Wire break
– Short circuit
Module related:
– Wrong module type
– Module missing
Slave related:
– Power supply 2 error
– Internal bus error
The CI854/CI854A supports the operation of PROFIBUS DP-V0 diagnostics. The
diagnostic data transferred from the slave to the master is mapped by the
CI854/CI854A to the unit status of the PROFIBUS slave unit or the related I/O-unit
and is indicated as error or warning in the UnitStatus in Control Builder M for the
specific unit.
Only that diagnostic data configured within the hardware definition file is operated
by the system. The configuration includes
– Selection of diagnostic to be operated by the system.
– Mapping of the diagnostic information within the diagnostic frame on
PROFIBUS to the specific HW unit (slave or I/O unit).
– Definition of the corresponding bit in the unit status for the specific
diagnostic information. Use of device specific codes in
ErrorsAndWarnings and ExtendedStatus.
– Definition if the diagnostic information shall be indicated as error or
warning.
– Definition of the presented text within unit status and alarm/event for the
specific diagnostic information.
– Definition if in addition an alarm or event shall be generated for the
specific diagnostic information. If yes also the severity has to be defined.
For S800 I/O and S900 I/O the configuration for the diagnostics is already specified
in the hardware definition files that are provided with the system. For other slaves
the configuration for PROFIBUS diagnostics can be done via the DeviceImport
Wizard. The Device Import Wizard provides a dialog to pick up the diagnostic data
from the GSD-file and map it to the DeviceSpecific and ExtendedStatus bits of the
HwStatus for the related slave unit or I/O-unit. The dialog also supports the
configuration of alarms/events based on the diagnostic data. For more information
please refer to the online help for the GSD Import Tool.
DP Master Class 1 (DPM1) and Class 2 (DPM2)
TheDP master class 1 is the master that is in cyclic data transmission with the
assigned slaves. To get into the cyclic communication the DPM1 has to configure
the slave before.
The DP master class 2 is used for engineering and configuration. It does not have
cyclic data transmission with the slave devices. Normally a DPM2 is only connected
temporarily to the bus. A DPM2 can have class 2 communication to the slave
devices before the slaves are configured via DPM1 and cyclic communication is
active.
System Behavior
For a DPM1 master the following operating states are defined:
Stop
No data communication between the DPM1 and the slaves.
The CI854/CI854A is of type DP master class 1 (DPM1) and class 2 (DPM2).
Clear
The DPM1 reads the input information of the slaves and keeps the outputs of the
slavs in a fail-safe state (“0” output).
Operate
The DPM1 is in the data transfer phase. In cyclic data communication, inputs are
red from the slaves and output information written to the slaves.
The reaction of the system to a fault during the data transfer phase of the DPM1, for
example a failure of a slave, is determined by the “Auto Clear Modus” defined via
the BP flag configuration in the settings tab for CI854/CI854A. If this parameter is