
8 Examples of Cobots in Everyday Life
Collaborative robots (cobots) are designed for direct interaction with human beings, whether in a shared space or close proximity.
In the industrial sector, these machines are proving themselves to be worthy teammates, carrying out tasks such as packing, welding, material handling, palletizing, labeling, inspecting product quality, and assembling. As well as enabling workers to pursue more value-adding and creative activities, cobots can drive inclusivity in industrial businesses by supporting employees with physical disabilities.
Cobots are a fast-expanding segment of industrial automation, with the industry projected to grow to $2.2 billion by 2026. But what does 2024 have in store?
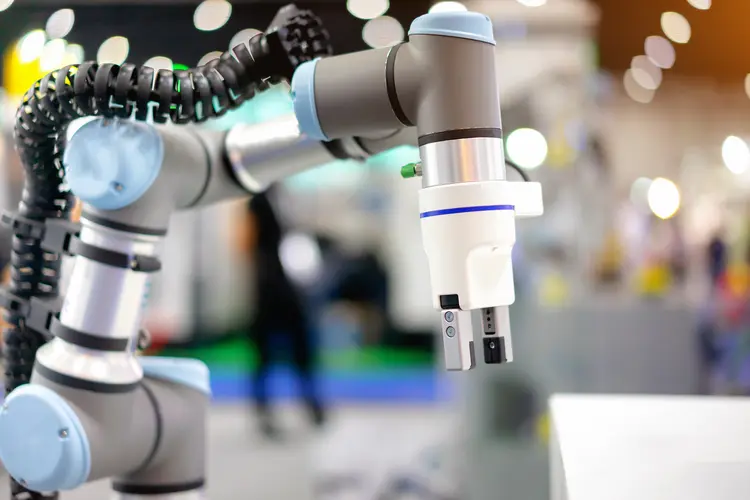

Is 2024 the Year of the Cobot?
Joe Campbell, Senior Manager of Applications Development and Strategic Marketing at Universal Robots, believes that cobot automation will become more sophisticated yet more straightforward to use in the coming years, driving increased demand among original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). The company’s sales of cobots for integration in OEM solutions grew by 50% in 2022.
The industrial sector will enjoy a rise in turnkey solutions, lightweight cobots that drive modularity in production, and higher-payload and longer-reach cobots.
Other industries also will benefit from increasingly sophisticated cobots. In agribusiness, for example, they can increase yield, support monitoring and forecasting, address labor shortages, and improve safety. In healthcare, cobots are assisting surgeons in the operating room, and in hospitality, they can serve food and drinks, clean high-touch areas, and even scoop ice cream.
Let’s take a look at some of the most impressive cobots on the market today.
1. Singrow: Agriculture Cobot
Singapore-based Singrow develops innovative agri-technology solutions designed to guarantee premium quality fruits and vegetables and revolutionize urban farms.
The company has worked with Universal Robots and Augmentus to develop an AI-powered cobot for use in its harvesting and pollination systems. The robot has been programmed to identify the flowers and the fruits of strawberries; facilitating more efficient pollination when it identifies a flower and selecting the fruit once it has ripened.
Thanks to this technology, Singrow’s indoor farms are 40% more energy efficient and produce a 20% higher yield than a conventional strawberry farm. Technology solutions like this are especially welcome in Singapore, where large open spaces are in short supply.
2. Welding Cobots
Until very recently, welding was dismissed as a task too complex for a cobot to handle. But now, a large portion of cobot turnkey systems are expected to accommodate welding applications.
Universal Robots reported that its welding channel grew by more than 80% in the first nine months of 2022.
Sheet metal manufacturer Raymath, for example, deployed four of Universal Robots’ cobot welders in 2022. These machines manage hard-to-staff processes and weld at double the speed of a human employee, resulting in 4X productivity improvement.
3. UR20: Cobot for Small Industrial Spaces
Universal Robots had a busy last couple of years, also launching the UR20 cobot.
This machine, which is built for 20 kg payloads, faster speeds, and superior motion control, is expected to transform industries including palletizing and welding. As well as being capable of tending to several machines in the same cycle, its 1,750 mm stretch means it can reach much further into machines. The UR20 is the lightest robot in its class, weighing in at just 64 kg.
Universal Robots says this next-generation cobot will “handle more tasks, fit more applications, and assist in more environments than ever before.”
4. Whiz: Cleaning Cobot
In a post-COVID world, autonomous vacuum cleaners like Whiz increasingly are commonplace. Introduced by Japanese-based SoftBank Robotics in 2019, this fully autonomous cobot is already in operation in hotels, schools, senior living facilities, and universities.
The AI-powered cobot cleans up to 15,000 square feet per charge, and users gain near-time visibility into when and where cleaning was performed. Whiz also is fitted with sensors so it can recognize when people are close by or approaching and emit a friendly alert.
The cobot won the equipment category for the ISSA 2019 Innovation Award, and more than 20,000 units have been deployed globally.
5. Rita and Chippy: Restaurant Cobots
Restaurant chain Chili’s Grill & Bar enlisted Bear Robotics to develop a cobot called Rita, who can seat customers, serve meals, and even sing to diners on their birthdays. First piloted in 2020, Rita is now present in 51 restaurants across eight states.
Another restaurant chain, Chipotle Mexican Grill, has also invested in cobot development. Chippy, designed by Miso Robotics, is an AI-powered machine that cooks tortilla chips for customers via the restaurant’s signature technique. Last September, Chipotle announced it would debut Chippy at its site in Fountain Valley, Calif.


.jpg)
















































.jpg)
.jpg)





.jpg)



.png)
.jpg)

.jpg)
_lVjBYb.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)







.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)











.jpg)




.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)








