
Top 13 Innovative Technology in Construction for 2024
Finally, AI and ML are used in predictive maintenance, highlighting when construction machinery or building systems, such as electrical systems, will require replacing or repairing. This prevents equipment failures, which can lead to project delays and increased costs.
5. Building Information Modeling
Building information modeling (BIM) is a construction technology used for planning, design, and development, providing construction professionals with an intelligent digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of structures and buildings.
Before the advent of BIM, construction firms used 2D blueprints or, more recently, computer-aided design (CAD) to map out building plans. However, these technologies had their limitations, making it difficult for stakeholders to visualize requirements and measurements and access granular detail.
A BIM tool, on the other hand, provides users with accurate and agile 3D models and includes information about parts and materials, finance, logistics, and procurement.
Today, the technology is deemed so essential that it is sometimes mandated for construction projects. Not only does BIM ensure efficiency, quality, and safety, but it also drives collaboration among architects, engineers, real estate developers, contractors, and manufacturers, who can share information via a common data environment (CDE).
6. Blockchain Technology
Three major challenges in the construction industry are transparency, accountability, and inefficiency, not least because projects so often involve multiple stakeholders and subcontractors with conflicting priorities and requirements. Blockchain technology — which enables transparent information sharing within a business network — addresses these challenges in several ways.
Firstly, it enables seamless tracking of products and materials across even the most complex of supply chains, highlighting issues such as theft and fraud.
Secondly, blockchain facilitates timely and cost-effective money transfers between multiple parties and across different regions. This is particularly beneficial when different stakeholders require different forms of payment. The technology ensures that every transaction — and its associated data — is tracked and logged securely and transparently. Increasingly, BIM and blockchain technology solutions are being integrated to support a more robust contracting process.
Thirdly, the technology can track safety violations that occur on construction sites to ensure contractors are held accountable. Any data relating to a violation will be stored on a blockchain.
Finally, blockchain-powered project management platforms record all project data to enhance cross-team collaboration and drive operational efficiencies.
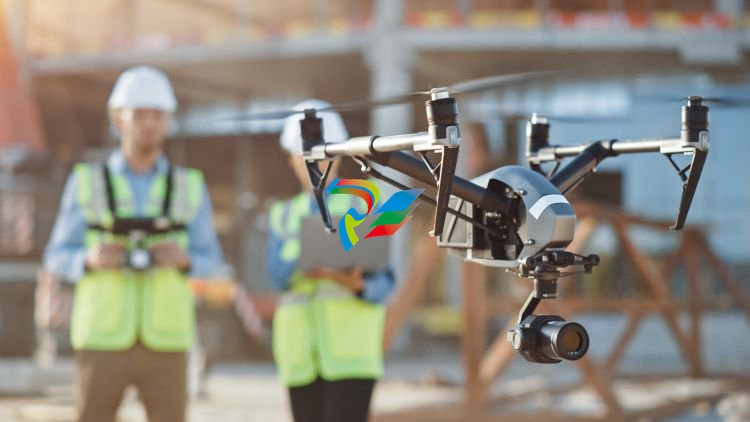
7. Drones

Gorodenkoff / Shutterstock.com
The construction sector has experienced a 239% growth in drone use year over year, with companies leveraging these devices for land and site analyses, planning and design, equipment tracking, project reporting, security surveillance, and cross-team collaboration.
Drone usage lowers costs, drives operational efficiencies, reduces risk, and improves data accuracy. For example, surveying a large job site using human workers is time-intensive and labor-intensive. Drone surveyors, however, can cover 120 acres of land each hour, which equates to a 60-fold improvement in surveying efficiency.
This saves money since less labor is required while helping companies adhere to strict project deadlines. In addition, since drones can access hard-to-reach and hazardous areas, they offer a safer means of site monitoring and data collection.
8. 3D Laser Scanner
A 3D laser scanner uses specialized software and a laser probe to capture a physical object’s exact size and shape as a digital 3D representation.
The technology’s ability to measure minute details and create highly accurate point clouds means it is perfectly suited to a construction site’s contoured surfaces and complex geometries.
Indeed, the demand for 3D laser scanning in the construction industry is expected to grow by $10 billion by the end of 2024.
The technology proves useful throughout a project’s life cycle — from design and construction to operations and renovations. As well as improving accuracy, reducing manual labor, driving collaboration, and enhancing critical project data collection, 3D laser scanners can lower costs by 50% compared to 2D scanning.
Despite the many benefits associated with laser scanning, upfront costs are high, and skilled workers are required to operate the technology.
9. 4D Building Information Modeling
A 4D BIM model consolidates 3D BIM models created during a specific time period to produce a virtual construction sequence. Put plainly, 4D BIM provides a simulation of construction activities over time.
The technology provides full visibility of a project and the teams working on it, enabling project leads to monitor progress, keep large projects on schedule, identify errors, and make informed decisions regarding the future of a project.



















.jpg)












































.jpg)
.jpg)





.jpg)



.png)
.jpg)

.jpg)
_lVjBYb.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)







.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)











.jpg)





