
Top 13 Innovative Technology in Construction for 2024
Today, the construction sector most commonly uses the technology to win subsequent project bids since it is a great way to showcase historic work. Some teams are also using it to optimize processes and reduce costs.
10. 3D Printing
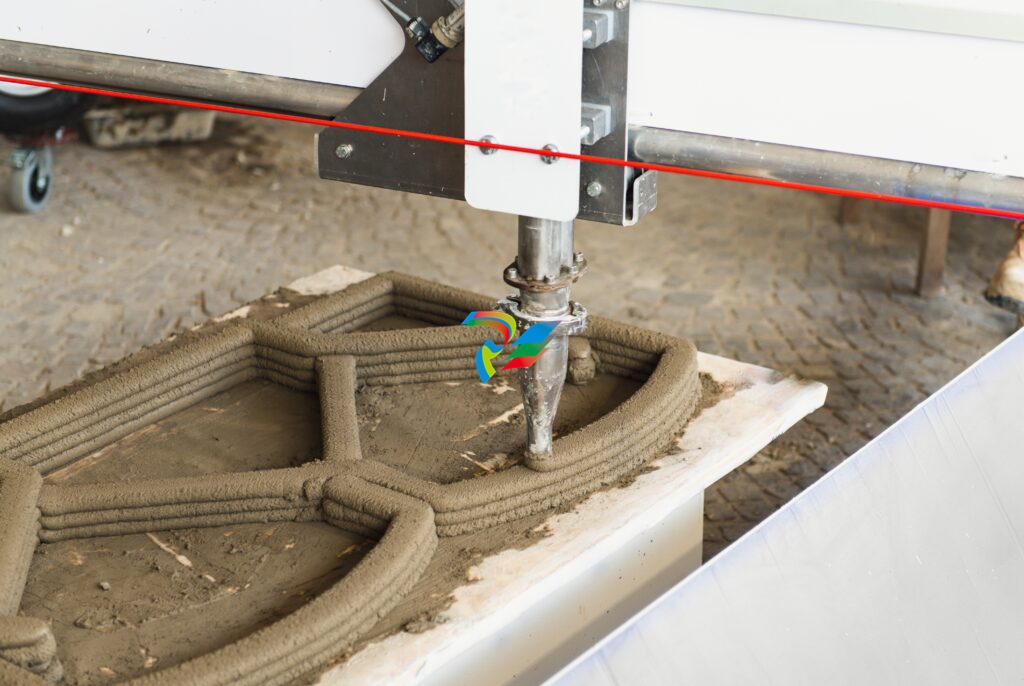
Fabio Pagani / Shutterstock.com
It’s no exaggeration to say that 3D printing is revolutionizing the construction sector.
For starters, 3D printing renders project-halting component shortages a thing of the past. As long as appropriate raw materials are available, construction workers can print whatever they need whenever they need it.
This technology is also supporting the shift to sustainable construction by enabling a precise amount of material to be used and reducing on-site waste by up to 60%. Even last-minute design choices won’t result in additional waste; fine-tuning of designs and product customization can occur right up until the point of construction.
Additionally, 3D printing reduces construction workers’ exposure to risk by taking on formerly manual tasks.
11. Resource and Workforce Management Software
Resource and workforce management software typically helps companies streamline and automate processes relating to personnel, such as forecasting, staffing, and scheduling.
In construction, the pace of change is fast and project leads must juggle multiple stakeholders and contractors at any given time. Labor shortages, safety compliance issues, and scheduling conflicts present further challenges. A resource or workforce management tool alleviates these pressures by supporting communication, planning, data management, rostering, and actuals.
It optimizes the existing workforce by ensuring the right people are in the right place at the right time, consolidates critical workforce data into a centralized system to enable informed decision-making, and manages project timelines and budgets. In addition, these solutions can significantly reduce work-related accidents via effective on-the-job training.
12. Sensor Data
Sensor data is generated when a sensor device detects input from the physical environment surrounding it and provides a response. Typically, that response—or output—is used to relay important information to an end user.
In construction, sensor data plays a vital role in ensuring the safety of on-site workers and future inhabitants of a space. To provide a few examples:
Vibration sensors detect movement within structures to warn of stability issues
Humidity sensors monitor environmental conditions to prevent damage to materials
Gas sensors monitor the levels of certain elements in the air to warn of air pollution
Proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of a nearby object or material to warn of hazards
Increasingly, sensor data devices possess wireless connectivity, which enables remote monitoring and control.
13. Advanced Takeoff and Estimating Tools
In an age when rapidly rising materials costs and increasingly thin profit margins are placing huge pressures on the construction industry, meticulous budgeting is paramount.
That’s where advanced takeoff and estimating technologies come in handy. The former identifies and quantifies the tools, materials, and labor required for a construction project, while the latter calculates the costs associated with each of these project components.
The software enables team leads to accurately plan and budget projects to ensure resources are effectively allocated and client bids are more competitive. While takeoffs and estimations can be carried out manually, digital tools offer a substantial return on investment (ROI) since they are more accurate and efficient, increase collaboration, and reduce costs.







.jpg)















































.jpg)
.jpg)





.jpg)



.png)
.jpg)

.jpg)
_lVjBYb.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)







.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)











.jpg)




.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)


