EMERSONTest Platform for Automation System
the fieldbus. The devices which are configured to receive the data are called
subscribers.
Unscheduled communication- These transmissions are done with PN (Probe Node) or
PT (Pass Token) and take place between transmissions of scheduled messages. The
LAS sends a PN (Probe Node) message to see whether any device changes have been
made. The changes are added to a live list. It is possible for a device to transmit
unscheduled messages after it has received a PT (Pass Token) from the LAS.
The User Application is a standard user application defined by Fieldbus Foundation.
This layer is not defined by the OSI-model. [9]
Profibus
The Profibus that is used in the test platform is Profibus DP (Decentralized Periphery).
Profibus DP is the most common Profibus.
The OSI-model for Profibus communication consists of three layers;
The Physical Layer defines the physical transmission characteristics. The signals are
sent using UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter). With UART, data are
transmitted as streams of characters. Every character starts with a start bit (a 0) and
ends with a stop bit (a 1). The start bit allows the receiver to recoginize the start of a
new character and the stop bit makes sure that there will be a transition at the start of
the stop bit. [10]
The Communication Stack is a communication layer which defines the Bus Access
Protocoll. In a Profibus DP system the communication type is master/slave and both
multi-master and mono-master systems are possible. The protocoll used is Media Acces
Control (MAC), which specifies the procedure when a station is permitted to transmit
data on the bus. The MAC must ensure that only one station has the right to transmit
data at a time.
Hence, the requirements on the MAC protocol are that the following should be
accomplished:
• During communication between master stations it must be ensured that each of
these masters gets sufficient time to execute its communication tasks within a
precisely defined time interval.
• Cyclic, real time data transmission is to be implemented as fast and as simple as
possible for communication between a master and its slaves. [11]
The multi-master system manages communication by having a token that is sent
between the masters. When a master has the token, it can communicate with its slaves,
see figure 1.6. [12]
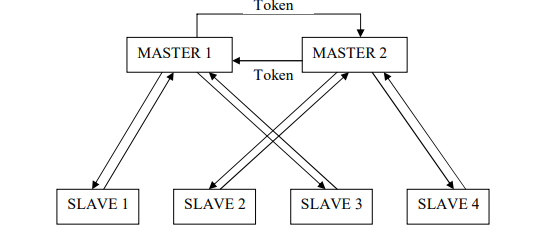
Figure 1.6. The multi-master communication of Profibus. The multi-master system manages
communication by having a token that is sent between the masters. When a master has the token, it can
communicate with the slaves.
The User Layer is defined as a standard user layer. [13]
1.2.2 Description of the Software tools in DeltaV
The automation system has many different software applications. For this process the
applications that have been used are: A tool for organizing the database, a tool for
creating control modules and an animation tool for creating operator interfaces.
The Database
A database contains controllers, I/O and fieldbus cards in the system and control
modules.
The Control Modules
In DeltaV the control of the system can be organized in control modules. A control
module can be very simple and contain only one or two input parameters. It can also be
more complex with for instance PID-control.
There are several types of control modules. Which one is used depends on its purpose.
The most important control modules are;
• Function Block Diagrams (FBD)
An FBD is always necessary to be able to send signals from the computer to the
process or get signals from the process to the computer. An FBD consists of, as
the name tells us, function blocks. A function block can be an input block, for
instance it can contain a signal from a temperature transmitter. If this signal value
should be shown on the operator interface, there must be a reference from the
module containing this block to the operator interface. For each signal, only one
input/output block can be used. It is possible to get the signal at another place, for
instance in a different control module, by referring to it. Other function blocks are,
for instance, multipliers and PID blocks.
• Sequential Function Charts (SFC)
An SFC is a control module for determining the sequence of execution. A SFC
consists of a bipartite graph (two states are always separated by a transition). In a
State, actions can be permormed. This means that parameter values can be set,
for instance a light connected to a relay that gets a signal from the automation
system can be switched on. Transitions contains the conditions that need to be
fulfilled for the process to change states. In an SFC references are made to the
FBDs. For instance, if it is desired to have a transition when the pressure is above
1200 mbar, there must be a reference to the input block in the specific FBD that