Food and Beverage Automation
### Title: Food and Beverage Automation: Revolutionizing the Industry In the food and beverage industry, automation has emerged as a powerful force that is transforming every aspect of production, from processing and packaging to distribution and quality control. With the increasing demands for higher productivity, improved quality, and enhanced food safety, food and beverage automation is playing a crucial role in meeting these challenges and driving the industry forward. #### 1. Introduction to Food and Beverage Automation Food and beverage automation involves the integration of various advanced technologies such as robotics, sensors, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and software systems into the processes within this industry. These technologies work together to automate repetitive tasks, monitor critical parameters, and optimize the overall production flow, reducing the reliance on manual labor and minimizing the potential for human error. Robotic systems are being widely used in food and beverage manufacturing. They can perform a diverse range of tasks, including picking and placing food items, sorting products based on specific criteria, and even carrying out delicate operations like handling fragile bakery items or fresh fruits without causing damage. For example, robotic arms equipped with specialized grippers can accurately transfer cookies from a conveyor belt to packaging trays at a high speed, ensuring consistent and efficient packaging. Sensors are another essential component of food and beverage automation. They are strategically placed throughout the production process to monitor parameters like temperature, humidity, pressure, and the presence of contaminants. In a dairy processing plant, for instance, temperature sensors ensure that milk is pasteurized at the correct temperature to kill harmful bacteria while maintaining its quality. Humidity sensors in a bakery help control the drying process of bread to achieve the desired texture. PLCs act as the control centers of automated systems. They receive input from sensors and execute programmed logic to control various equipment such as pumps, valves, mixers, and conveyors. Based on the real-time data collected, PLCs can adjust the operation of machinery to maintain optimal production conditions and ensure the smooth running of the production process.
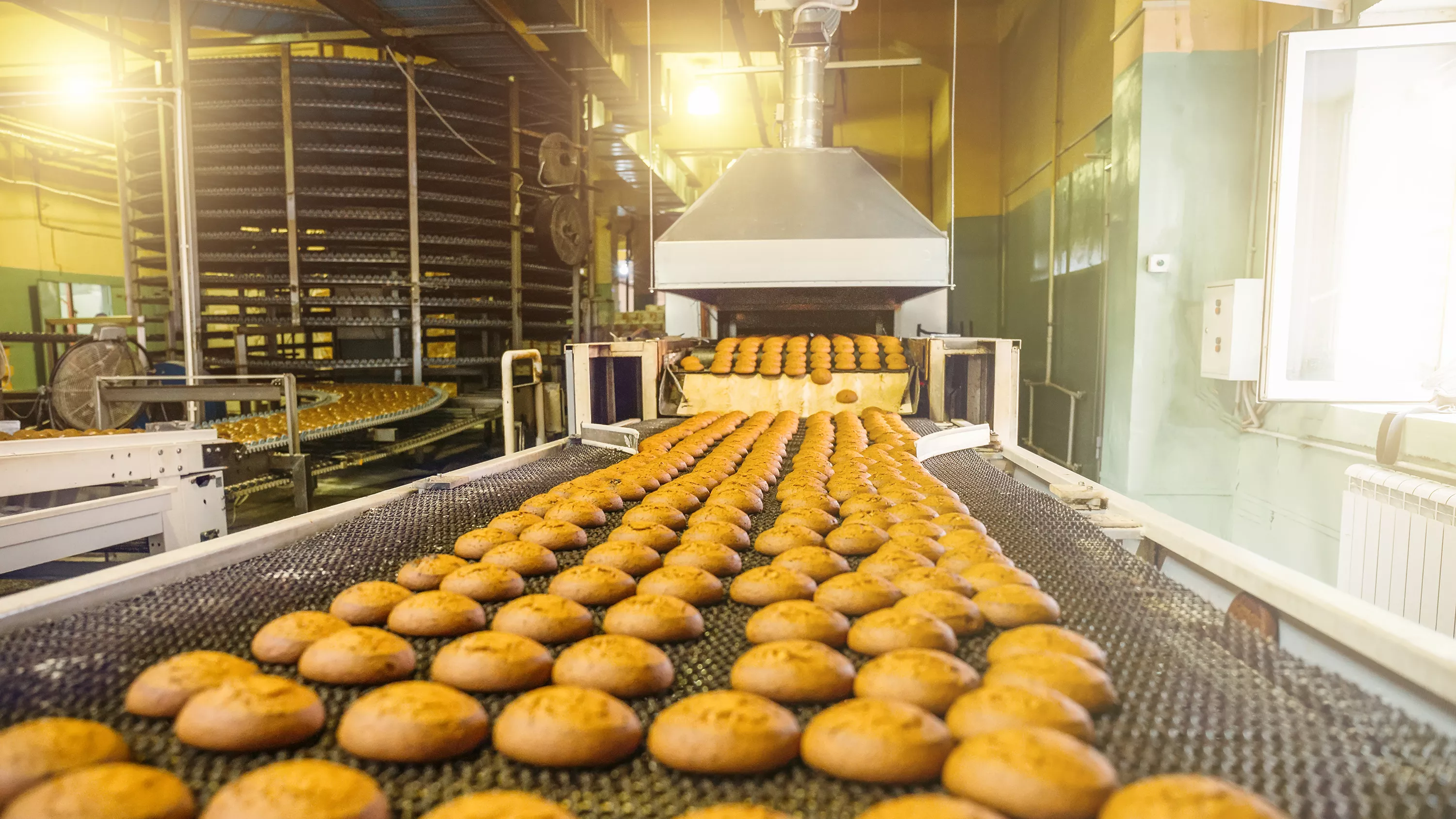

#### 2. Applications in Different Areas of the Food and Beverage Industry - **Processing**: - In food processing, automation is used to precisely control the mixing of ingredients. Automated mixing systems can accurately measure and combine different components in the right proportions to create consistent product formulations. For example, in the production of sauces or beverages, these systems ensure that the flavor and quality remain uniform across batches. - Cooking and baking processes are also automated. Industrial ovens and cookers with automated temperature and time controls can produce large quantities of baked goods or cooked foods with precise doneness and flavor profiles. In meat processing, automated cutting and slicing machines can handle large volumes of meat with high precision, improving efficiency and reducing waste. - **Packaging**: - Packaging is a key area where automation has made significant strides. Automated packaging machines can fill containers with liquids, powders, or solid food items at high speeds. They can also seal packages securely, apply labels accurately, and even perform secondary packaging tasks like palletizing cases of products. In the beverage industry, filling and capping machines can handle thousands of bottles per hour, ensuring that each bottle is filled to the correct level and capped tightly. - Vision systems integrated with packaging automation can detect defective products or packaging errors. For example, they can identify if a label is misaligned or if there is a foreign object in a package, allowing for immediate removal or correction of the faulty item before it reaches the market. - **Quality Control**: - Automation plays a vital role in ensuring food quality and safety. Automated inspection systems use techniques like spectroscopy, X-ray imaging, and machine vision to detect contaminants, check for proper ingredient distribution, and verify the integrity of packaging. In a snack production line, for instance, machine vision can spot broken or misshapen chips and remove them from the production stream. - Microbiological testing can also be automated to some extent. Automated sampling and analysis systems can quickly detect the presence of harmful microorganisms in food products, enabling prompt corrective actions to prevent foodborne illnesses. - **Distribution**: - In the distribution phase, automation helps in inventory management and order fulfillment. Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) in warehouses can efficiently store and retrieve food and beverage products, reducing the time and labor required for stock handling. Barcode and RFID technology enable accurate tracking of products throughout the supply chain, ensuring timely deliveries and minimizing losses due to expired or damaged goods. #### 3. Benefits of Food and Beverage Automation - **Enhanced Productivity**: Automation allows for continuous operation without breaks, enabling food and beverage companies to increase their production output significantly. Machines can work at a much faster pace than humans in many repetitive tasks, such as filling bottles or packaging products. This increased productivity helps meet the growing market demands and can give companies a competitive edge. - **Improved Quality**: With precise control over processing parameters and the ability to detect and remove defective products, automation ensures consistent product quality. The use of automated quality control systems reduces the likelihood of human errors in inspection and testing, resulting in higher-quality food and beverage products that meet or exceed consumer expectations. - **Increased Food Safety**: By closely monitoring critical parameters like temperature, humidity, and contamination levels, automation helps maintain a safe production environment. Automated systems can quickly respond to any deviations from safety standards, minimizing the risk of foodborne illnesses and ensuring that only safe products reach consumers. - **Cost Savings**: Although the initial investment in automation equipment may be high, in the long run, it can lead to significant cost savings. Automation reduces labor costs by replacing manual tasks, minimizes waste through precise ingredient usage and production processes, and can lower maintenance costs with predictive maintenance enabled by sensor data. #### 4. Challenges and Future Trends - **Complexity and Customization**: Food and beverage products come in a vast array of forms, sizes, and consistencies, which requires highly customized automated solutions. Developing and integrating these complex systems can be challenging and time-consuming. However, as technology advances, more modular and adaptable automation solutions are emerging to address this issue. - **Cleaning and Sanitation**: Maintaining hygiene in food and beverage production facilities is of utmost importance. Automated equipment must be designed in a way that allows for easy and thorough cleaning to prevent the buildup of food residues and the growth of bacteria. New materials and designs are being developed to make automated systems more hygienic and compliant with strict food safety regulations. - **Consumer Perception**: Some consumers may have concerns about the use of automation in food production, fearing that it could compromise the quality or authenticity of the products. Food and beverage companies need to communicate effectively with consumers about the benefits of automation, such as improved food safety and quality, to address these concerns. - **Integration of Emerging Technologies**: The future of food and beverage automation will see a deeper integration of technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain. AI can be used for optimizing production processes based on real-time data analysis, predicting equipment failures, and improving quality control. IoT will expand the network of connected devices, enabling better coordination between different parts of the production and supply chain. Blockchain technology has the potential to enhance transparency and traceability in the food supply chain, allowing consumers to know exactly where their food comes from and how it was produced. In conclusion, food and beverage automation is revolutionizing the industry by offering numerous benefits in terms of productivity, quality, food safety, and cost savings. Despite the challenges it presents, the continued integration of advanced automation technologies will play a crucial role in shaping the future of the food and beverage sector, enabling it to meet the evolving demands of consumers and the marketplace.





























.png)