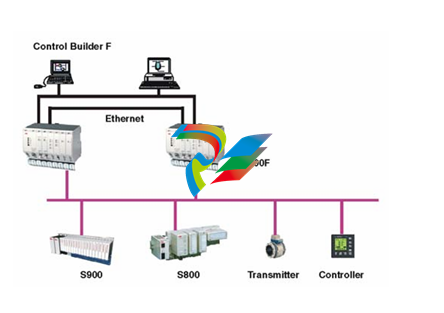
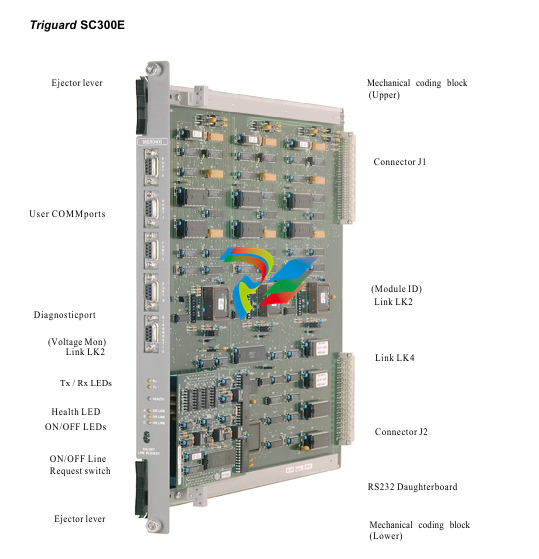
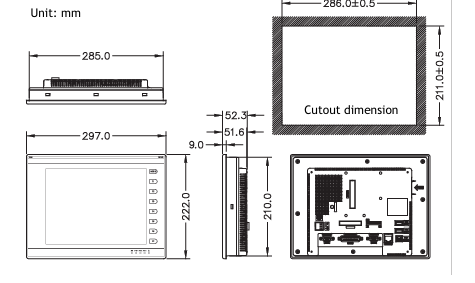
DCS; Industrial control system
Product
Article
NameDescriptionContent
Argument
Current Location:
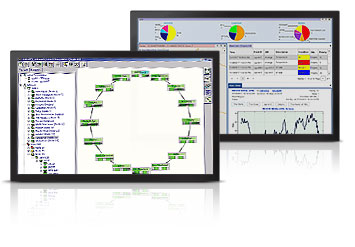
PRODUCT SHOW
Description
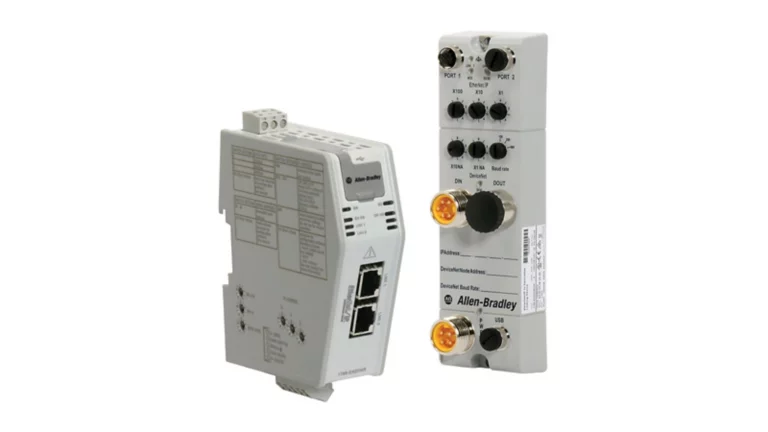
600 EtherNet-IP to DeviceNet Linking Devices: A Detailed Description
1. Introduction
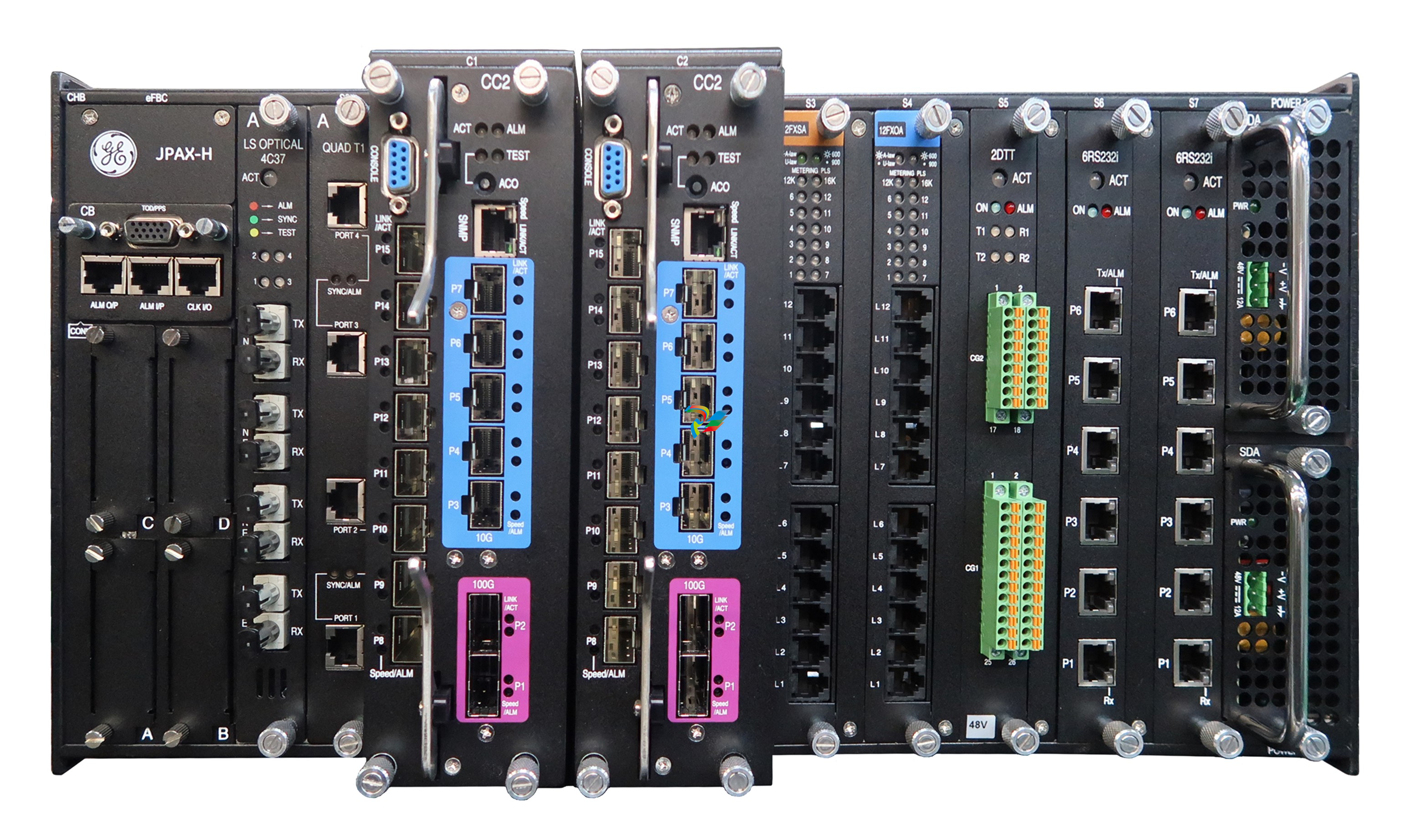
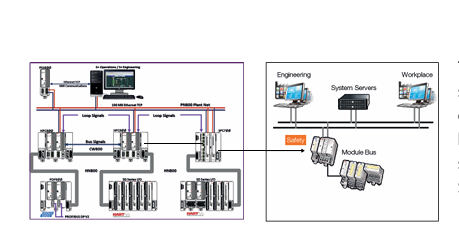
The 600 EtherNet-IP to DeviceNet Linking Devices are crucial components in industrial automation systems that aim to bridge the communication gap between two widely used industrial network protocols, namely EtherNet/IP and DeviceNet. These devices play a significant role in enabling seamless data exchange and interoperability between different devices and subsystems within a factory or industrial environment, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency and flexibility of automation processes.
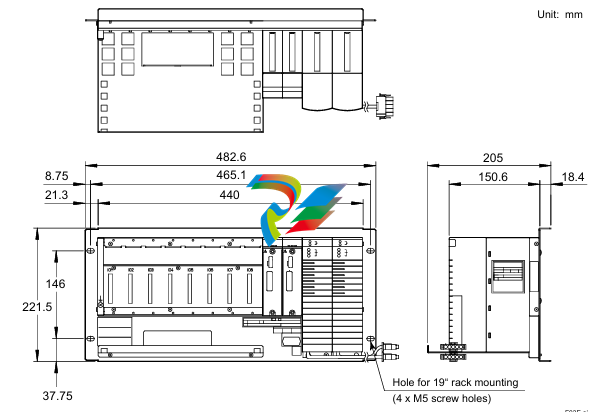
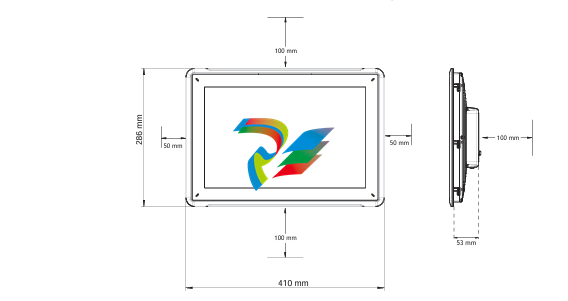
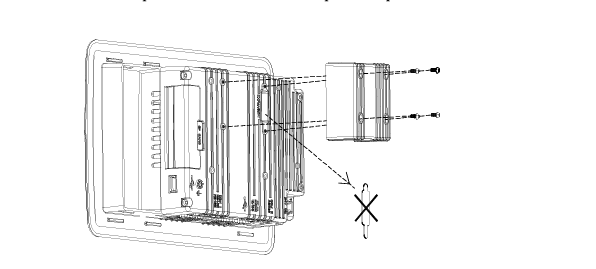
2. Physical Design and Construction

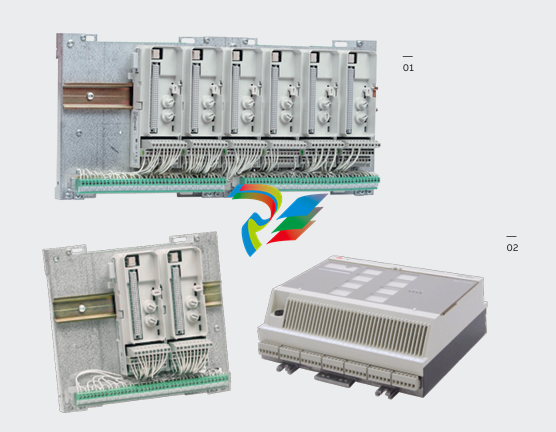
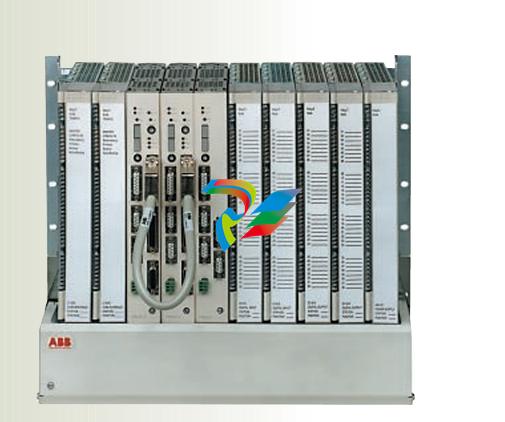
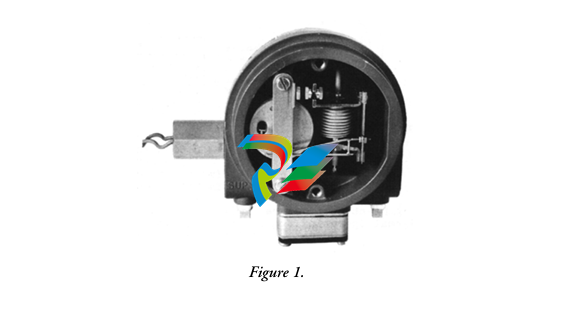
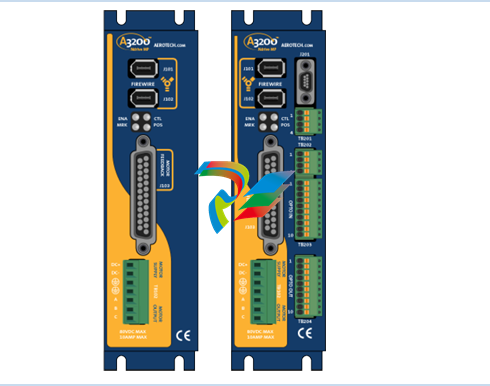
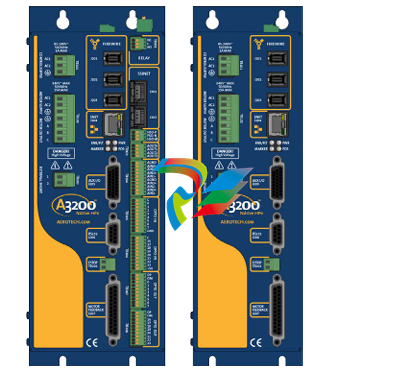
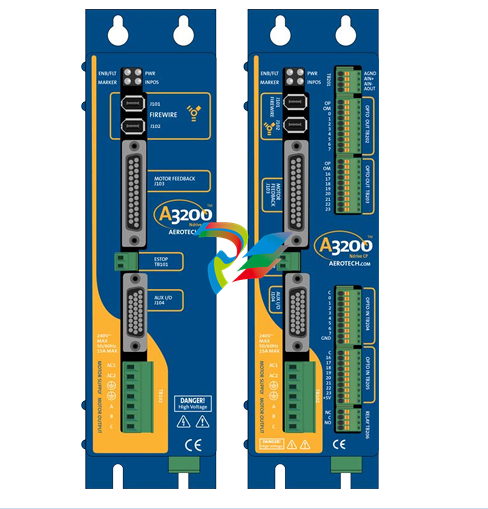
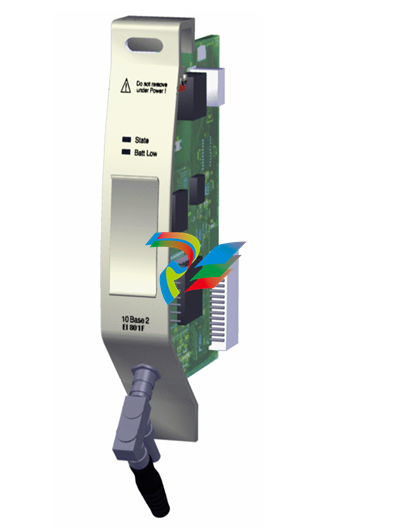
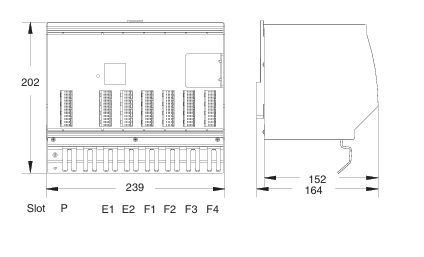
- Compact and Rugged Design: The 600 EtherNet-IP to DeviceNet Linking Devices typically feature a compact form factor, which allows for easy installation in control cabinets or other space-constrained areas within an industrial setting. Despite their small size, they are built with rugged materials such as high-quality plastics or metal alloys to withstand the harsh conditions often present in factories, including exposure to dust, vibration, temperature variations, and electromagnetic interference.
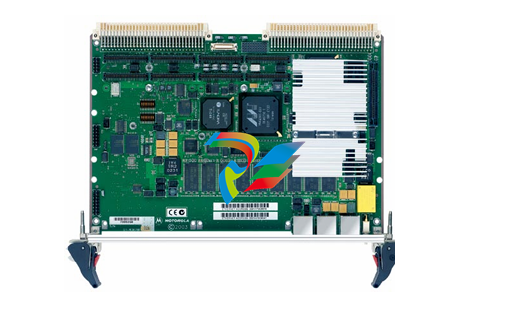
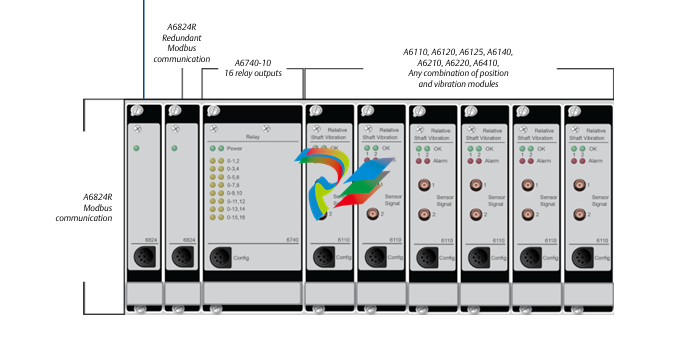
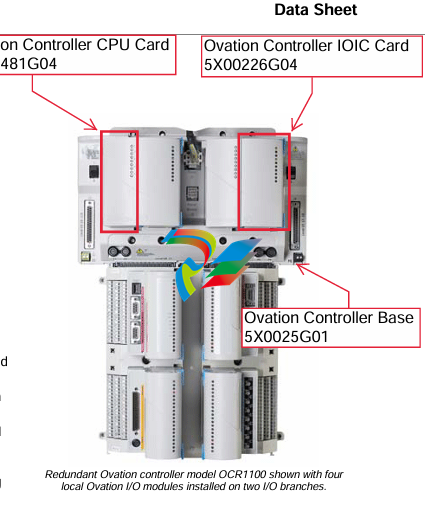
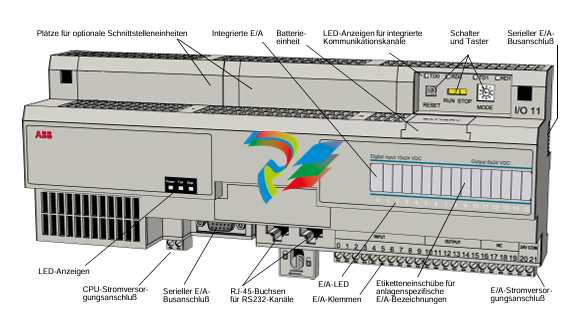
- Connection Interfaces: These devices are equipped with a variety of connection interfaces to facilitate their integration into existing systems. On the EtherNet/IP side, they usually have standard Ethernet ports, often compliant with RJ45 connectors, which enable connection to EtherNet/IP-enabled devices like programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), or other networked equipment. On the DeviceNet side, there are specific DeviceNet connectors designed to interface with DeviceNet-compatible sensors, actuators, remote I/O modules, and other devices that operate on the DeviceNet network.
- Mounting Options: They offer flexible mounting options to suit different installation preferences. For example, they can be mounted on DIN rails, which are commonly used in industrial control panels for easy installation and removal. Alternatively, they may also support panel mounting for a more permanent and customized installation setup, depending on the specific requirements of the application.
3. Communication Protocol Conversion
- EtherNet/IP and DeviceNet Compatibility: The primary function of these linking devices is to translate and transfer data between the EtherNet/IP and DeviceNet protocols. They are designed to understand the specific communication rules, message formats, and addressing schemes of both protocols. On the EtherNet/IP side, they can handle various EtherNet/IP services such as explicit messaging for configuration and diagnostic purposes, as well as implicit messaging for real-time data transfer. Similarly, on the DeviceNet side, they are capable of interacting with DeviceNet devices following its unique communication model, which includes features like cyclic and acyclic data exchange.Data Mapping and Transformation: The devices perform data mapping and transformation operations to ensure that information can be accurately conveyed between the two networks. For instance, data received from a DeviceNet sensor, such as a temperature reading or a position value, is appropriately formatted and mapped into the EtherNet/IP data structure before being sent to an EtherNet/IP device that might be a PLC for further processing. Conversely, control commands or configuration data from an EtherNet/IP device are converted into the DeviceNet-compatible format and forwarded to the relevant DeviceNet actuators or devices.Protocol Conversion Logic: Inside the linking devices, there is sophisticated protocol conversion logic implemented in either hardware or software (or a combination of both). This logic ensures that the conversion process is seamless and efficient, taking into account factors like data integrity, transmission speed, and synchronization between the two networks. It continuously monitors the communication on both sides, manages the flow of data, and makes necessary adjustments to maintain reliable and timely data exchange.
Purchase history
| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|
Total 0 Record
Customer Reviews
Satisfaction :
5 Stars
No evaluation information