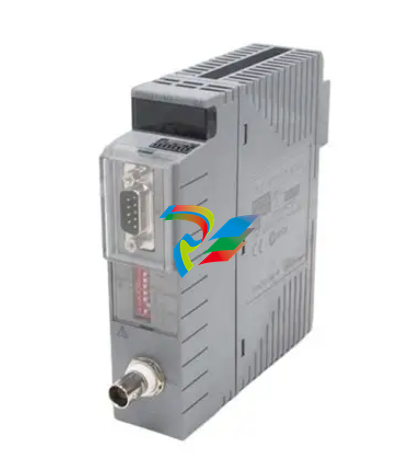
A-BSLC 500 EtherNet/IP Adapter
The producing device contains the path information that steers the message
along the proper route to reach its consumers. Since the producing device
holds this information, other devices along the path simply pass this
information; they do not store it.
This has the following significant benefits:
• You do not need to configure routing tables in the bridging modules,
which greatly simplifies maintenance and module replacement.
• You maintain full control over the route taken by each message, which
enables you to select alternative paths for the same end device.
Understand the Producer/
Consumer Model
The CIP producer and consumer networking model replaces the old source
and destination (master and slave) model. The producer and consumer model
reduces network traffic and increases speed of transmission. In traditional I/O
systems, controllers poll input modules to obtain their input status. In the CIP
system, input modules are not polled by a controller. Instead, they produce
(multicast or unicast) their data periodically or at a cyclic rate.
Unicast is the default for version 20 with multicast as a selectable option. The
frequency of update depends upon the options chosen during configuration
and where on the network the input module resides. The input module,
therefore, is a producer of input data, and the controller is a consumer of the
data.
The controller also produces data for other controllers to consume. The
produced and consumed data is accessible by multiple controllers and other
devices over the EtherNet/IP network. This data exchange conforms to the
producer and consumer model.
Support of Direct
Connections
The EtherNet/IP adapter only supports direct connections. A direct connection
is a real-time data transfer link between a Logix controller and a 1746/1747 I/O
module through the 1747-AENTR adapter. Direct I/O connections occur at a
cyclic rate specified by the RPI during configuration
Install Your Adapter
This chapter describes how to install the 1747-AENTR adapter and connect it to
the EtherNet/IP network.
The following table lists where to find specific information.
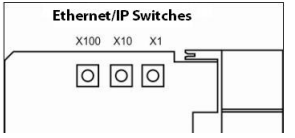
Set the Network Address
Switches
The network address switches are set to 999 and DHCP enabled, by default.
You can set the network Internet Protocol (IP) address in the following ways:
• Use the network address switches on the module.
• Use a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server, such as
Rockwell Automation BootP/DHCP.
• Retrieve the IP address from nonvolatile memory.
The adapter reads the network address switches first to determine if the
switches are set to a valid number. You set the node address by using the
network address switches. Valid settings range from 001…254.
When the switches are set to a valid number, the adapter’s IP address is
192.168.1.xxx (where xxx represents the number set on the switches).
The adapter’s subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 and the gateway address is set to
0.0.0.0. The adapter does not have a host name assigned, or use any Domain
Name System when using the network address switch settings.
If the switches are set to an invalid number (for example, 000 or a value greater
than 254 excluding 888), the adapter checks to see if DHCP is enabled. Setting
the switches to 888 restores default factory settings.
Topic Page
Set the Network Address Switches 15
Determine Power Requirements 18
Install the Adapter Module in the Chassis 18
Connect Your Adapter to the Ethernet/IP Network through RJ-45 Connection 19
Chapter Summary 2
Enable Web Server in Static IP mode
1. Set the switches to 000 and cycle power to the adapter.
The module LED flashes red and the four-character status display scrolls
the message “Web Server Enabled”.
2. Set the switches to the desired IP address and cycle power to the adapter.
3. In your web browser, enter the IP address of the adapter.
The web server home page displays.
Disable Web Server in Static IP mode
1. Set the switches to 901 and cycle power to the adapter.
The module LED flashes red and the four-character status display scrolls
the message “Web Server Disabled”.
2. Set the switches to the desired IP address and cycle power to the adapter.
3. In your web browser, enter the IP address of the adapter.
The web server home page does not display.
Enable Web Server in DHCP mode
Before you begin, verify that you have an active DHCP server on your network.
1. Set the switches to 000 and cycle power to the adapter.
The module LED flashes red and the four-character status display scrolls
the message “Web Server Enabled”.
2. Set the switches to 999 and cycle power to the adapter.
3. In RSLinx software, check the IP address that was assigned to the
adapter by the DHCP server and verify the connection.
4. In your web browser, enter the IP address of the adapter.
The web server home page displays.
Disable Web Server in DHCP mode
Before you begin, verify that you have an active DHCP server on your network.
1. Set the switches to 901 and cycle power to the adapter.
.png)

























.png)