A-BSLC 500 EtherNet/IP Adapter
Important User Information
Read this document and the documents listed in the additional resources section about installation, configuration, and
operation of this equipment before you install, configure, operate, or maintain this product. Users are required to familiarize
themselves with installation and wiring instructions in addition to requirements of all applicable codes, laws, and standards.
Activities including installation, adjustments, putting into service, use, assembly, disassembly, and maintenance are required to
be carried out by suitably trained personnel in accordance with applicable code of practice.
If this equipment is used in a manner not specified by the manufacturer, the protection provided by the equipment may be
impaired.
In no event will Rockwell Automation, Inc. be responsible or liable for indirect or consequential damages resulting from the use
or application of this equipment.
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for illustrative purposes. Because of the many variables and
requirements associated with any particular installation, Rockwell Automation, Inc. cannot assume responsibility or liability for
actual use based on the examples and diagrams.
No patent liability is assumed by Rockwell Automation, Inc. with respect to use of information, circuits, equipment, or software
described in this manual.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual, in whole or in part, without written permission of Rockwell Automation, Inc., is
prohibited.
Throughout this manual, when necessary, we use notes to make you aware of safety considerations.
Overview
This chapter provides an introduction to the features and functionalities of the
1747-AENTR SLC™ 500 EtherNet/IP Adapter. It includes the following sections.
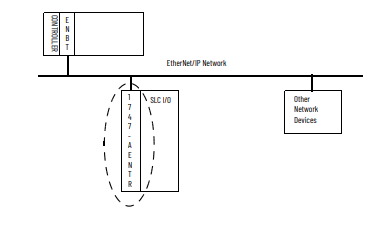
Module Description The 1747-AENTR Adapter enables CompactLogix™ and ControlLogix®
processors to control SLC™ I/O modules. It is primarily designed to enable
migration of existing SLC controlled systems to Logix-based systems.
The adapter mainly acts as a gateway between the SLC backplane and
EtherNet/IP and typically replaces an SLC controller in the 1746 rack. On
remote SLC racks, it replaces the 1747-ASB module or the ControlNet® adapters
1747-ACN15 and 1747-ACNR15.
Control of the backplane I/O is accomplished with a CompactLogix or
ControlLogix controller communicating through an EtherNet/IP router in the
Logix backplane, across EtherNet/IP, and into the 1747-AENTR gateway.
As a gateway between the SLC backplane and EtherNet/IP, the 1747-AENTR
module is a CIP™ server (for both Explicit Messaging and I/O) on the Ethernet
port, and an SLC host on the 1746 backplane.
Connections can be made to support 1746 and 1747 analog, digital, and
specialty I/O modules installed in the backplane.
For the complete list of supported I/O modules, see the table, List of I/O
Modules Supported by the 1747-AENTR Adapter on page 27.
Topic Page
Module Description 9
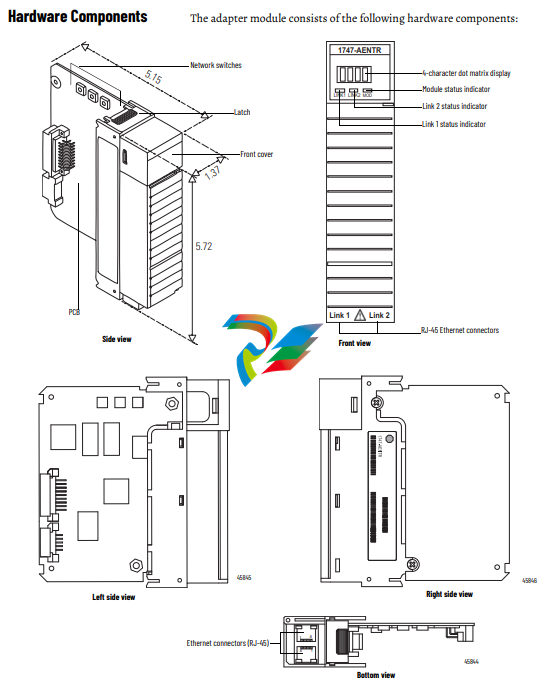
Hardware Components 10
The 1747-AENTR in a Logix System 11
Hardware/Software Compatibility 11
Diagnostic Indicators 11
What the Adapter Does 11
Use of the Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) 12
Understand the Producer/Consumer Model 12
Support of Direct Connections 12
IMPORTANT Studio 5000 Logix Designer® application (previously RSLogix 5000®)
revision 21 and later, and firmware revision 2.001 and later supports:
• multiple chassis, with a maximum number of three chassis;
• a maximum of 30 SLC I/O modules;
• a maximum of 96 Class 1 connections;
• up to 8 Class 3 connections.
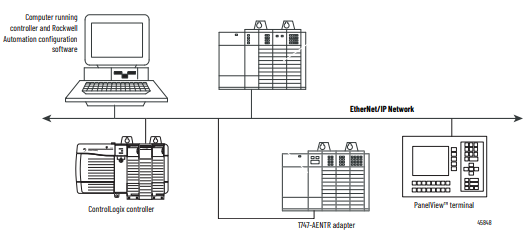
The 1747-AENTR in a
Logix System
In this example, the I/O modules communicate with the controller through the
1747-AENTR adapter. The controller can produce and consume tags to the I/O.
Configuration of devices and the network is done through the personal
computer running the controller and configuration software
Hardware/Software
Compatibility
The adapter and the applications described in this manual is compatible with
the following firmware revisions and software releases
roduct Firmware Revision/
Software Versions
1747-AENTR 1.001 or later
Logix controller v20 or later
RSLogix 5000 or Logix Designer v20 or later
RSLinx® software v2.59 or later
Diagnostic Indicators The module has the following diagnostic indicators:
• Link 1 and Link 2 status indicator
• Module indicator
• 4-character status display
What the Adapter Does The 1747-AENTR EtherNet/IP adapter performs the following primary tasks:
• Control of real-time I/O data (also known as implicit messaging) – the
adapter serves as a bridge between I/O modules and the network
• Support of messaging data for configuration and programming
information (also known as explicit messaging)
Use of the Common
Industrial Protocol (CIP)
The adapter uses the Common Industrial Protocol (CIP), the application layer
protocol specified for EtherNet/IP, the Ethernet Industrial Protocol. It is a
message-based protocol that implements a relative path to send a message
from the producing device in a system to the consuming devices.
The producing device contains the path information that steers the message
along the proper route to reach its consumers. Since the producing device
holds this information, other devices along the path simply pass this
information; they do not store it.
This has the following significant benefits:
• You do not need to configure routing tables in the bridging modules,
which greatly simplifies maintenance and module replacement.
• You maintain full control over the route taken by each message, which
enables you to select alternative paths for the same end device.
Understand the Producer/
Consumer Model
The CIP producer and consumer networking model replaces the old source
and destination (master and slave) model. The producer and consumer model
reduces network traffic and increases speed of transmission. In traditional I/O
systems, controllers poll input modules to obtain their input status. In the CIP
system, input modules are not polled by a controller. Instead, they produce
(multicast or unicast) their data periodically or at a cyclic rate.
Unicast is the default for version 20 with multicast as a selectable option. The
frequency of update depends upon the options chosen during configuration
and where on the network the input module resides. The input module,
therefore, is a producer of input data, and the controller is a consumer of the
data.
The controller also produces data for other controllers to consume. The
produced and consumed data is accessible by multiple controllers and other
devices over the EtherNet/IP network. This data exchange conforms to the
producer and consumer model.
Support of Direct
Connections
The EtherNet/IP adapter only supports direct connections. A direct connection
is a real-time data transfer link between a Logix controller and a 1746/1747 I/O
module through the 1747-AENTR adapter. Direct I/O connections occur at a
cyclic rate specified by the RPI during configuration
Install Your Adapter
This chapter describes how to install the 1747-AENTR adapter and connect it to
the EtherNet/IP network.
The following table lists where to find specific information.
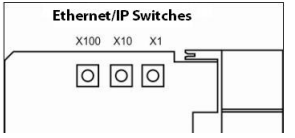
Set the Network Address
Switches
The network address switches are set to 999 and DHCP enabled, by default.
You can set the network Internet Protocol (IP) address in the following ways:
• Use the network address switches on the module.
• Use a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server, such as
Rockwell Automation BootP/DHCP.
• Retrieve the IP address from nonvolatile memory.
The adapter reads the network address switches first to determine if the
switches are set to a valid number. You set the node address by using the
network address switches. Valid settings range from 001…254.
When the switches are set to a valid number, the adapter’s IP address is
192.168.1.xxx (where xxx represents the number set on the switches).
The adapter’s subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 and the gateway address is set to
0.0.0.0. The adapter does not have a host name assigned, or use any Domain
Name System when using the network address switch settings.
If the switches are set to an invalid number (for example, 000 or a value greater
than 254 excluding 888), the adapter checks to see if DHCP is enabled. Setting
the switches to 888 restores default factory settings.
Topic Page
Set the Network Address Switches 15
Determine Power Requirements 18
Install the Adapter Module in the Chassis 18
Connect Your Adapter to the Ethernet/IP Network through RJ-45 Connection 19
Chapter Summary 2
Enable Web Server in Static IP mode
1. Set the switches to 000 and cycle power to the adapter.
The module LED flashes red and the four-character status display scrolls
the message “Web Server Enabled”.
2. Set the switches to the desired IP address and cycle power to the adapter.
3. In your web browser, enter the IP address of the adapter.
The web server home page displays.
Disable Web Server in Static IP mode
1. Set the switches to 901 and cycle power to the adapter.
The module LED flashes red and the four-character status display scrolls
the message “Web Server Disabled”.
2. Set the switches to the desired IP address and cycle power to the adapter.
3. In your web browser, enter the IP address of the adapter.
The web server home page does not display.
Enable Web Server in DHCP mode
Before you begin, verify that you have an active DHCP server on your network.
1. Set the switches to 000 and cycle power to the adapter.
The module LED flashes red and the four-character status display scrolls
the message “Web Server Enabled”.
2. Set the switches to 999 and cycle power to the adapter.
3. In RSLinx software, check the IP address that was assigned to the
adapter by the DHCP server and verify the connection.
4. In your web browser, enter the IP address of the adapter.
The web server home page displays.
Disable Web Server in DHCP mode
Before you begin, verify that you have an active DHCP server on your network.
1. Set the switches to 901 and cycle power to the adapter.
The module LED flashes red and the four-character status display scrolls
the message “Web Server Disabled”.
2. Set the switches to 999 and cycle power to the adapter.
3. In RSLinx software, check the IP address that was assigned to the
adapter by the DHCP server and verify the connection.
4. In your web browser, enter the IP address of the adapter.
The web server home page does not display.
Enable Web Server in User-set IP mode
1. Set the switches to 000 and cycle power to the adapter.
The module LED flashes red and the four-character status display scrolls
the message “Web Server Enabled”.
2. Set the switches to 999 and cycle power to the adapter.
3. In RSLinx software, change the Port Configuration setting to “Manual
IP”, set the desired IP address, and cycle power to the adapter.
4. In your web browser, enter the IP address of the adapter.
The web server home page displays.
Disable Web Server in User-set IP mode
1. Set the switches to 901 and cycle power to the adapter.
The module LED flashes red and the four-character status display scrolls
the message “Web Server Disabled”.
2. Set the switches to 999 and cycle power to the adapter.
3. In RSLinx software, change the Port Configuration setting to “Manual
IP”, set the desired IP address, and cycle power to the adapter.
4. In your web browser, enter the IP address of the adapter.
The web server home page does not display.
Determine Power
Requirements
The Ethernet adapter requires 5V DC with current consumption of 470 mA.
The power is supplied through backplane from SLC power supply. Remember
to consider this requirement when planning your system configuration.
Install the Adapter Module
in the Chassis
After you set the appropriate switch assemblies for your adapter module,
follow these procedures for installation.
See the Industrial Controller Wiring and Grounding Guidelines publication
1770-4.1 for proper grounding and wiring methods to use when installing your
module.
1. Remove power from the I/O chassis before inserting (or removing) the
module.
2. Align the circuit board with the chassis card guide in the left slot.
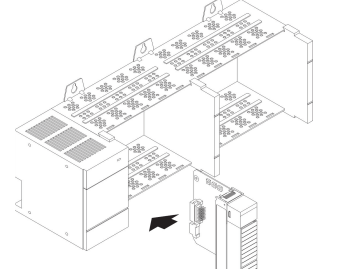
. Install the module in slot 0 of the chassis by aligning the circuit board
with the chassis card guide.
The 1747-AENTR module must be installed only in slot 0 (leftmost slot)of
the chassis.
Press firmly and evenly to seat the module in its backplane connectors.
To remove the module, press the releases at the top and bottom of the
module and pull it out.
ATTENTION: Do not force the module into the backplane connector. If you
cannot seat the module with firm pressure, check the alignment. Forcing the
module can damage the backplane connector or the module.
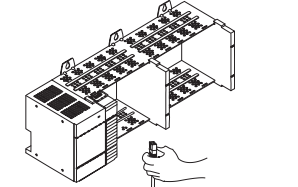
Connect Your Adapter to the Ethernet/IP Network through RJ-45 Connection Connect your 1747-AENTR adapter module to an Ethernet/IP network as shown in the following example: Wire the RJ-45 connectors as shown. To connect the module to the network, follow these steps: 1. Attach the cables with the RJ-45 connectors to the two Ethernet ports on the bottom of the module. ATTENTION: Do not force the module into the backplane connector. If you cannot seat the module with firm pressure, check the alignment. Forcing the module can damage the backplane connector or the module. WARNING: If you connect or disconnect the communication cable with power applied to this module or any device on the network, an electrical arc can occur. This could cause an explosion in hazardous location installations. Be sure that power is removed or the area is nonhazardous before proceeding. 1 8 8 1 Signal 1 TxData+ 2 TxData3 Recv Data+ 4 Reserved 5 Reserved 6 Recv Data7 Reserved 8 Reserv
• Module Settings
- Switches
• SLC Backplane Statistics
- I/O Errors
- I/O Scans Completed
- Maximum Scan Time
- Average Scan Time
Use the Network Settings Page
To use the Network Settings page for network related information, follow this
procedure.
1. Click Network Settings tab at the top of the page or panel on the left.
This opens the Network Settings page.
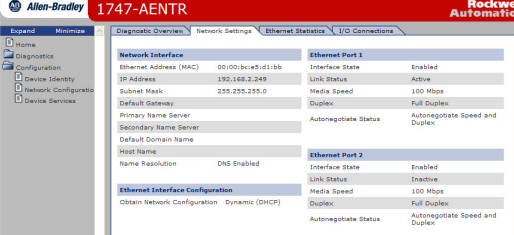
2. From the Network Settings page, you can view the following: • Network Interface - Ethernet Address (MAC) - IP Address - Subnet Mask - Default Gateway - Primary Name Server - Secondary Name Server - Default Domain Name - Host Name - Name Resolution • Ethernet Interface Configuration - How the Network Configuration was obtained - Static or Dynamic
• Ethernet Port 1 and 2
- Interface State
- Link Status
- Media Speed
- Duplex
- Autonegotiate Status
Use the Ethernet Statistics Page
To use the Ethernet Statistics page for information about the Ethernet link and
interface and media counters, use this procedure.
1. Click Ethernet Statistics tab at the top of the page or from the panel on
the left.
The Ethernet Statistics page open
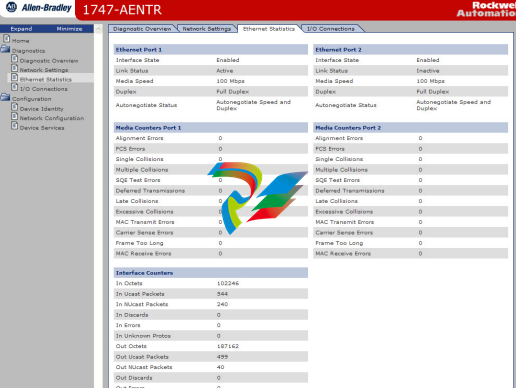
From the Ethernet Statistics page, you can view the following:
• Ethernet Port 1 and Port 2
- Interface State
- Link Status
- Media Speed
- Duplex
- Autonegotiate Status

.png)


.png)

























.png)