
ABBRER 133 Bus Connection Module
About this manual
Copyrights
The information in this document is subject to change without notice and should not be construed as a
commitment by ABB Oy. ABB Oy assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document.
In no event shall ABB Oy be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequential damages of any nature
or kind arising from the use of this document, nor shall ABB Oy be liable for incidental or consequential damages.
arising from use of any software or hardware described in this document. This document and parts thereof must not b
e reproduced or copied without written permission from ABB Oy, and the contents thereof must not be imparted to a th
ird party nor used for any unauthorized purpose. The software or hardware described in this document is furnished under a
license and may be used, copied, or disclosed only in accordance with the terms of such license. Copyright © 2005 ABB Oy Al
l rights reserved.
Trademarks
ABB is a registered trademark of ABB Group. All other brand or product names mentioned in this document may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Guarantee
Please inquire about the terms of guarantee from your nearest ABB representative
Use of symbols
This document includes caution and information icons that point out safety-related conditions or other important information. The corresponding icons should be interpreted as follows: Although caution hazards are associated with equipment or property damage, it should be understood that operation of damaged equipment could, under certain operational conditions, result in degraded process performance leading to personal injury or death. Therefore, comply fully with all caution notices. The caution icon indicates important information or warning related to the concept discussed in the text. It might indicate the presence of a hazard which could result in corruption of software or damage to equipment or property. The information icon alerts the reader to relevant facts and

General
The RER 133 Bus Connection Module acts as an interfacing unit between an RE_54_ host device and a SPA, Modbus or DNP 3.0 system. The RER 133 module converts RS-232 signals to RS-485 signals. RS-485 can be connected by using 2- or 4-wire mode. The RER 133 module is connected by a cable to the RS-232 D-type connector marked X3.2 on the rear panel of the RE_ 54_ host device. RER 133 is not a stand alone device. An RE_ 54_ host device is always required to power the module. No external power supply is supported. RER 133 supports communication speeds from 300 to 19200 bits/s. Collision detection and collision avoidance is supported for communication speeds 4800, 9600 and 19200 bits/s. A RER 133 delivery includes the RER 133 Bus Connection Module, a connection cable (1MRS120542) and this manual.
Principle of operation
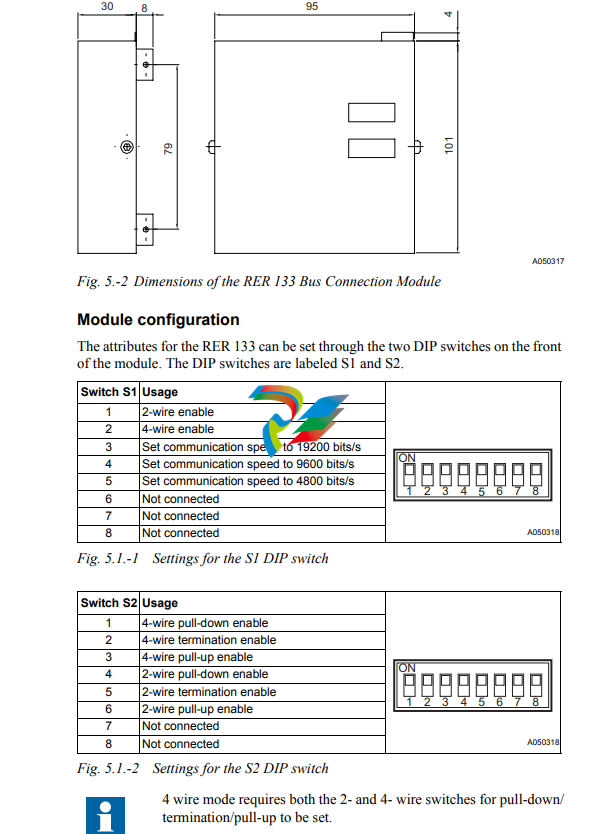
The RER 133 Bus Connection Module is designed to work with RE_ 54_ products. The module utilizes the RS-232 communication port located on the rear panel of the RE_ 54_. The module is not designed to be connected to any other ABB product, nor to any third party products. The signal levels and the functionality of the RER 133 module are defined in the RS-485 standard. RER 133 module is a regular type of RS-485 interface, meaning that a maximum of 32 nodes can be connected in a daisy chain type of bus configuration. Collision detection on the RS-485 bus is supported when a maximum of 32 nodes are connected to the same daisy chain. In order for collision detection to operate, the communication speed has to be set to 4800, 9600 or 19200 bits/s. These speeds are set by using the DIP switches on the front of the module. For an example on how to set these DIP switches, please see section ìModule configurationî on page 9. When collision detection is not used, the communication speed does not have to be set. A050315 Fig. 4.-1 Daisy chain REF 542 and REF 542plus are not supported by RER 133.
Construction and installation
The RER 133 module is mounted on the side of the RE_ 54_ host device and is connected by the supplied cable to the 9-pin female type D-connector (X3.2) of the RE_ 54_ host device.
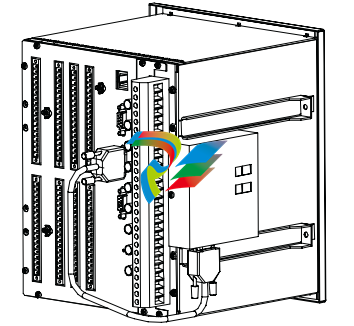
Only the cable supplied with the RER 133 may be used to connect the RER 133 module to the RE_ 54_.
Interfaces
The RS-485 bus used by SPA, Modbus and DNP 3.0 requires a daisy chain topology. A daisy chain topology means a node-to-node connection, where nodes are chained using cables of minimal length. The cables must be point to point, no stars, rings or other topologies are allowed. The bus must be terminated at both ends using 120Ω resistors. The RER 133 includes as an option the use of internal termination resistors. These resistors are enabled through DIP switch S2. Pull-up and pull-down resistors must be used in one of the nodes, in order for the receivers to be able to determine the state of the bus when it is idle. These resistors can be enabled through DIP switch S2. Please see sections ìModule configurationî on page 9 and ìConfiguration examplesî on page 10 for the correct settings. The RS-232 interface (X1) of the RER 133 module is shown in Fig. 6.-1.




























.png)


.png)

























.png)



































































