
MOLEXDocument Edition: 1.2 Date: January 17, 2012 This document applies to the SST-PB3-VME-1 and SST-PB3-VME-2 interface cards. Copyright ©2012 Molex Inc. This document and its contents are the proprietary and confidential property of Molex Inc. and/or i
Document Edition: 1.2
Date: January 17, 2012
This document applies to the SST-PB3-VME-1 and SST-PB3-VME-2 interface cards.
Copyright ©2012 Molex Inc.
This document and its contents are the proprietary and confidential property of Molex Inc. and/or
its related companies and may not be used or disclosed to others without the express prior written
consent of Molex Inc. and/or its related companies.
SST is a trademark of Molex Inc. All other trademarks belong to their respective companies.
At Molex, we strive to ensure accuracy in our documentation. However, due to rapidly evolving
products, software or hardware changes occasionally may not be reflected in our documents. If
you notice any inaccuracies, please contact us (see Appendix A of this document).
Written and designed at:
Molex Incorporated
216 Bathurst Drive
Waterloo, Ontario, Canada N2V 2L7
Hardcopies are not controlled.
Purpose of this Guide
This guide contains technical and product-related information on the SST-PB3-VME-1
and SST-PB3-VME-2 network interface cards.
The SST-PB3-VME-1 consists of a single Profibus network interface (or channel), and the
SST-PB3-VME-2 comprises two independent interfaces, controlled by independent CPUs.
Each CPU executes downloadable application firmware modules, which enable application-level
product behavior. For more details, refer to relevant firmware documentation.
Note
An application running on one channel does not affect the performance
of other channels, as it does not share memory or processor resources
with them.
Note
In this manual, the SST-PB3-VME-1 and SST-PB3-VME-2 will be
referred to as the card, except where product differences apply.
Conventions
This guide uses stylistic conventions, special terms, and special notation to help enhance your
understanding.
Style
The following stylistic conventions are used throughout this guide:
Bold indicates field names, button names, tab names, and options or selections
Italics indicates keywords (indexed) or instances of new terms and/or specialized
words that need emphasis
CAPS indicates a specific key selection, such as ENTER, TAB, CTRL, ALT,
DELETE
Code Font indicates command line entries or text that you would type into a field
Underlining indicates a hyperlink
“>” delimiter indicates how to navigate through a hierarchy of menu selections/options
“0x” or “-H” indicates a hexadecimal value
Terminology
The following special terms are used throughout this guide:
Card the SST-PB3-VME-1 or SST-PB3-VME-2 network interface card
Channel a Profibus network interface on the card
Firmware Module the embedded software module that gets loaded to the card’s
memory and runs on the card. This is the operating system of the
card, enabling it to respond to commands from the host and
manage network communications.
Host the computer system in which the card is installed
.bin an unencrypted firmware module for the card
.ss3 an encrypted firmware module for the card
Special Notation
The following special notations are used throughout this guide:
Warning
Warning messages alert the reader to situations where personal injury
may result. Warnings are accompanied by the symbol shown, and
precede the topic to which they refer.
Caution
Caution messages alert the reader to situations where equipment damage
may result. Cautions are accompanied by the symbol shown, and
precede the topic to which they refer.
Note
A note provides additional information, emphasizes a point, or gives a
tip for easier operation. Notes are accompanied by the symbol shown,
and follow the text to which they refer.
Warnings and Cautions
The card is an electrical component and must be treated with the following precautions:
Warning
Only qualified electrical personnel familiar with the construction/
operation of this equipment and the hazards involved should install,
adjust, operate, and/or service this equipment. Read and understand this
guide in its entirety before proceeding. Failure to observe this precaution
could result in severe bodily injury or, in extreme cases, loss of life.
Warning
You must provide an external, hand-wired emergency stop circuit
outside the programmable controller circuitry. This circuit must disable
the system in case of improper operation. Uncontrolled machine motion
may result if this procedure is not followed. Failure to observe this
precaution could result in bodily injury.
Caution
The card contains static-sensitive components. Careless handling may
severely damage the card. Do not touch any of the connectors or pins on
the card. When not in use, the card should be stored in an anti-static bag.
Failure to observe this precaution could result in damage to or
destruction of the equipment.
1.2 Card Features
The card is a VME interface for communication with Profibus networks. Each channel can:
• Act as a DP master
• Act as a DP slave
• Send and receive FDL (layer 2) messages
• Support Master Class 1 and Master Class 2 messaging
• Support simultaneous operation in all of the above modes
• Support the standard Profibus baud rates of 9.6K, 19.2K, 93.75K, 187.5K, 500K, 1.5M,
3M, 6M and 12M baud
• Support 16-bit transfers (VME D16) with both VME A24 (standard) and A16 (short I/O)
address transfers
Note
For A16 short I/O cycles, registers are located on the odd byte addresses
(0x01, 0x03, and so on) and are 8 bits wide.
Note
Applications running on one channel do not affect the performance of
other channels and do not share memory or processor resources with
other channels.
1.3 Byte Ordering
The card uses Intel-style (little endian) byte ordering for multi-byte entities LSB-low address and
MSB-high address. If your host system uses Motorola (big endian) byte ordering (MSB-low
address and LSB-high address), you must compensate for byte ordering in software.
The following language macro will compensate for byte ordering in a 16-bit data entity:
#define SWAP_WORD (WordData) ((WordData<<8) | (WordData>>8))
Hardware Description
The main features of the card are described in more detail in the following sections.
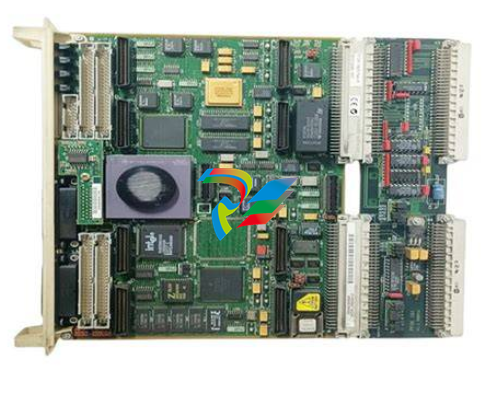
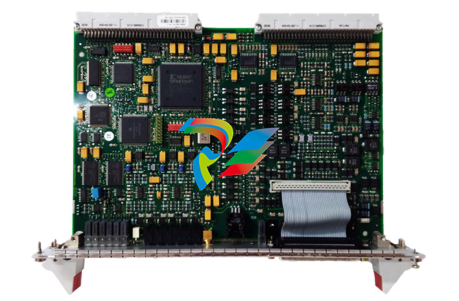
Figure 1: The SST-PB3-VME-1 and SST-PB3-VME-2 Interface Card
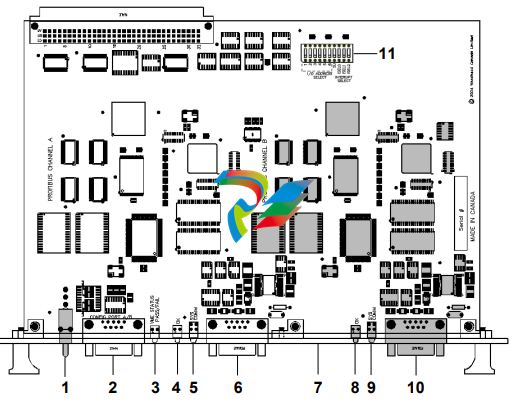
1.4.2 Profibus Connector
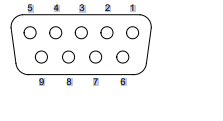
The card has one standard Profibus DB9 female connector per channel. Pin numbers are
identified in the following figure.
Figure 3: The Profibus DB9 Female Connector
5 4 3 2 1
9 8 7 6
Note
The recommended male connector is the Brad Harrison PA9D01-42
Diagnostic D-Sub Connector.
The recommended cable is Belden 3079A. Examples include:
• Brad Harrison 85-0001 PVR 2 conductor with shield, UL-listed Profibus cable
• Bosch Comnet DP #913 548 Flexible Profibus Cable
• Bosch Comnet DP #917 201 Trailing Profibus Cable
• Bosch Comnet DP #917 202 Massive Profibus Cable
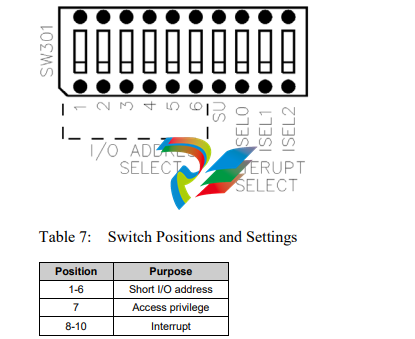
1.4.3 DIP Switch (S1)
The card has a 10-position DIP switch that must be set before the card is installed.
The DIP switch is used to set the base I/O address used to configure the card.
Figure 4: DIP Switch (Shown in Off Position)
2.1 System Requirements
To install and operate the card, the following system requirements must be met:
• A controller that conforms to VMEbus spec VME64 (VITA 1.1 1997)
• Minimum 256K window in host memory map
• The ability to generate and accept 16-bit data transfers (VME D16) with both VME A24
standard address and VME A16 short I/O address transfers
• If interrupts are required, you will need a physical interrupt. On the 2-channel card, this
will be shared between channels.
2.2 Handling Precautions
The card contains components that are sensitive to electrostatic discharge (ESD).
Do not touch the card without following these precautions:
Caution
• Always follow correct ESD procedures before handling the card.
We strongly recommend the use of a grounding wrist strap.
• Never touch any of the card’s connectors or pins. Handle the card by
its edges or bracket.
• When the card isn’t in your computer, always store it in its protective
anti-static bag




































.png)


.png)

























.png)




























































