
ABB ACV 700 Frequency Converters
 Chapter 1 - System Description
Chapter 1 - System Description
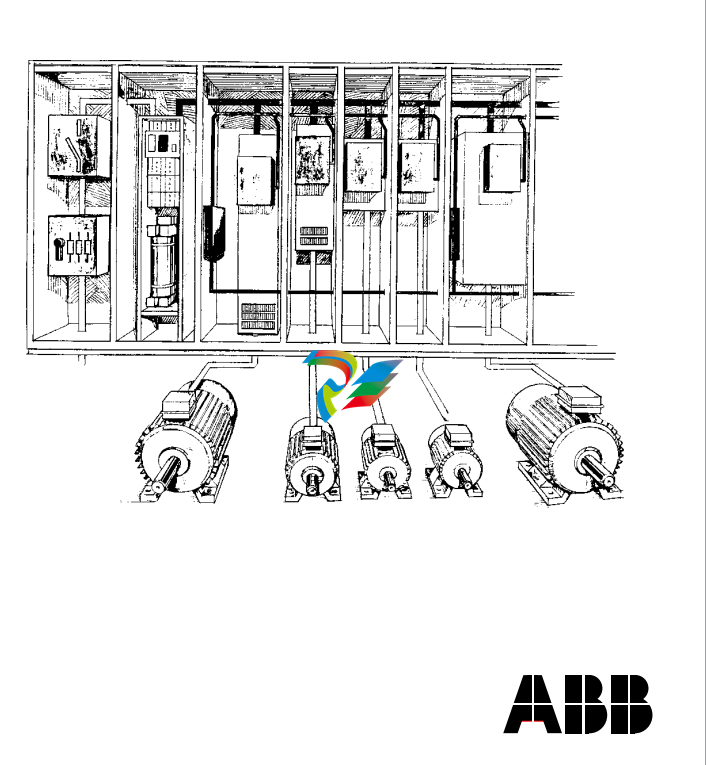
This manual describes the ACV 700 drive system to the application engineers and other persons involved with ACV 700. The drive has a multidrive configuration. It consists of a supply section including connection devices (main fuses and main contactor or circuit breaker), rectifier devices (a diode or thyristor bridge), capacitors for smoothing of the DC voltage, optional devices, if specified, and a number of drive sections. The power range for the supply sections is 40 - 2500 kVA and the power range for the drive sections is 9 - 2500 kVA. Depending on the required power and voltage, the drive sections are based on either an IGBT or GTO thyristor power stage. The control system is implemented by using the Common Drive Control, CDC, and the Digital Drive Control, DDC. The basic part of the CDC is the Application Controller, the APC. The APC is designed to give a flexible, compact and efficient system for controlling AC or DC drives. The APC is programmable by using function blocks. The DDC performs the inverter control functions. Programming can be done using two alternative tools, the Function Chart Editor, FCE or the AdvaBuild for Windows, the Drives version. Various drive configurations are possible using one or multiple APCs and their communication capabilities. In small systems one APC is connected to up to four Digital Drive Controllers (DDC). The drive configuration can be used in master/ follower applications when the master drive is of moderate complexity and the followers fairly simple. A consequence of multiplexing is that the performance of the drive controller interface decreases.
 System Description
System Description
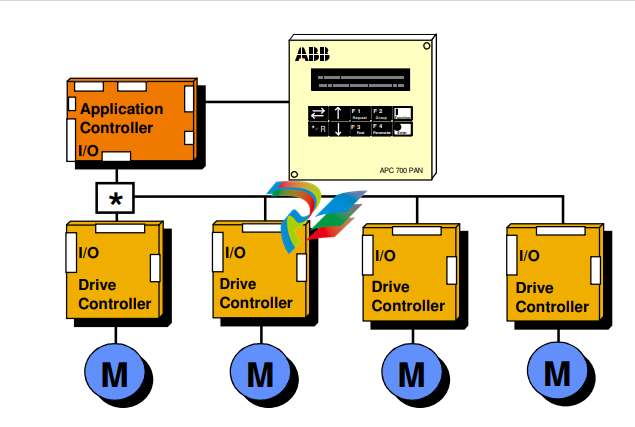
Figure 1 - 1 Small drive system. In distributed multicontroller systems, several
APCs are interconnected by Advant Fieldbus 100 (AF100). Common control
functions can be distributed to separate nodes. No overriding automation
system is used in this configuration, but one or several application controllers
can communicate with external systems over communication boards. A personal
computer (PC) can be connected through one of the APCs and can be used for tool functions.
The concept of the control system is called Common Drive Control, CDC. The standard control functions of the drive section, such as speed and torque control, are located in the Digital Drive Controller, DDC. The application dependent control functions are located in the Application Controller, APC. Typical APC functions are section start and stop logic, internal and external interlocking, speed reference chain, load share control, drive-specific settings, logger functions, and system communication. Function blocks can be combined to macro blocks, which can perform application specific tasks such as crane control, lever control, remote panel control, etc. Each APC can control up to four DDCs. The APC is usually located in the drive section. The APC communicates with other APCs and with the centralised operator control devices via the AF100 communication bus. The APC and the DDC communicate via an optic fibre link. If the solution includes more than one DDC, an optic distributor board is
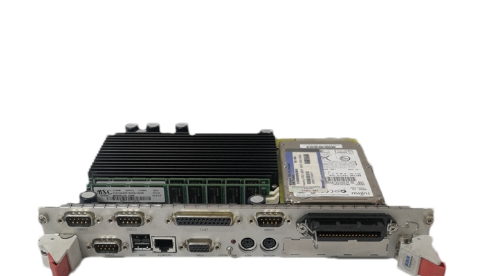
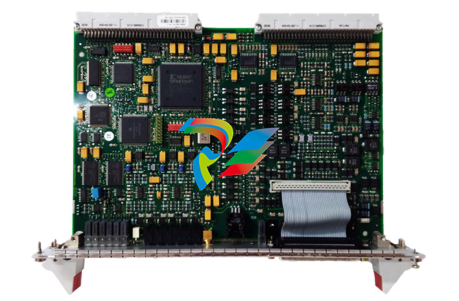
APC is designed to give a flexible, compact and efficient system for controlling AC- and DC-drives. APC is programmed by using function blocks. APC can be supplied with unstable + 24 VDC voltage (connector X1) that can vary in the range 19 - 30 VDC. Maximum input power consumption is 15 VA (0.63 A at 24 VDC). This power consumption includes 2 optional communication boards. APC can handle power supply failure with max. duration of 5 ms (i.e. voltage is below 19 V). When the APC board is slid into the CDC board rack, a 64 pole parallel bus (connector X8) on APC slides into the CDC board rack bus connector. AdvantFieldBus 100 (AF 100) is a high speed serial bus (connector X6), which is used for communication between APCs or between an APC and an overriding system such as ABB's MasterPiece 90. The communication board YPK 112A is used to connect the APC to the AF 100. RS-485 bus, a 8 pole screw terminal connector X2, is a low speed serial bus, which is used to connect remote I/O devices and control panels to the APC. Also other APCs can be connected to each other via this bus. The bus has to be grounded at one point to the same ground as the APC. Maximum length of the bus is 300 m. PC-Link, a standard 9 pole female D-connector X4, can be used to connect a personal computer to the APC. Physical interface is a standard non isolated RS-232C (V24) without any handshaking signals. Recommended maximum length of the cable between APC and PC is 5 m. Drive link, an optic link, is used to connect the APC to an AC or a DC drive. Optical fibres are connected to receiver V32 and transmitter V33. Communication speed is 1.5 Mbps. Max. length of the fibre is 15 m with standard attenuation cable (Hewlett-Packard HFBR-R or equivalent) and 25 m with extra low attenuation cable (HewlettPackard HFBR-E or equivalent). For standard I/O signals there is a 26-pole ribbon cable, connector X3, on APC. A separate terminal block board SNAT 602 TAC is always needed for field signal connections. The ribbon cable should be made as short as possible. Unshielded ribbon cable can be used provided that the cable is not longer than 2 m.




























.png)


.png)

























.png)



































































