
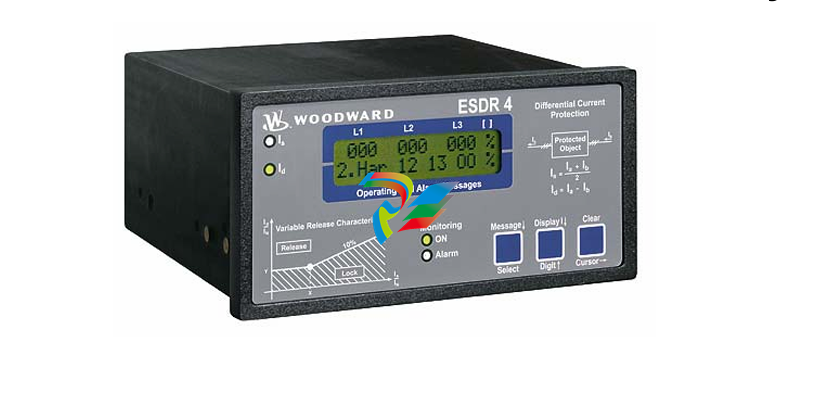
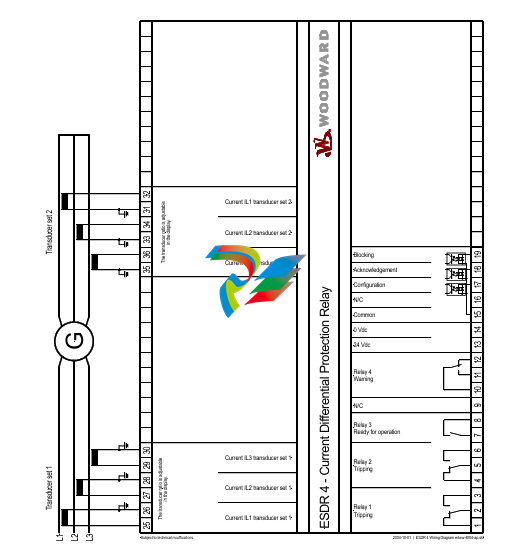
Woodward ESDR 4 Current Differential Protection Relay
ESDR 4
Current Differential Protection Relay
The ESDR 4 is a three-phase current differential protection relay for generators and motors (protected object).
The currents flowing in the individual lines are each measured using a current transformer on both sides of the
protected object. They form the protection area boundary or zone. All two or three-phase short circuits and line
to-earth faults within this protection area are detected by the ESDR 4 as fault currents which initiate tripping.The
unit does not trip if fault currents occur outside the protection zone. In this way, a selective protection is guaran
teed.

The unit monitors six (6) measured currents via isolated inputs. The unit calculates internally the restraint current
(Is) and the differential current (Id) separately for each phase. The actual values of the calculated parameters (Dif
ferential current Id und Restraint current IS) are shown on the display either as absolute values or as a percentage
of the generator rated current (selectable in locked input mode).
Theoretically the currents Ia and Ib are equal, both in fault-free operation and outside the protection zone (Figure
4-1-a).The difference is zero and the differential protection does not initiate. However, in practice current differ
entials do occur (= spurious currents), even in fault-free operation. They result, for example, from summation or
phase angle errors in the CTs, which are influenced by deviating burden values. These spurious currents remain
small inside the operating range, but increase with increasing load and are especially high when one or more CTs
become saturated (e.g. in the case of an external short circuit). In order to prevent a tripping of the relay due to
spurious currents, the trigger threshold is not held statically constant but increases in relation to the restraint cur
rent Is. Spurious currents need to be taken into account when adjusting the trip characteristic.
When a fault occurs inside the protection area (Figure 4-1-b), unequal currents flow in the CTs, which result in a
current differential. If this exceeds the differential protection threshold, the relay will trip.
Monitoring of the Differential Current
The monitoring of the differential current is carried out in two stages..
The first monitoring level serves as a warning and can be enabled or disabled. Should the adjustable warning
characteristic be exceeded, a text appears in the display and a relay contact is enabled. The pick-up time and the
dropout delay of the relay output are adjustable. The warning stage of the monitoring is auto-resetting.
The second stage of monitoring (main stage) serves to initiate tripping. In contrast to the first stage, it offers the
possibility to monitor the overstepping of an adjustable tripping characteristic (Id < In) and additionally, a fixed
tripping-threshold of 100%, relative to the generator rated current (Id > In). The trigger-delay for each limit value
may be independently adjusted, thus allowing a shorter triggering time at higher differential currents. When one
or both tripping characteristics are exceeded, a text display is initiated and two relay contacts are energized. The
tripping characteristics possess a 2% hysterisis relative to the generator rated current. .
The signal relay is only automatically reset if the function "automatic reset relay" in the Entry field on the screen
is configured to "on". Otherwise, the resetting is carried out by pressing the "Clear" button on the front of the
unit or via the discrete input terminal 18 "reset".
The two monitoring levels can also be used to change the characteristics of the control function (stage 1: small
value and a long time; stage 2: high value and a short time)
Tripping Characteristic
The following figure shows the tripping and warning characteristics (with sample values for X12. Y1.and Y2). It
represents the tripping and warning thresholds (Y) relative to the restraint current (X) The positions of the corner
points are determined by the coordinates P (X12/Y2) and P (X12/Y1). The selection of these positions is depend
ent on the generator being protected. The following gives the ranges of tripping and warning thresholds:
IS / IN
IS / IN
IS / IN
0 to X12
X12 to 5 × IN
> 5 × IN
The threshold Id is independent of the restraint current..
The threshold Id is dependent on the restraint current. A change of 100% in the
restraint current causes an increase of 10% in the tripping threshold.
The threshold Id stays constant at 85%.
Different characteristics can be chosen for the first and second monitoring levels, whereby the horizontal position
(X-coordinate) is valid for both stages. The vertical position (Y-coordinate) can be chosen separately for each
monitoring level. This results in a fixed difference in thresholds of the first and second monitioring levels for
each restraint current Is.
Control Inputs
Configuration
Terminal 17
Acknowledgement
Terminal 18
Blocking
Terminal19
Relays
Tripping (relay 1)
Terminals 1/2/3
Tripping (relay 2)
Terminals 4/5/6
Warning (relay 4)
Terminals 11/12/13
Ready for operation
(relay 3)
Terminals 7/8
When this input is energized, the unit locks into Configuration mode and stays in this



























































































.png)


.png)





















