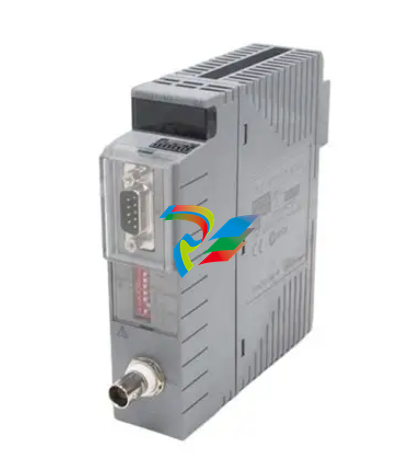
GE VMIVME-5576 Fiber-Optic Reflective Memory with Interrupts
this mode of operation, the first of the two transfers is used
unless an error is detected in which case the second transfer
is used. In the event that an error is detected in both transfers,
the node removes the transfer from the system. The
probability of both transfers containing an error is 10-20. or
about one error every 372.000 years at maximum data rate.
PROTECTION AGAINST LOST DATA — Data
received by the node from the fiber-optic cable is error
checked and placed in a receive FIFO. Arbitration with
accesses from the VMEbus then takes place and the data is
written to the node’s SRAM and to the node’s transmit FIFO.
Data written to the board from the VMEbus is placed directly
into SRAM and into the transmit FIFO. Data in the transmit
FIFO is transmitted by the node over the fiber-optic cable to
the next node. Data could be lost if either FIFO were allowed
to become full.
The product is designed to prevent either FIFO becoming
full and overflowing. It is important to note the only way that
data can start to accumulate in FIFOs is for data to enter the
node at a rate greater than 6.2 or 3.2 Mbyte/s in redundant
mode. Since data can enter from the fiber and from the
VMEbus, it is possible to exceed these rates. If the transmit
FIFO becomes half-full, a bit in the Status Register is set and,
if armed, an interrupt is generated. This condition is an
indication to the software in the node that writes to the
Reflective Memory should be suspended until the FIFO
becomes less than half-full. If the half-full indication is
ignored and the transmit FIFO becomes full, then writes to the
Reflective Memory will be acknowledged with a bus error.
With VMEbus writes being blocked by the bus error, data
cannot overflow in the receive FIFO.
NETWORK MONITOR — There is a bit in a Status
Register that can be used to verify that data is traversing the
ring (that is, the ring is not broken). This can also be used to
measure network latency.
SPECIFICATIONS
Memory Size: 256 Kbyte, 512 Kbyte, or 1 Mbyte
Access Time:
400 ns (worst-case arbitration)
200 ns (best-case arbitration)
TRANSFER SPECIFICATION
Transfer Rate:
6.2 Mbyte/s (longword accesses) without redundant
transfer
3.2 Mbyte/s (longword accesses) with redundant transfer
COMPATIBILITY
VMEbus: This product complies with the VMEbus
specification (ANSI/IEEE STD 1014-1987. IEC 821 and
297), with the following mnemonics:
A32: A24: D32/D16/D08 (EO): Slave: 39/3D:09/0D
Form factor: 6U
Memory: Addressable on 256 Kbyte boundaries for
256 Kbyte memory option
Addressable on 512 Kbyte boundaries for 512 Kbyte
memory option
Addressable on 1 Mbyte boundary for 1 Mbyte memory
option
INTERCONNECTION
Cable Requirements: Two fiber-optic cables
Cable Length: 2.000 m maximum between nodes
Configuration: Daisy chain ring up to 256 nodes
PHYSICAL/ENVIRONMENTAL
Temperature Range: 0 to 55 °C, operating-40 to 85 °C, storage
Relative Humidity: 20 to 80 percent, noncondensing
Power Requirements: 5.0 A maximum at +5 VDC
MTBF: 142.400 hours (217F)
DATA TRANSFERS
Data written into the Reflective Memory is broadcast to
all nodes on the network without further involvement of the
sending or receiving nodes. Data is transferred from memory
locations on the sending nodes to corresponding memory
locations on the receiving nodes.
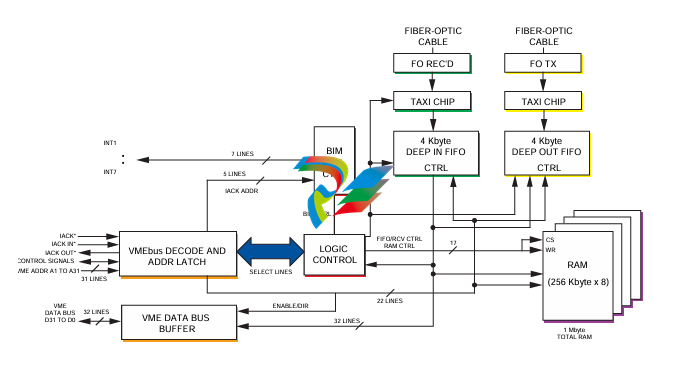
A functional block diagram of the VMIVME-5576 is
shown in Figure 1.
TRADEMARKS
The VMIC logo is a registered trademark of VMIC.
Other registered trademarks are the property of their
respective owners.

























.png)