A-BPowerFlex 700 Adjustable Frequency AC Drive
(16) Temperature rating is for IP20, NEMA / UL Type 1. For IP00, NEMA Type Open the temperature rating is 65 °C for the control board and 40 °C for the heat sink entry air.
(17) 40 °C = 104 °F; 45 °C = 113 °F; 50 °C = 122 °F; 55 °C = 131 °F
Cable Recommendations
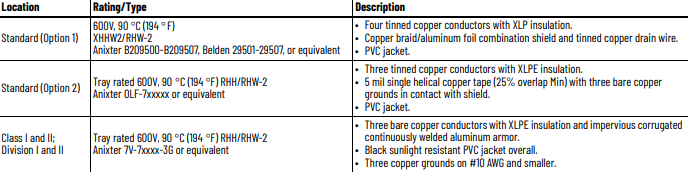
Power Cable Types Acceptable for 200…600 Volt Installations
Various cable types are acceptable for drive installations. For many installations, unshielded cable is adequate, provided it can be separated
from sensitive circuits. As an approximate guide, allow a spacing of 0.3 meters (1 foot) for every 10 meters (32.8 feet) of length. In all cases,
long parallel runs must be avoided. Do not use cable with an insulation thickness less than or equal to 15 mils (0.4mm/0.015 in.). Use Copper
wire only. Wire gauge requirements and recommendations are based on 75 °C (167 °F). Do not reduce wire gauge when using higher
temperature wire. See table below.
Unshielded
THHN, THWN or similar wire is acceptable for drive installation in dry environments provided adequate free air space and/or conduit fill rates
limits are provided. Do not use THHN or similarly coated wire in wet areas. Any wire that is chosen must have a minimum insulation
thickness of 15 mils and should not have large variations in insulation concentricity.
Shielded/Armored Cable
Shielded cable contains all general benefits of multi-conductor cable with the added benefit of a copper braided shield that can contain
much of the noise that is generated by a typical AC drive. Strong consideration for shielded cable should be given in installations with
sensitive equipment such as weigh scales, capacitive proximity switches and other devices that may be affected by electrical noise in the
distribution system. Applications with large numbers of drives in a similar location, imposed EMC regulations or a high degree of
communications/ networking are also good candidates for shielded cable.
Shielded cable may also help reduce shaft voltage and induced bearing currents for some applications. In addition, the increased impedance
of shielded cable may help extend the distance that the motor can be located from the drive without the addition of motor protective devices
such as terminator networks.
Consideration should be given to all general specifications that are dictated by the environment of the installation, including temperature,
flexibility, moisture characteristics and chemical resistance. In addition, a braided shield should be included and be specified by the cable
manufacturer as having coverage of at least 75%. An additional foil shield can greatly improve noise containment.
A good example of recommended cable is Belden 295xx (xx determines gauge). This cable has four (4) XLPE insulated conductors with a
100% coverage foil and an 85% coverage copper braided shield (with drain wire) surrounded by a PVC jacket.
Other types of shielded cable are available, but the selection of these types may limit the allowable cable length. Particularly, some of the
newer cables twist four conductors of THHN wire and wrap them tightly with a foil shield. This construction can greatly increase the cable
charging current required and reduce the overall drive performance. Unless specified in the individual distance tables as tested with the
drive, these cables are not recommended and their performance against the lead length limits supplied is not known.
Maximum Motor Cable Lengths
For information on maximum motor cable lengths, see the Wiring and Grounding Guidelines for Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) AC Drives,
publication DRIVES-IN001.
Power Wiring
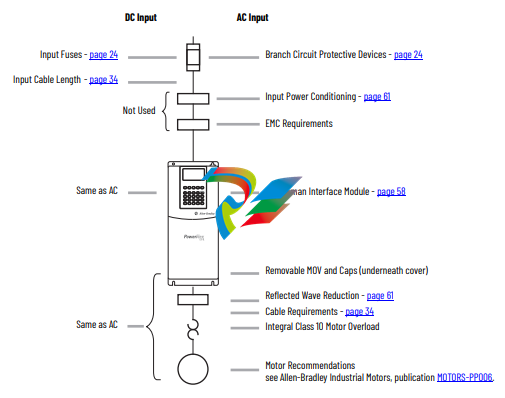
The PowerFlex 700 has the following built in protective features to help simplify installation:
• Ground fault protection during startup and running ensures reliable operation
• Electronic motor overload protection increases motor life
• Removable MOV to ground and common mode capacitors to ground ensure compatibility with ungrounded systems. These devices
must be disconnected if the drive is installed on a resistive grounded distribution system, an ungrounded distribution system, a B
phase grounded distribution system or impedance grounded system. These devices must also be disconnected if the drive power
source is a regenerative unit (such as a bus supply and brake) or is DC fed from an active converter.
• 6 kV transient protection provides increased robustness for 380…480V system voltages
There are many other factors that must be considered for optimal performance in any given application. The block diagram below highlights
the primary installation considerations. Consult the Wiring and Grounding Guidelines for Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) AC Drives, publication
DRIVES-IN001 for detailed recommendations on input power conditioning, dynamic braking, reflected wave protection and motor cable
types.





.png)


.png)

























.png)