EMERSONDeltaV SISTM Logic Solver
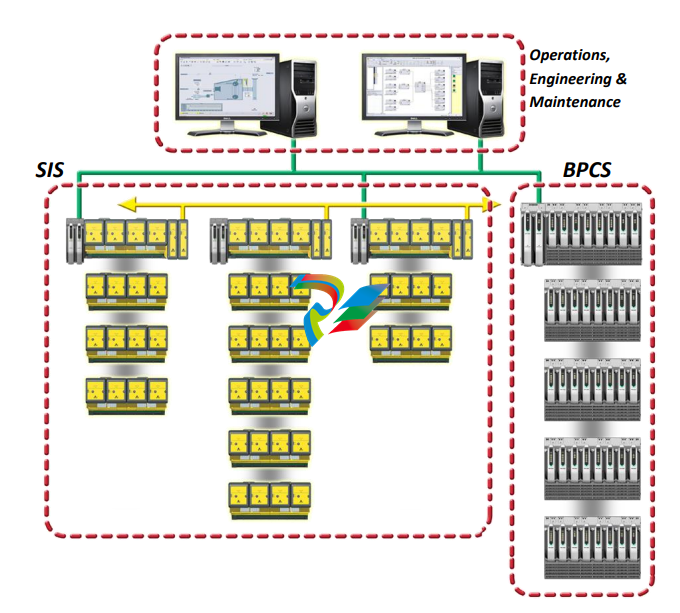
Control Network: The DeltaV Control Network provides
communication between the nodes in the DeltaV network.
Refer to the Installing Your DeltaV Digital Automation
System manual for complete information on the Control
Network.
Local Bus: The Local Bus provides communication
between DeltaV controllers and Logic Solvers and
between DeltaV controllers and SISnet Repeaters.
Local Peer Bus (SISnet): Logic Solvers communicate
with other Logic Solvers and with local SISnet Repeaters
through the carriers over a 2 channel local peer bus. The
same message is broadcast over both channels. The local
peer bus must be terminated at both ends. The local peer
bus is terminated at the left end through the 2-wide
power/controller carrier and at the right end through a
terminated 1-wide carrier.
The SISnet Repeaters can be located anywhere on a local
peer bus – between the DeltaV Controller(s) and the
terminated 1-wide carrier.
Remote Peer Ring: SISnet Repeaters hosted by one
DeltaV controller communicate with SISnet Repeaters
hosted by a different DeltaV controller over a fiber-optic
remote peer ring. A local SISnet Repeater collects locally
generated messages that have been designated as global
variables into a single message and sends it to the next
SISnet Repeater in the ring. Upon receipt of a message,
the receiving SISnet Repeater broadcasts it on its local
peer bus (SISnet) and forwards the message to the next
SISnet Repeater in the ring. A global message is
forwarded around the ring once. The primary SISnet
Repeaters form one fiber-optic ring and the secondary
form a separate, independent ring.
Carrier extender cables and local peer bus extender
cables connecting a DeltaV controller and 8-wide carrier
with standard DeltaV I/O and DeltaV SIS Logic Solvers to
a second 8-wide carrier (hosted by the same controller)
are installed with Logic Solvers, SISnet Repeaters, and a
terminated 1-wide carrier. Logic Solver messages are
communicated to a remote DeltaV SIS (hosted by a
separate controller) through fiber-optic cables.
DeltaV SIS Product Data Sheet
May 2013 – Page 5 DeltaV SIS Logic Solver
Unique Redundancy Methodology
Introduction to Redundancy
Unlike other SIS Logic Solvers, the SLS 1508 is rated
suitable for use in SIL 3 applications in simplex mode.
Redundant SLS 1508 Logic Solvers run in parallel at all
times. Both read the inputs from the I/O terminals, both
execute the logic and both drive the outputs at the I/O
terminals. There is no concept of primary and backup or
master and slave, which is unlike any other SIS. The only
difference between the two is that one communicates with
both the engineering and operator workstations and the
dedicated safety network (SISnet); this is the one with the
Active light on the bezel. The other (Standby) is
communicating only on the SISnet.
In the event that a failure is detected in one of the SLS
1508 Logic Solvers, it automatically goes to a failed state.
In this condition all its output channels are de-energized;
this has no impact on the other Logic Solver or the
physical outputs because the other Logic Solver continues
to read inputs, execute logic and drive outputs. The
transition from redundant to simplex mode is therefore
completely bumpless.
Redundancy
The redundant SLS 1508 Logic Solver modules are
connected to the field at the redundant terminal block. No
control strategy configuration is required to take
advantage of SLS 1508 Logic Solver redundancy, as the
system’s auto-sense capability automatically recognizes
the redundant pair of Logic Solvers.
An integrity error alarm in a redundant Logic Solver pair
will notify the operator of a failure. Both Logic Solvers in a
redundant pair are monitored for integrity alarms at all
times.
Events that can cause integrity alarms include:
Hardware failure within a Logic Solver
Communications failure between a Logic Solver and
the SISnet
Communications failure between a redundant pair of
Logic Solvers
Communications failure between a Logic Solver and
an DeltaV Controller
Removal of a Logic Solver from the carrier
The health and status of both Logic Solvers and their
channels are available in the diagnostics explorer.
When one of a redundant pair of SLS 1508 Logic Solvers
is removed online there is no disturbance to the process.
When the missing Logic Solver is replaced with another
Logic Solver, the new Logic Solver completes its power-up
self-tests before the active Logic Solver cross-loads the
current database. In safe areas, failed Logic Solvers can
be replaced under power. In hazardous areas, appropriate
installation procedures must be followed.
Automatic proof testing can be selected on a redundant
pair of Logic Solvers. The desired proof-test interval is set
in the configuration and the Logic Solvers perform the





.png)


.png)

























.png)