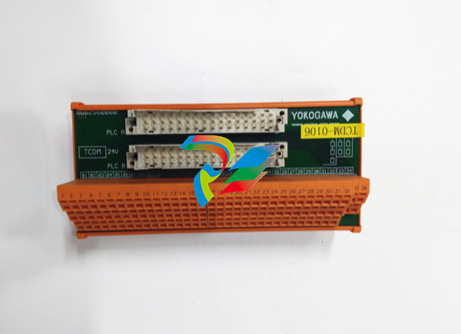
EMERSONIPMC7126E/7616E I/O Module
synchronous transfer rate across a 16-bit bus.
Note SCSI signals leading to connector P15 go through zero ohm resistors (R92-R100) before
terminating at P15. When the host board’s PMC slot 2 is populated, and there is an IPMC
module in slot 1, there exists a possibility for contention on these signals.
Figure 1-1. IPMC761 with Default Switch Setting
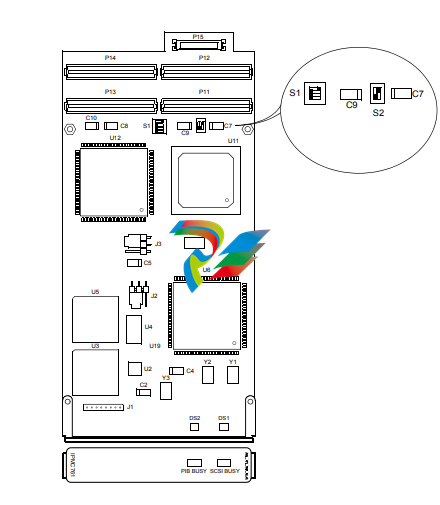
Table 1-1. IPMC761 Jumpers
Jumper Description Setting
J1 Reserved 9PLD programming
header
N/A
J2 Port 3 Transmit Clock 1-2: driven by IPMC761
2-3: received by IPMC761
J3 Port 4 Transmit Clock 1-2: driven by IPMC761
2-3: received by IPMC761
Figure 1-2. IPMC761 Functional Block Diagram
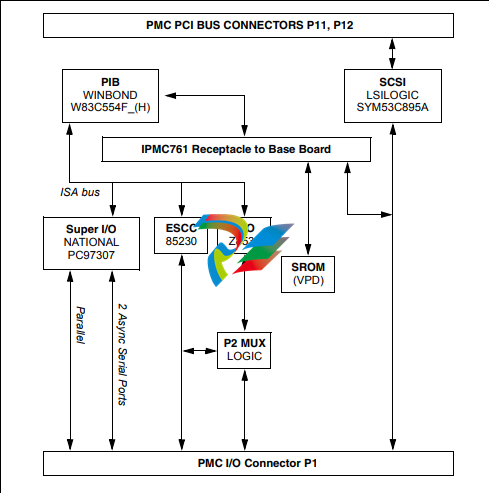
Figure 1-3. IPMC712 with Default Switch Settings
Table 1-2. IPMC712 Jumpers
Jumper Description Setting
J1 Reserved 9PLD programming
header
N/A
J2 Port 4 Receive Clock 1-2: driven by IPMC712
2-3: received by IPMC712
J3 Port 4 Transmit Clock 1-2: driven by IPMC712
2-3: received by IPMC712
J5 Clock Loopback MAX207 14/15in connects to R1out
Figure 1-4. IPMC712 Functional Block Layout
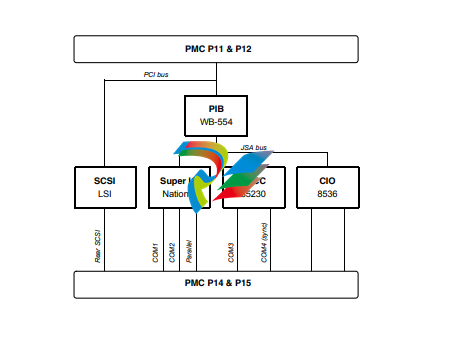
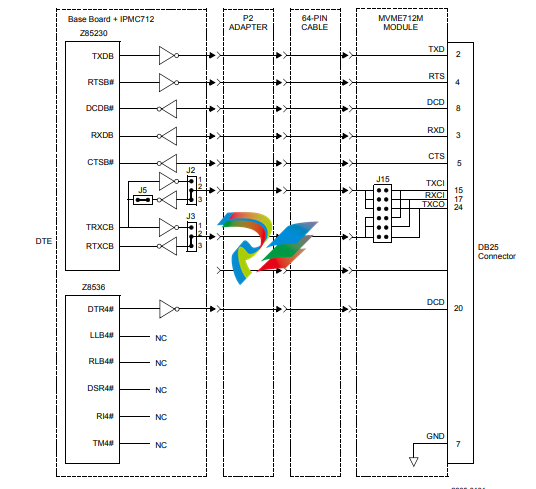
Figure 1-5. IPMC712 Serial Port 4 Clock Configuration
ISA Local Resource Bus
PCI-to-ISA Bridge (PIB)
The PIB (W83C554F) contains the ISA Bridge I/O Registers necessary for various functions.
These registers are also accessible from the PCI bus.
Super I/O
The Super I/O device (PC97307) provides the following functions on the IPMC:
■ Two synchronous serial ports (COM1 and COM2)
■ Parallel printer port
ESCC
Two DTE synchronous/asynchronous serial ports are provided by the ESCC device (Z85230).
Since the Z85230 device does not have all modem control lines, a Z8536 CIO device (described
below) is used to provide the missing lines.
A PAL device is used to perform decode for the Z85230 and the Z8536 for register accesses
and pseudo interrupt acknowledge cycles in the ISA I/O space. DMA supports for the Z85230
is provided by the PIB.
The clock input to the Z85230 PCLK pin is a 10 MHz clock. The Z85230 supplies an interrupt
vector during a pseudo interrupt acknowledge cycle. The vector is modified based upon the
interrupt source within the device.
All modem control lines from the ESCC are multiplexed/demultiplexed through connector P2 by
the P2MX function due to pin limitation of the connector.
CIO
The CIO device (Z8536) is used to provide the modem control lines not provided by the Z85230
ESCC. In addition, the device has three independent 16-bit counters/timers. The clock input to
the Z8536 PCLK pin is a 5 MHz clock.
Static ROM (SROM)
Both modules contains one +3.3V, 256 x 8 serial EEPROM device (AT24C02) onboard. This
device provides for Vital Product Data (VPD) storage of the module hardware configuration. The
serial EEPROM is located on the baseboard’s I2C bus at address $A4.
Input/Output Modes
Both modules are designed to be plugged into PMC slot 1 of the base board. As stated earlier,
these SBCs have two P2 I/O modes (IPMC and PMC) that are user configurable. The user
should configure the baseboard for the IPMC module being used.
The jumpers route the on-board Ethernet port 2 to row C of connector P2. When used, both
modules are backwards compatible with the MVME761 rear transition module and P2 adapter
card (excluding PMC I/O routing) used on the MVME2600/2700. The rear panel Ethernet is not
available when using the IPMC712.
LEDs
Both modules use two LEDs to provide PMC status.
■ The module’s green SCSI LED is lit when the SCSI device is Master
■ The module’s green PIB LED is lit when the PCI bus grant to the PIB is asserted
PCI Signaling Voltage Level
Both modules will operate with only +5V signaling levels.
RS232 Interface
On the IPMC712 module, the four serial ports are used to communicate at RS232 voltage levels
(P14). The first three ports are fixed asynchronous ports, while the remaining port can be
configured as either a synchronous or an asynchronous port.
For additional handshaking signals, the IPMC712 module has the following features:
■ Port 1 has RTS and CTS
■ Ports 2, 3, and 4 have RTS, CTS, DTR, DCD
■ Port 4 has configurable serial clock signals RTxC and TRxC
Jumpers J2, J3 and J5 determine the sources for these two signals, refer to Figure 1-5 on
page 7.
This chapter discusses the configuration and installation of IPMC modules on an MVME6100,
MVME5500, or MVME5100 SBCs.
For additional information pertaining to the MVME51005E, refer to the information contained in
the MVME51005E Single Board Computer Installation and Use manual before proceeding with
these instructions contained in this chapter.
Packaging
As a precautionary measure, IPMC modules are sealed in an anti-static package to protect
them from static discharge. Observe standard handling practices of static sensitive equipment.
Configuring the IPMC Modules
There are two user configurable switches on the IPMC712 and IPMC761 I/O modules. Switches
S1 and S2 are described in Chapter 3, Programming.
Installing IPMC Modules on Host Board
Both the IPMC712 and the IPMC761 modules are installed on PMC slot 1 of the host board. As
a general reminder, IPMC modules must be installed on the host board prior to installing it into





.png)


.png)

























.png)