GE Fanuc Automation VMIVME-7750 Specifications
Based VME Single Board
Computer
Features:
• Up to 1.26 GHz Pentium® III processor with 512 Kbyte
advanced transfer cache
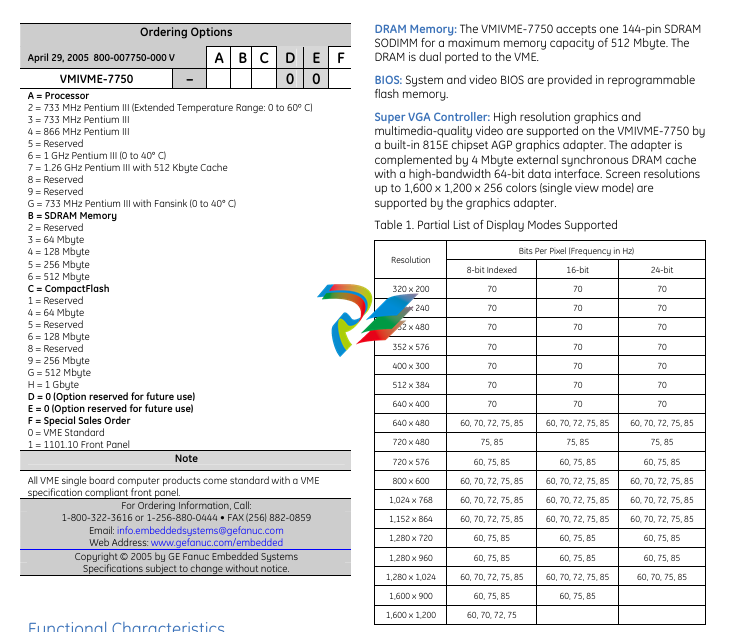
• Up to 512 Mbyte PC133 SDRAM using a single SODIMM
• Internal AGP SVGA controller with 4 Mbyte display cache
• Dual Etherne
• 133 MHz system bus via Intel® 815E chipset
t controllers supporting 10BaseT and 100BaseTX
• interfaces
• Remote Ethernet boo
ting
•
• PMC expansion site
Operating system support for Windows® XP, Wind
VxWorks®, Solaris™, QNX®, LynxOS®, and Linux®
ows 2000.
Mailboxes: The VMEbus interface provides four 32-bit
mailboxes, which are accessible from both the microprocessor
and the VMEbus providing interprocessor communication. The
mailboxes have the ability to interrupt the microprocessor when
accessed by VMEbus.
Interrupt Handler: The interrupt handler monitors, and can be
programmed to respond to any or all VMEbus IRQ* lines. All
normal-process VMEbus-related interrupts can be mapped to
PCI INTA# or SERR# interrupts. These include:
Mailbox interrupts
VMEbus interrupts
VMEbus interrupter IACK cycle (acknowledgment of
VMIVME-7750 VMEbus-issued interrupts)
All error processing VMEbus-related interrupts can be mapped
to PCI INTA# or SERR#. Note: PCI SERR# initiates a SBC NMI.
These include:
ACFAIL* interrupt
BERR* interrupt
SYSFAIL* interrupt
The interrupt handler has a corresponding STATUS/ID register
for each IRQ* interrupt. Once the handler receives an IRQ*, it
requests the VMEbus and, once granted, it performs an IACK
cycle for that level. Once the IACK cycle is complete and the
STATUS/ID is stored in the corresponding ID register, an
appropriate interrupt status bit is set in an internal status
register, and a PCI interrupt is generated. The PCI interrupt can
be mapped to PCI INTA# or SERR#.
Interrupter: Interrupts can be issued under software control on
any or all of the seven VMEbus interrupt lines (IRQ7* to IRQ1*). A
common ID register is associated with all interrupt lines. During
the interrupt acknowledge cycle, the interrupter issues the ID to
the interrupt handler.
The interrupter can be programmed to generate a PCI INTA# or
SERR# interrupt when a VMEbus interrupt handler
acknowledges a software-generated VMEbus interrupt.
Byte Swapping: The Intel 80x86 family of processors use little
endian format. To accommodate other VMEbus modules that
transfer data in big-endian format such as the 680x0 processor
family, the VMIVME-7750 incorporates byte-swapping
hardware. This provides independent byte swapping for both
the master and slave interfaces. Both master and slave
interface byte swapping are under software control.
The VMIVME-7750 supports high throughput DMA transfers of
bytes, words, and longwords in both master and slave
configurations.
If endian conversion is not needed, we offer a special “bypass”
mode that can be used to further enhance throughput. (Not
available for byte transfers.)
Master Interface: MA32:MBLT32:MBLT64
(A32:A24:A16:D32:D16:D8 (EO):BLT32)
The VMEbus master interface provides nine separate memory
windows into VMEbus resources. Each window has separate
configuration registers for mapping PCI transfers to the VMEbus
(that is, PCI base address, window size, VMEbus base address,
VMEbus access type, VMEbus address/data size, etc.). The
maximum/minimum window sizes for the nine windows are as
follows:
Window
Minimum Size
0. 4
Maximum Size
4 Kbyte
1 to 3. 5 to 7
4 Gbyte
64 Kbyte
Special Cycle
4 Gbyte
64 Mbyte
64 Mbyte
Slave Interface: Memory Access
SAD032:SD32:SBLT32:SBLT64
(A32:A24:A16:D32:D16:D8 (EO): BLT32)
The VMEbus slave interface provides eight separate memory
windows into PCI resources. Each window has separate
configuration registers for mapping VMEbus transfers to the PCI
bus (that is, VMEbus base address, window size, PCI base
address, VMEbus access type, VMEbus address/data size, etc.).
The maximum/minimum window sizes for the eight windows
are as follows:
Window
Minimum Size
0. 4
Maximum Size
4 Kbyte
4 Gbyte
1 to 3. 5 to 7
64 Kbyte
4 Gbyte
In addition, each window can be programmed to operate in
coupled or decoupled mode. In decoupled mode, the window
utilizes a write-posting FIFO and/or a read prefetching FIFO for
increased system performance. In coupled mode, the FIFOs are
bypassed and VMEbus transactions are directly coupled to the
PCI bus (that is, transfers on VMEbus are not completed until
they are completed on the PCI bus).
Enhanced Bus Error Handling: Enhancements over the
Universe chip’s bus error handling features are provided. A latch
and register are provided to allow the SBC to read the VMEbus
address that caused the bus error in all modes. The Universe
chip’s support is limited to decoupled mode.
Support for bus cycle timeout and assertion of bus error is
provided. The board may be configured to assert bus error upon
timeout regardless of its status as system controller. The
Universe chip asserts bus error only if it is system controller. In
addition, this board may be configured to assert an interrupt
upon bus cycle timeout.
Operating System and Software Support
The VMIVME-7750 provides embedded features beyond PC/AT
functionality. These features are supported by GE Fanuc
Embedded Systems software products aimed at developers
who are incorporating GE Fanuc Embedded Systems SBCs, I/O
boards, and workstations into systems. Windows XP/Windows
2000 and VxWorks are the most common operating systems
supported by GE Fanuc Embedded Systems software products.
Windows XP/Windows 2000: The IOWorks® software family is a
set of software components that can work together or
separately to provide a total development environment for any
application in a Windows XP/ Windows 2000 OS.
VMISFT-9422 VMEbus Access™ for Windows XP/Windows
2000: The VMEbus Access product is specifically designed for

























.png)