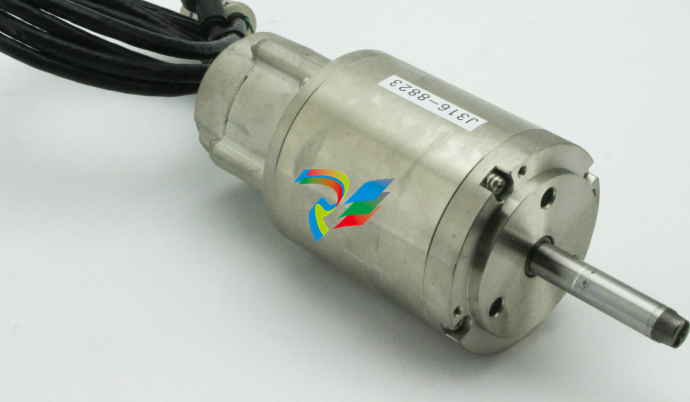
HarmonicHarmonic Drive™ servo
display. (Notice: Optional software is available.)
◆ Power supply terminals: r, s, R, S, T
Are provided for connecting the power supply. Control power is supplied to the [r, s] terminals, and main
power is supplied to the [R,S,T] terminals. (single Phase: R,S; or three phase: R,S,T).
◆ External regeneration resistor terminals: R1, R2
If the built-in regeneration resistor is insufficient in its capacity to handle frequent start/stop operations of
an actuator, an external resistor can be connected to these terminals.
◆ Actuator terminals: U, V, W
Accept an actuator cable. Connect each motor wire to the driver’s terminal marked with a same symbol.
If you confuse the symbols, the driver and the actuator may be in failure.
◆ Ground terminals (Protective earth)
Connect grounds here to prevent electrical shock.
1-7 Outlines of I/O ports
The CN2 connector provides input and output signals to and from a host device. The 50 pins of the
connector are assigned to the following signals in each of the [position mode] and the [speed mode].
(Notice: Do not connect signals to pins marked “-“.)
1-8 Operating display panel
The HA-655 driver provides a 6-digit LED display and four operation keys on the front panel. The panel
executes monitoring, tuning, setting, and JOG operation.
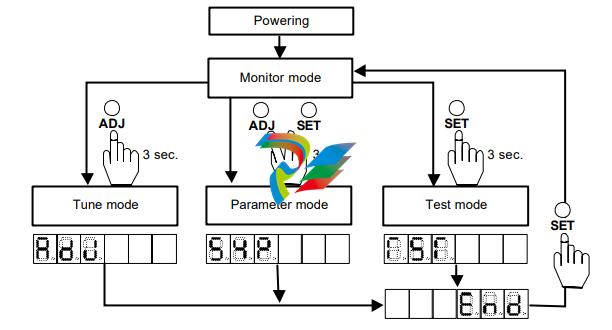
1-8-1 Outlines of operation modes
The HA-655 driver provides the following four modes: monitoring, tuning, setting, and operations.
◆ Monitor mode
The HA-655 driver displays position and speed commands, a current position from a motor-encoder, a
pulse count in an error counter, states of input and output signals, load conditions, alarm histories, and a
code number for the actuator for which the driver is set. The mode can be used for diagnosing an
abnormal driver.
After power supply, the monitor mode starts up and works as the hub of other three modes for operation.
◆ Tune mode
The tuning mode includes various parameters to control the actuator motion. Setting the most suitable
value for each parameter obtains the optimum performance of the actuator.
◆ Parameter mode
The parameter mode sets various parameter values relating to the fundamental operational functions
such as: specifications of the position mode or the speed mode, configurations of input signals, an
electronic gear function, limiting values of speed and torque, and parameters to communicate with a
host.
◆ Test mode
The test mode includes required functions for system tests; such as JOG operation functions, operations
of pseudo output signals, I/O signal monitors, and so on.
1-8-2 Selecting a mode
After powering the driver, the monitor mode starts up automatically. The [ADJ] and [SET] keys select a
mode.
1-9-2 Protective functions
The HA-655 driver provides the following alarms to protect the servo system, and presents an alarm
code on the preceding paragraph.
◆ Over speed (10)
If a motor exceeds its maximum speed or if motor rotates abnormally, the alarm occurs. To clear the
alarm, shut off the control power once and turn it on again.
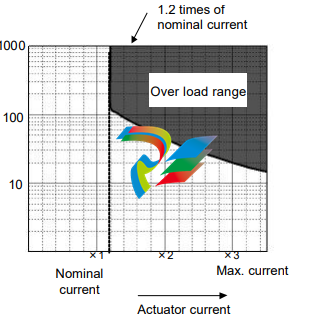
◆ Over load (20)
The driver always monitors the motor current, and if the current exceeds the curve in the figure below,
the overload alarm occurs.
For example:
(1) The alarm occurs if the current
slightly exceeds 1.2 times of
nominal current for a long
duration.
(2) The alarm occurs if the current of
three times of the nominal current
flows for 20 seconds.
It is possible to clear the alarm by
inputting signal to [CN2-2 clear:
CLEAR].
◆ Overheat (21)
The alarm occurs by activating the thermal switch of an IPM element in the HA-655 driver. To clear the
alarm after troubleshooting, shut off the control power once and turn it on again.
◆ Over current (30)
The alarm occurs when the servo control element of the driver detects excessive current. To clear the
alarm after troubleshooting, shut off the control power once and turn it on again.
◆ Abnormal regeneration (41)
The alarm occurs by activating the thermal switch of the regeneration resistor in the HA-655 driver at
100℃. To clear the alarm after troubleshooting, shut off the control power once and turn it on again.
◆ Encoder failure (50)
The alarm occurs when the encoder signal ceases. To clear the alarm after troubleshooting, shut off the
control power once and turn it on again.
The alarm also occurs when a built-in battery of the HA-655 driver for the absolute encoder is taken off in
spite of normal conditions. To clear the alarm, shut off the control power once and turn it on again.
◆ Abnormal encoder signal (51)
The alarm occurs when the driver has failed to receive two sequential signals. To clear the alarm after
troubleshooting, shut off the control power once and turn it on again.
◆ UVW failure (52)
The alarm occurs when the encoder UVW signals are abnormal. To clear the alarm after troubleshooting,
shut off the control power once and turn it on again.
◆ ABS system failure (53)
For the absolute encoder, the alarm occurs when all power supplies (power supply, built-in condenser,
and battery) for the encoder are failure. For example, it occurs at the first power supply after purchasing,





.png)


.png)

























.png)