HarmonicHarmonic Drive™ servo
Increasing or decreasing the single-turn encoder counter of the host device should be discriminated by
the phase shift or delay of phase-A against phase-B. Acquire the signal at rising and falling edge of the
signal.
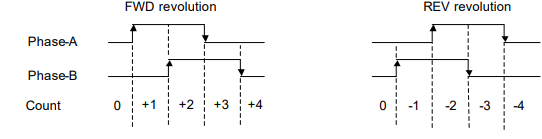
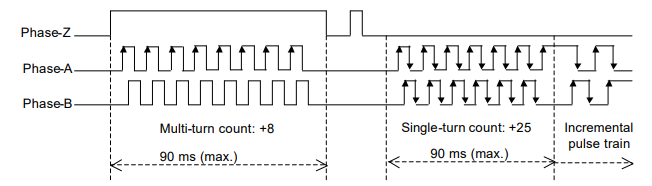
An example of signal transmission
The following is an example of the multi-turn count: 8, single-turn encoder count: 25 and an incremental
pulse train at a usual operation.
The actual resolvable position of the encoder (motor) can obtained by the calculation of:
(b) Acquiring from CN3 port (RS-232C)
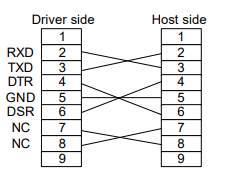
Connecter specifications
Connect an RS-232C cable having following specifications between the CN3 port of the HA-655 driver
and a RS-232C port of a host device.
Connecters: D-sub connecter having 9 female pins
Pin assignments:
Sending a command to HA-655 driver (host →HA-655)
The command should be 10 characters in length including a delimiter as illustrated below. The
HA-655 driver waits until receiving 10 characters without any processing. Make sure that the
message has 10 characters including a delimiter.
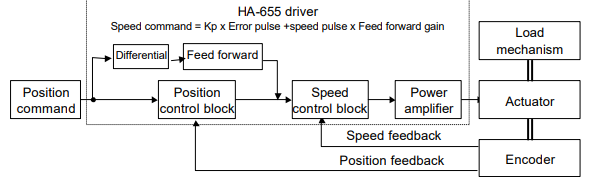
(1) The first function of the [position control block] is the [error count] calculation by the [error counter]
in the block subtracting a feedback count from a command count.
(2) The second function is the block that converts the [error count] to a [speed command] multiplying a
factor, and then transmits the [speed command] to the [speed control block]. The factor (Kp) is
called [position loop gain].
It is clear in the formula that a large [error pulse] is converted into a high [speed command] and a
zero pulse into a zero speed command, in other words, a stop command.
(3) If the [position loop gain (Kp)] is high, a small [error count] is converted into a higher [speed
command]. That is to say, higher gain provides the servo system with better response.
However, very high gain commands result in high [speed commands] from very minimal [error
count] which will result in overshooting. To compensate for the overshoot the [position control block]
generates a high speed reverse command, then overshoots in the opposite direction * * * finally
hunting motion may take place.
Conversely, if the [position loop gain (Kp)] is very low, you will get very slow positioning motion
(undershoot), and a poor servo response.
(4) In conclusion, it is important to set the optimum value to the [position loop gain (Kp)]. The HA-655
driver has been set with the most suitable value for general applications as a factory default. If the
load inertia is very heavy and the default is not suitable, tune it carefully.
◆ [Speed control block], [speed loop gain], and [speed loop integral compensation]
(1) The first function of the [speed control block] is to subtract a feedback signal from a command
signal.
(2) The second function is the block converts the difference to a [current command] multiplies it by a
factor, and then transmits the [current command (I)] to the [power amplifier]. The factor (Kv) is
called [speed loop gain].
It is clear in the formula that a significant [speed difference] is converted into a high [current
command] and zero difference into zero current command, in other words, a stop command.
(3) Just as with the [position loop gain], higher gain provides better response and excessive gain
results in hunting. Low gain requires no hunting but raises the occurrence of undershoots.
(4) The [speed loop integral compensation (Tv)] of The HA-655 driver makes less influence on load
fluctuation.
If the [speed loop integral compensation (Tv)] is smaller, the speed response to the load fluctuation
becomes better, but too small a value results in hunting. Excessive compensation requires no
hunting, but will result in a poor response for load fluctuation.
● Tuning method
[Tune mode]→[0.speed loop gain], and [1: speed loop integral compensation]
◆ Feed forward gain
(1) In the position mode The HA-655 driver controls the error count, (the difference between
[command pulse] and [feedback pulse]), to be [0]. At the beginning of inputting a command pulse
train, the actuator starts slowly because of small error count.
(2) The [feed forward] function may accelerate the actuator as much as possible, adding speed pulses
converted from the command pulse frequency directly to the driver’s speed control loop
) The relation between the feed forward and actuator motion is as follows:
Higher feeding allows for better following to command, but excessive feeding results in hunting and
erratic motion.
Low feeding requires no hunting but a poor following of the command.
● Tuning method
[Tune mode]→[3:Feed forward]
2-2-5 FWD inhibit and REV inhibit
The HA-655 driver provides [FWD inhibit] and [REV inhibit] input signal ports.
[FWD inhibit]: opening (OFF) the input inhibits forward rotation.
[REV inhibit]: opening (OFF) the input inhibits reverse rotation.
Opening (OFF) both inputs inhibits all rotation.
The inputs may be used to limit the motion range between limit sensors.
2-2-6 In-position
In the position mode, even though the driver controls the actuator to make the [error count 0], it is not





.png)


.png)

























.png)