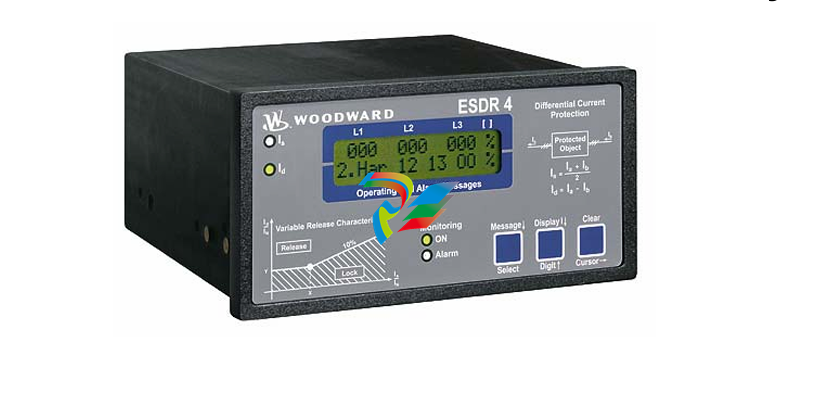
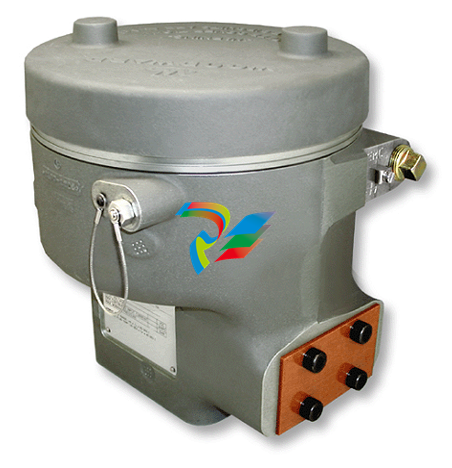
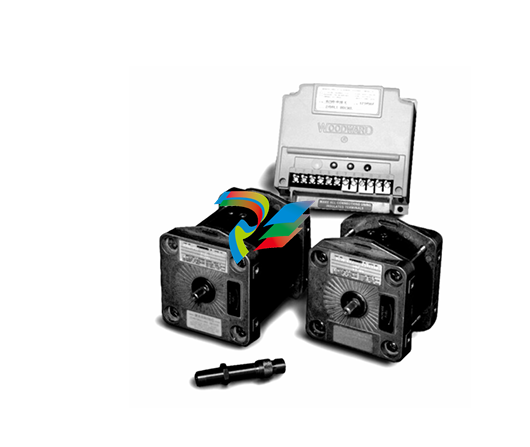
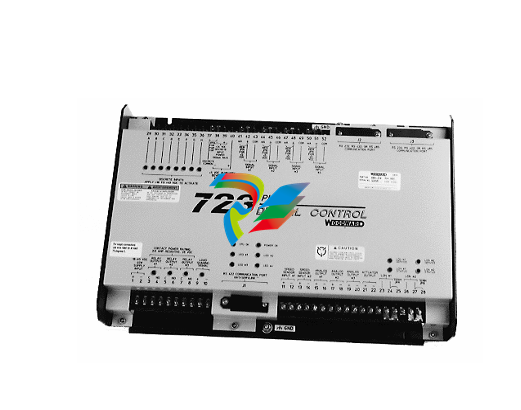
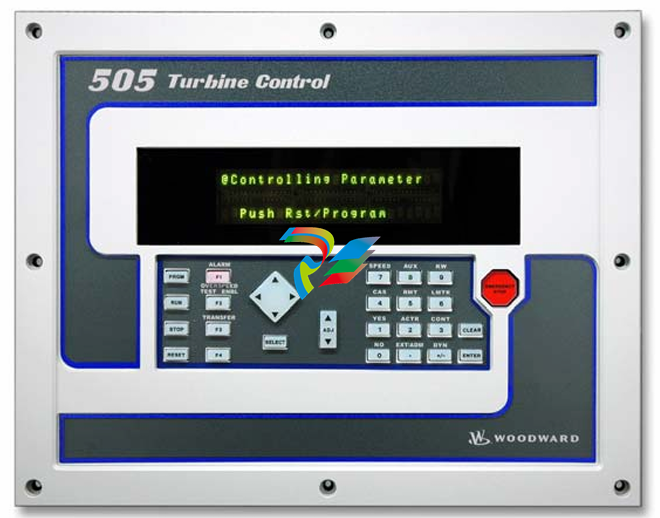
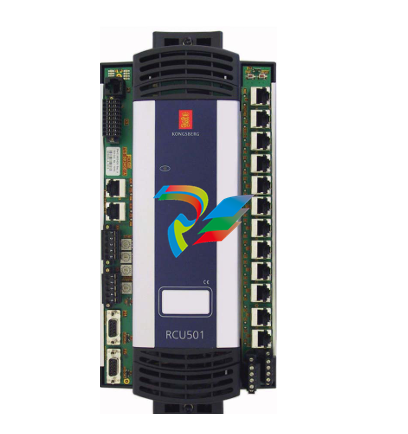
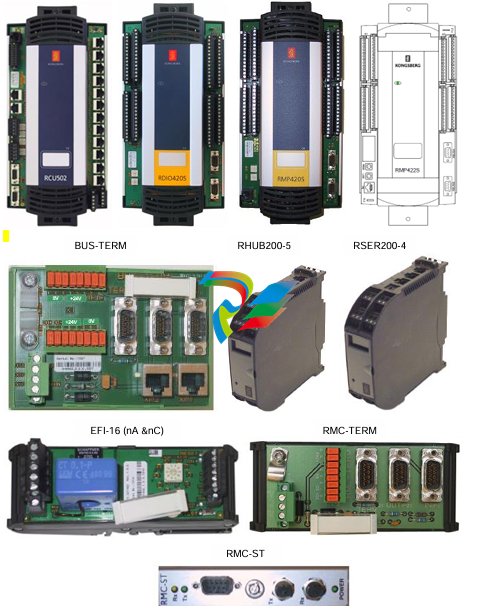
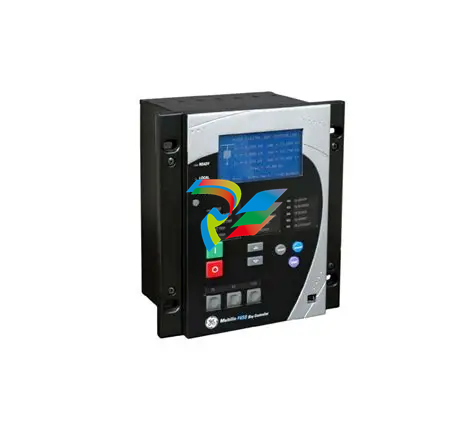
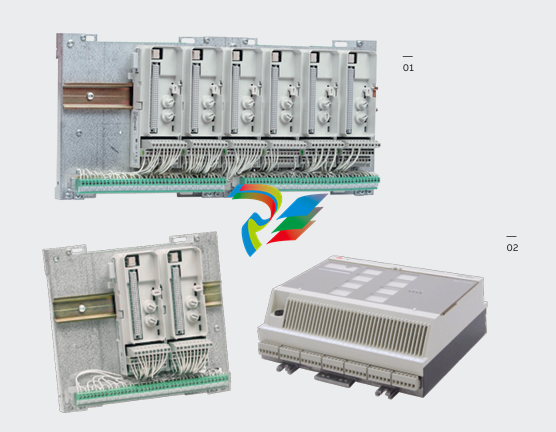
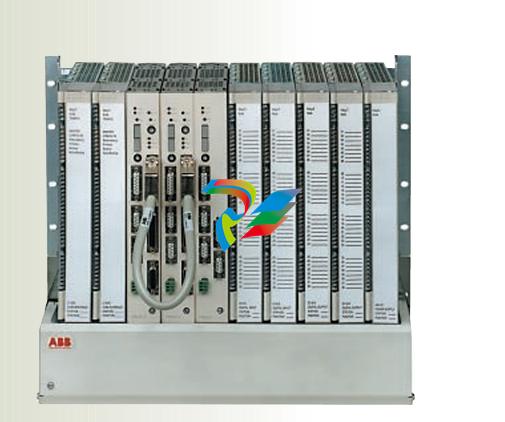
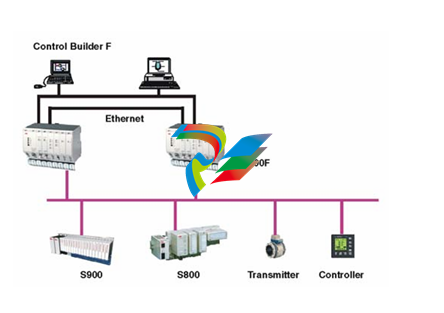
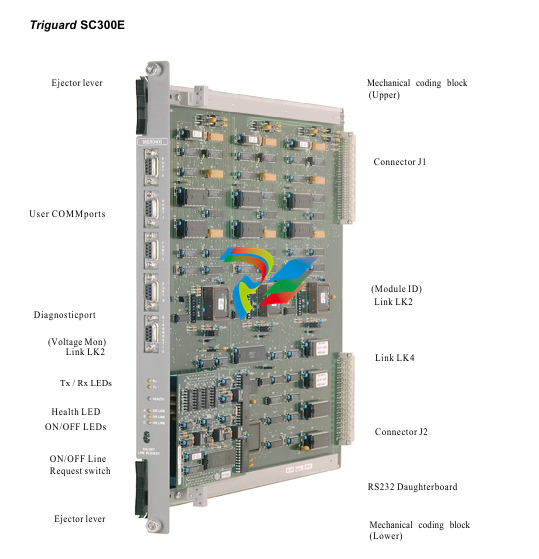
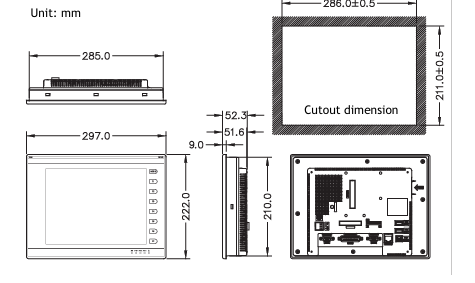
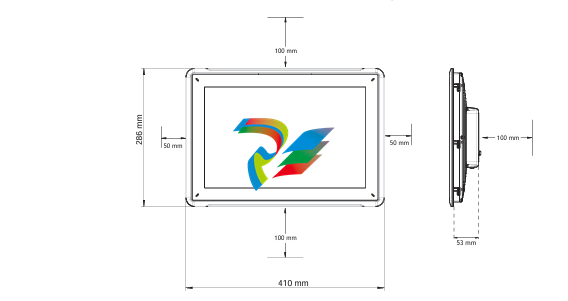
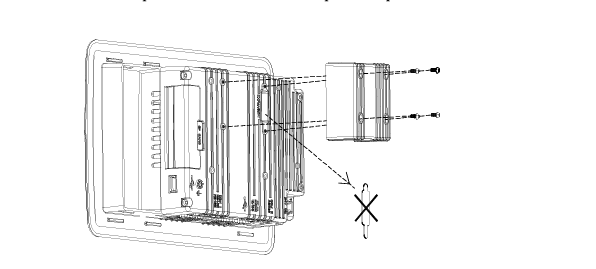
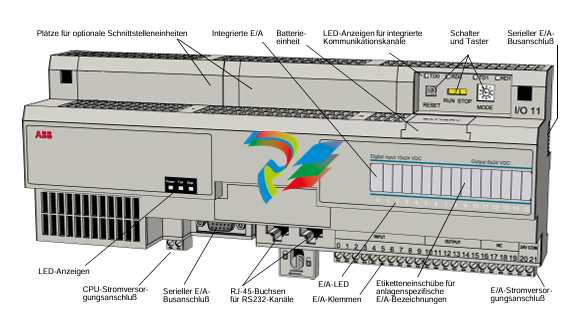
DCS; Industrial control system
Product
Article
NameDescriptionContent
Argument
Current Location:
PRODUCT SHOW
Description
1. Introduction
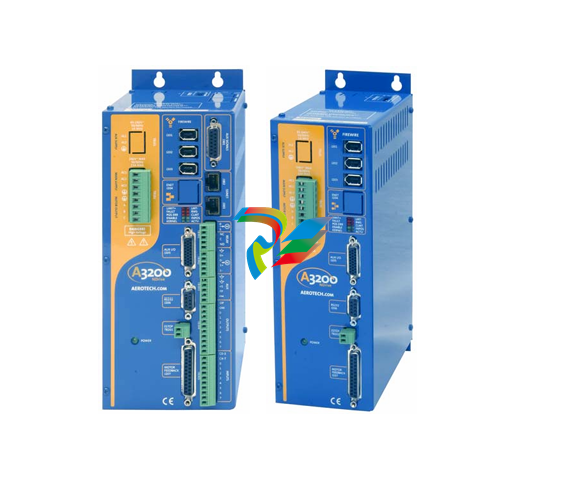
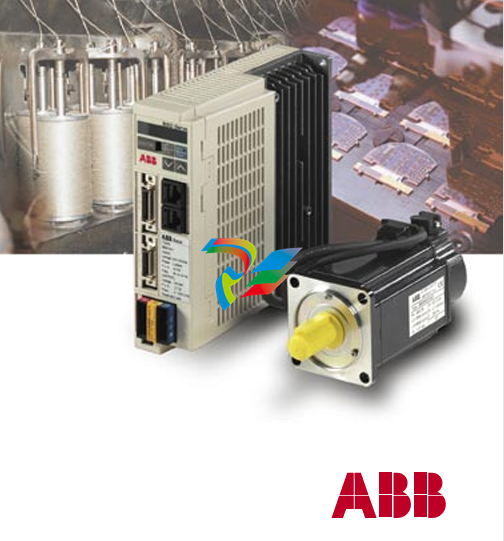
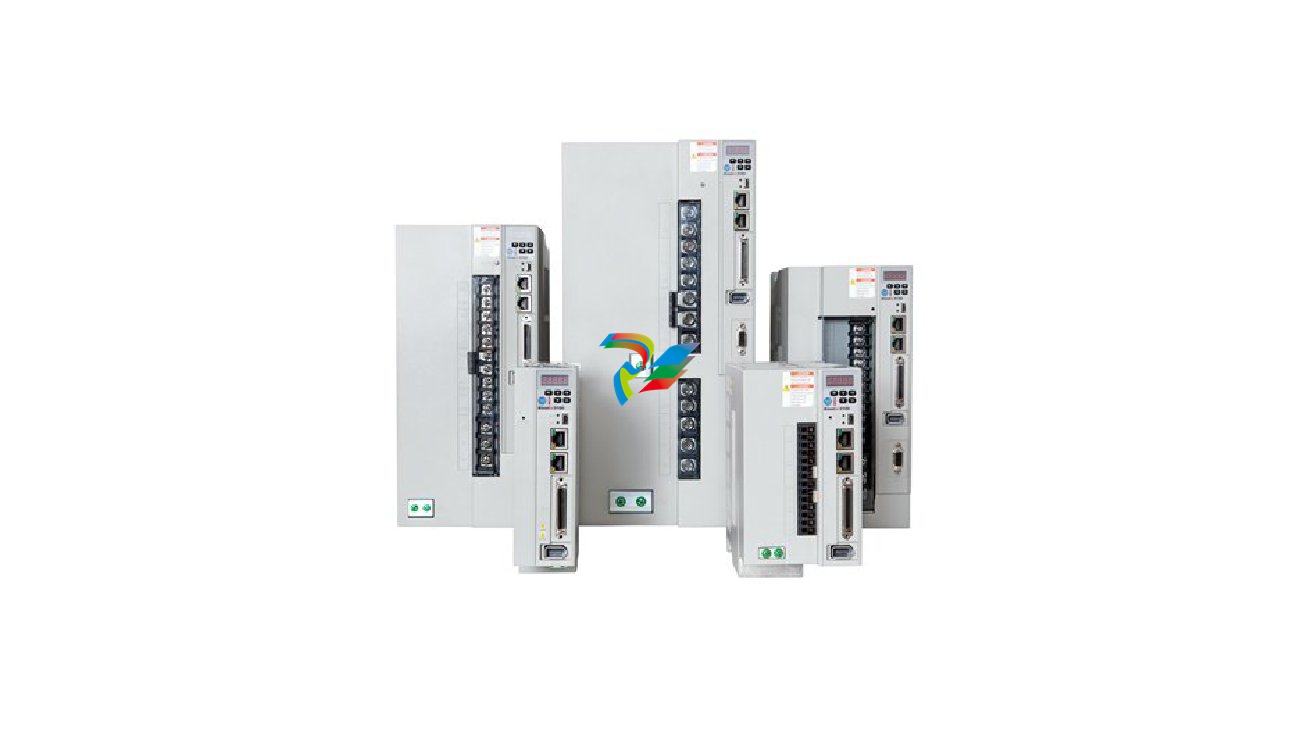
The Kinetix 5100 Servo Drives are advanced and highly capable devices that play a crucial role in the realm of motion control within industrial automation systems. They are designed to precisely control the movement of servo motors, enabling accurate positioning, speed regulation, and torque control for a wide variety of applications in manufacturing, robotics, packaging, and many other industries.
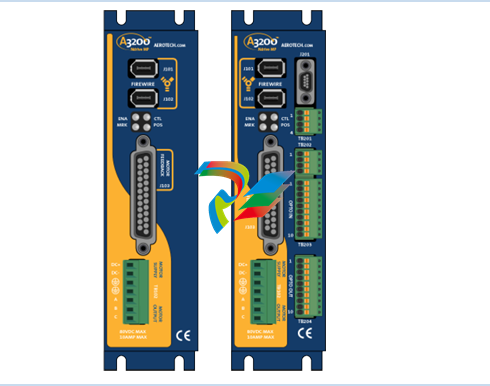
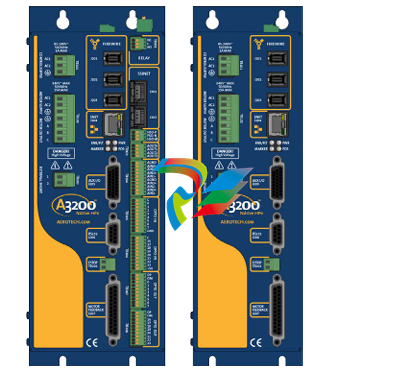
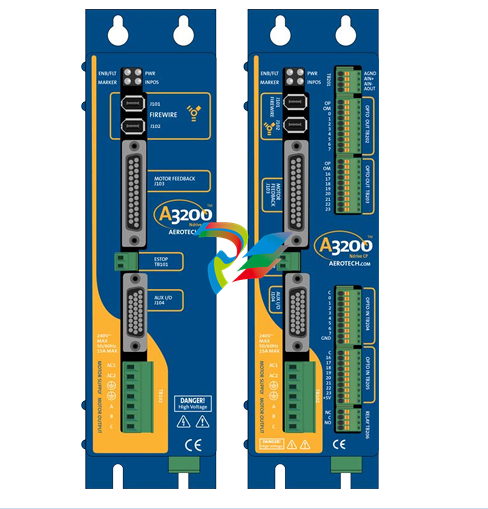
2. Physical Design and Construction
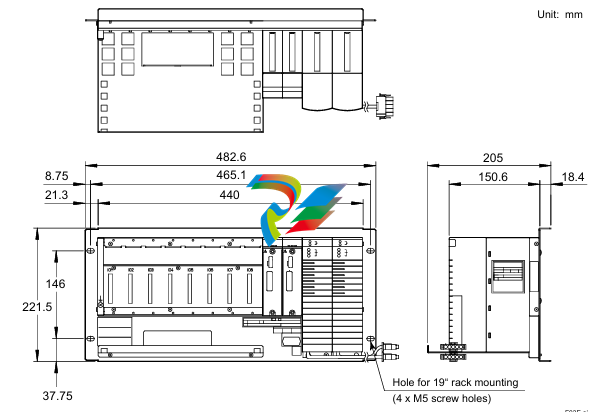
- Compact Form Factor: The Kinetix 5100 Servo Drives feature a relatively compact design, which makes them ideal for installation in tight spaces within control cabinets or on machine frames. Their small size doesn't compromise on functionality but rather allows for efficient use of available space in industrial settings where space is often at a premium.
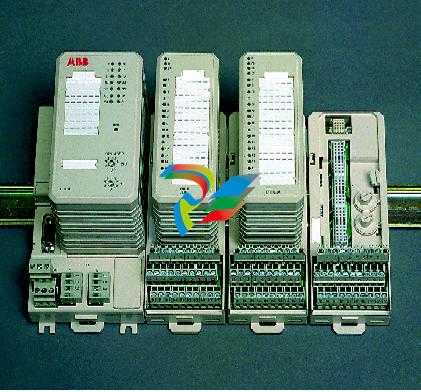
- Robust Housing: These drives are encased in a durable housing typically made from high-quality materials like rugged plastics or metal alloys. This housing protects the internal electronic components from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, vibration, and temperature variations that are commonly encountered in industrial environments. It ensures the long-term reliability and stable operation of the servo drive under harsh working conditions.
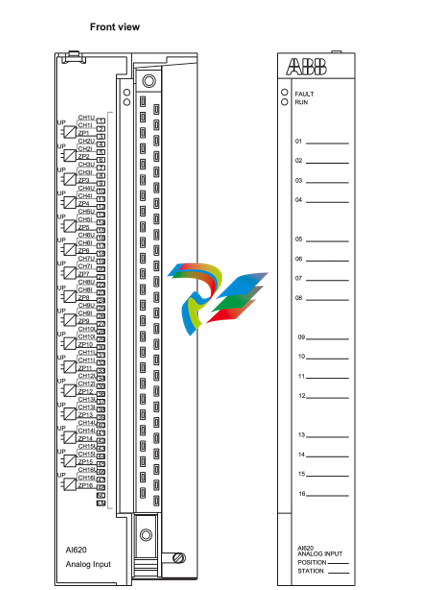
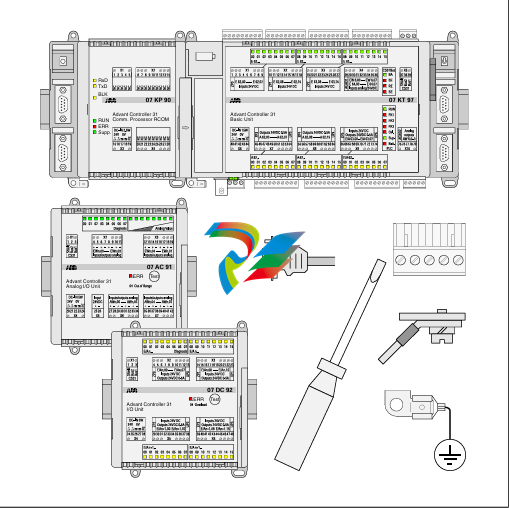
- Connection Interfaces: The drives come equipped with a variety of connection interfaces. On the power input side, there are terminals or connectors designed to handle the appropriate voltage and current levels for the specific application. For example, they can be configured to work with different AC or DC power supplies depending on the motor and system requirements. On the output side, there are connections to the servo motor, which are carefully engineered to provide a stable and reliable electrical connection for transmitting the control signals and power to drive the motor. Additionally, there are communication ports that enable the servo drive to interface with other components in the automation system, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), or other motion control devices.

3. Performance Capabilities
- Precise Positioning: One of the key features of the Kinetix 5100 Servo Drives is their ability to achieve highly precise positioning of the connected servo motor. They can control the motor to stop at exact angular or linear positions with extremely low error margins. This precision is achieved through advanced control algorithms and feedback mechanisms that constantly monitor the motor's position and make real-time adjustments to ensure accurate positioning. For instance, in a robotic assembly application, the servo drive can position the robotic arm's end effector with millimeter or even sub-millimeter accuracy to pick up and place components precisely.
- Speed Regulation: These drives offer excellent speed regulation capabilities. They can maintain a consistent speed of the servo motor over a wide range of operating conditions, regardless of variations in load or other external factors. Whether the motor is running at a slow, precise speed for delicate operations or at a high speed for rapid movements, the Kinetix 5100 Servo Drives ensure that the speed remains stable and within the desired tolerance levels. In a conveyor belt system in a manufacturing plant, for example, the servo drive can keep the belt moving at a constant speed to ensure smooth product flow.
- Torque Control: The ability to precisely control torque is another significant aspect of these servo drives. They can adjust the torque output of the servo motor according to the specific requirements of the application. This is crucial in applications where different levels of force need to be applied, such as in a CNC machining process where the cutting tool needs to exert the right amount of pressure on the workpiece. The servo drive can vary the torque based on the programmed instructions to achieve optimal machining results.
4. Control and Programming
- Multiple Control Modes: The Kinetix 5100 Servo Drives support various control modes to accommodate different application needs. These include position control mode, where the drive is tasked with moving the motor to a specific position; speed control mode, which focuses on maintaining a set speed; and torque control mode, as mentioned earlier, for regulating the motor's torque output. Users can switch between these modes depending on the stage of the process or the specific task at hand.
Purchase history
| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|
Total 0 Record
Customer Reviews
Satisfaction :
5 Stars
No evaluation information