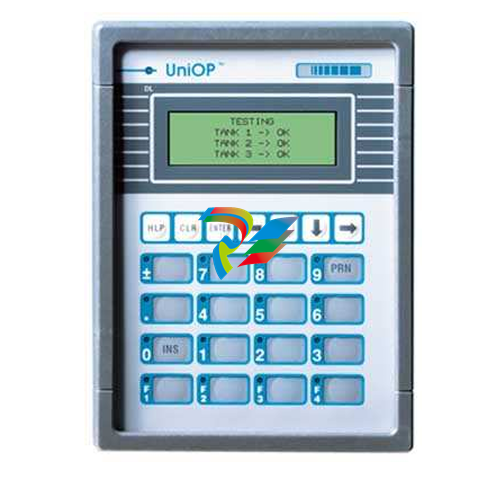
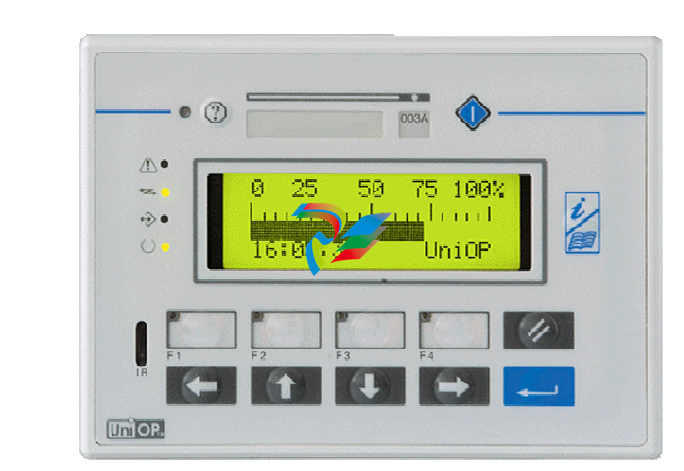
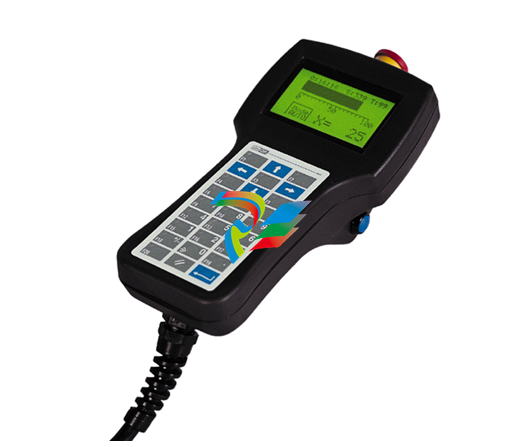
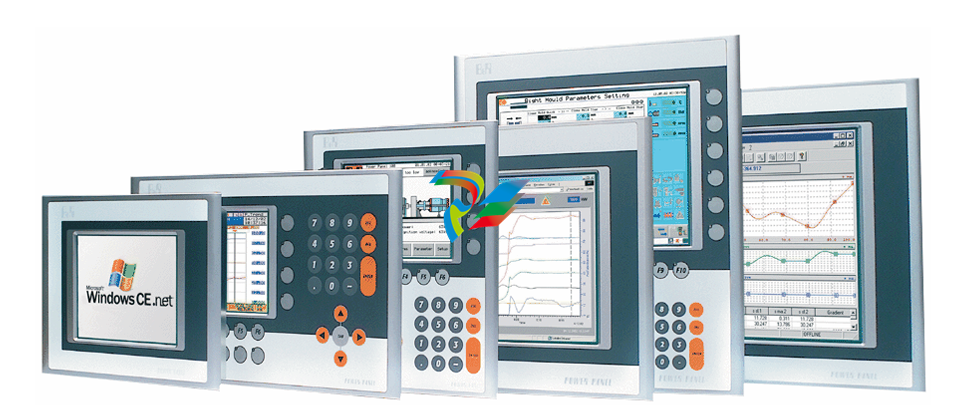
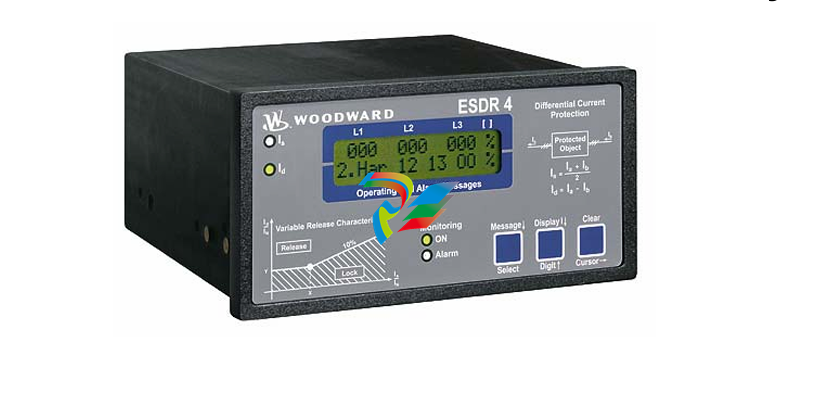
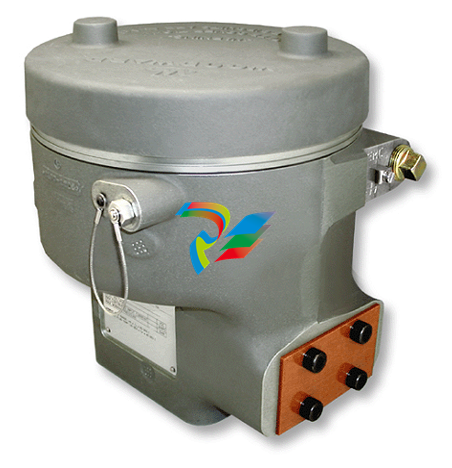
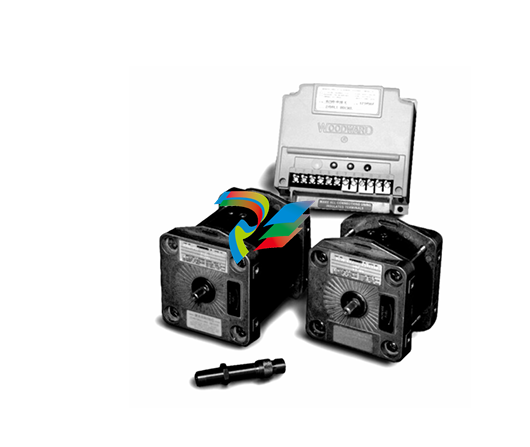
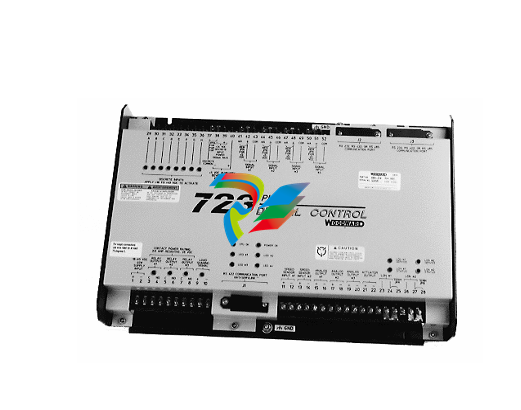
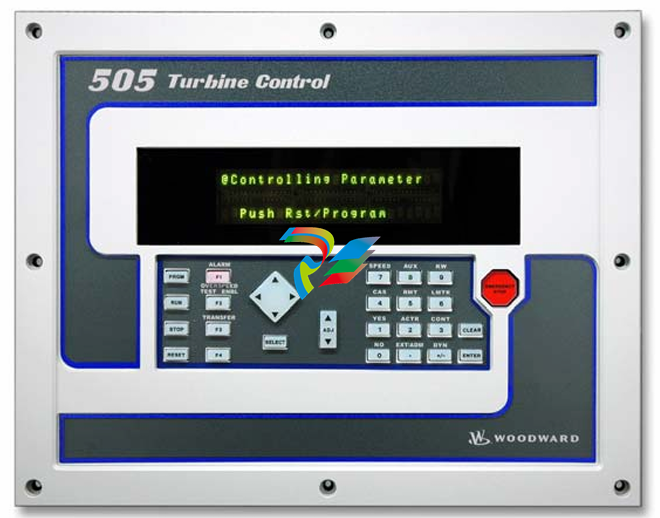
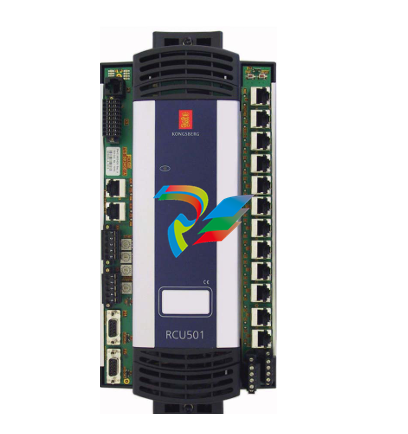
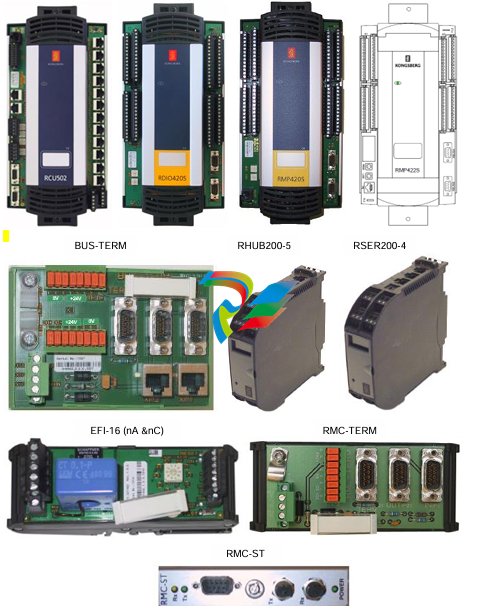
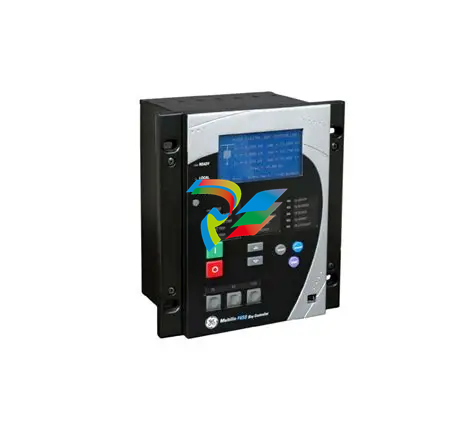
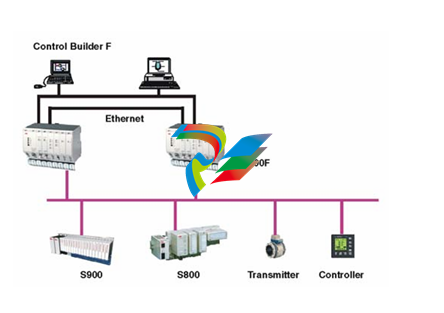
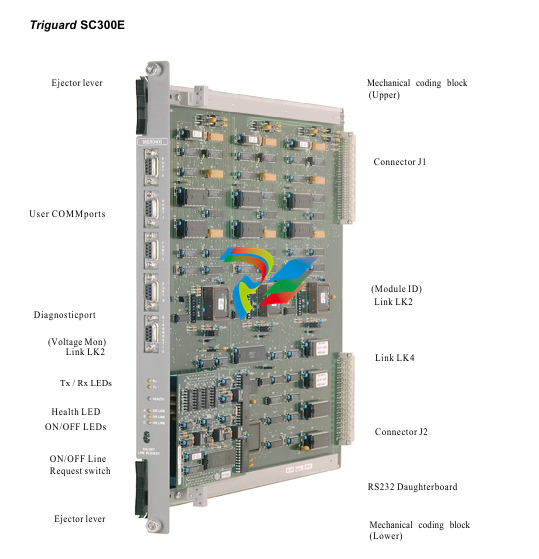
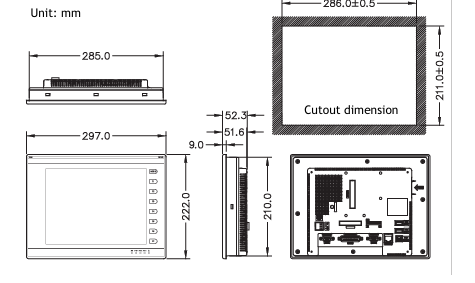
DCS; Industrial control system
Product
Article
NameDescriptionContent
Argument
Current Location:
PRODUCT SHOW
Description
Dual Speed Modules: A Detailed Description
1. Introduction
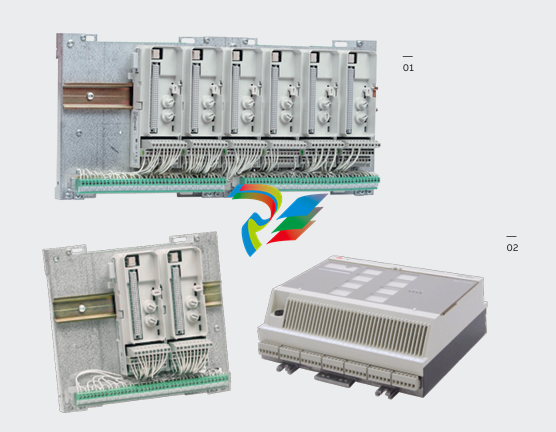
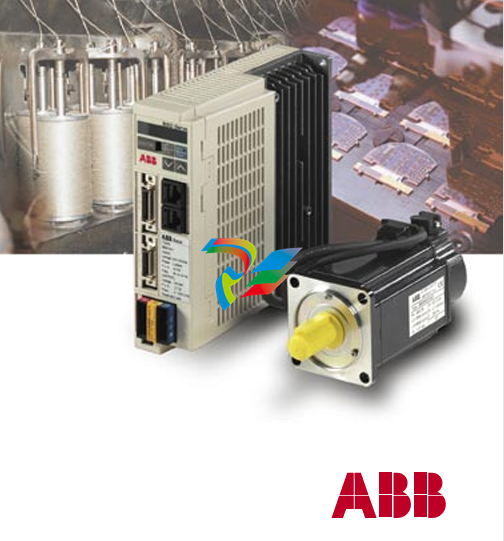
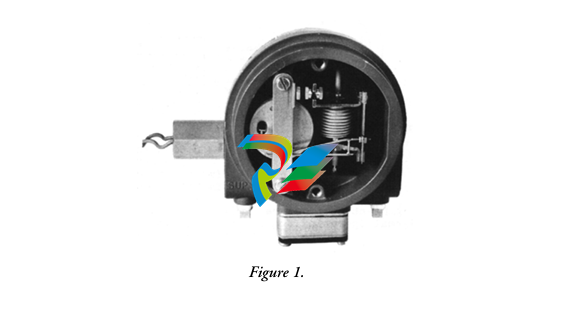
Dual Speed Modules are highly specialized components that play a significant role in various electrical and mechanical systems, particularly those where variable speed control is essential. These modules are designed to provide two distinct speed settings, enabling greater flexibility and efficiency in the operation of equipment, and are widely used in industrial, automotive, and even some consumer applications.
2. Design and Construction
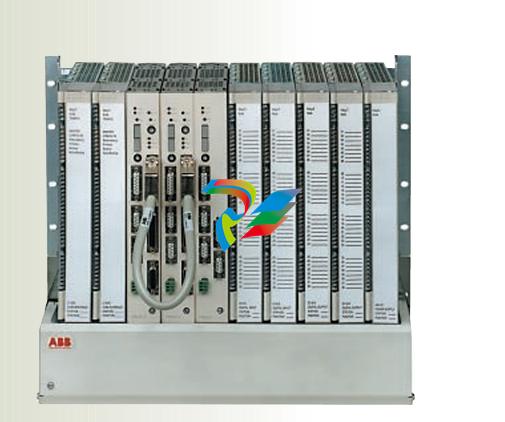
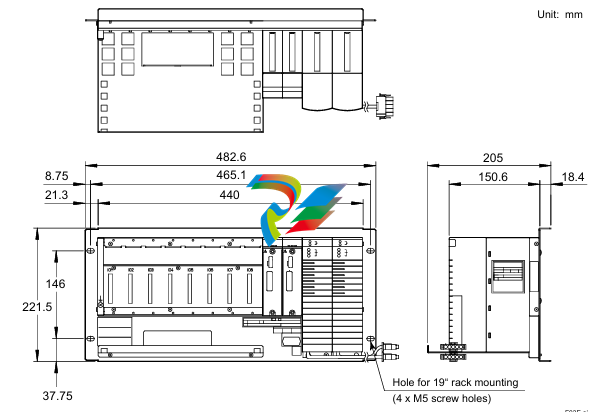
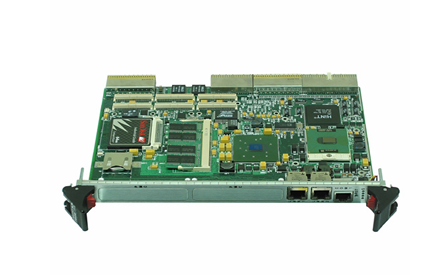
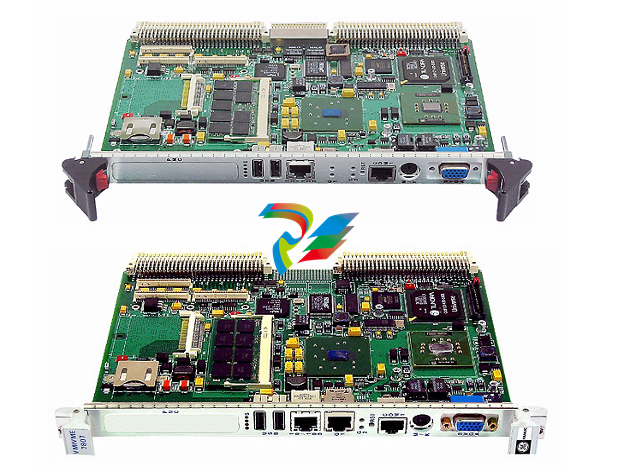
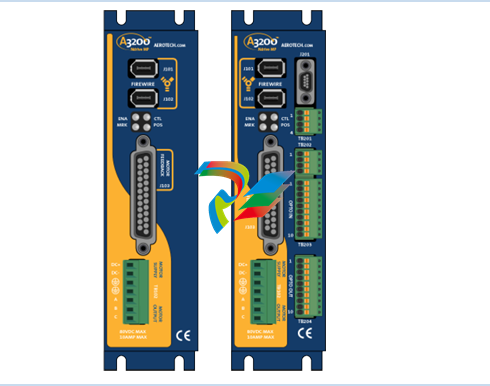
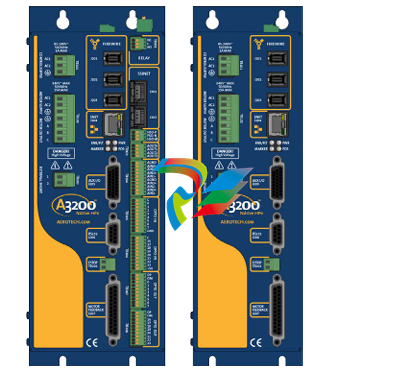
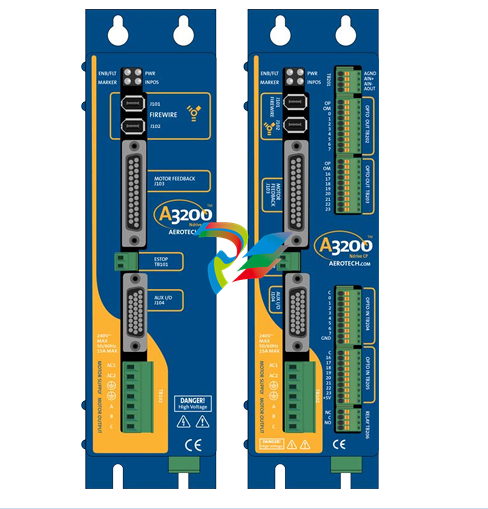
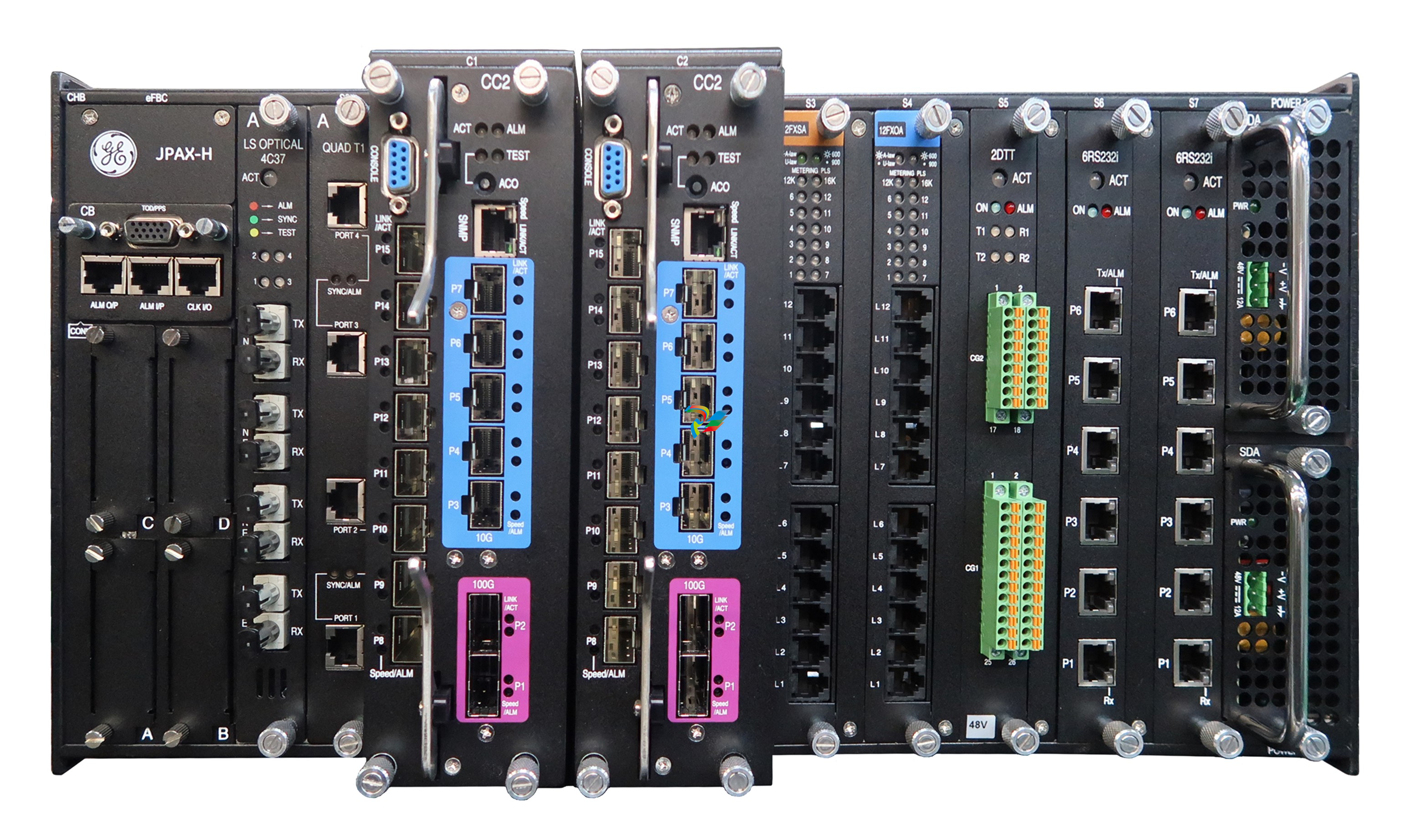
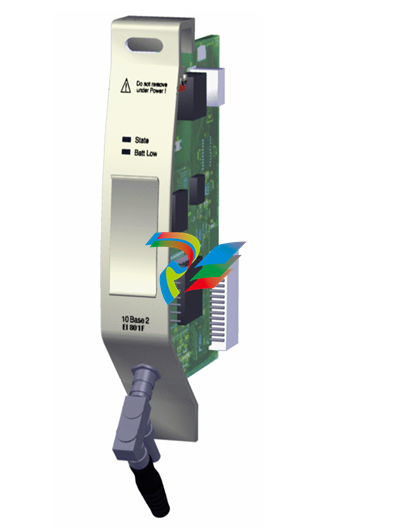
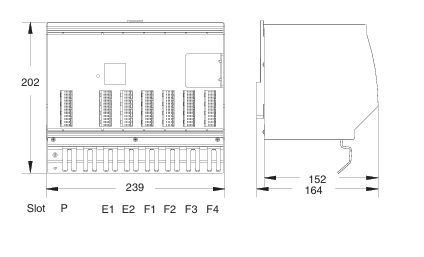
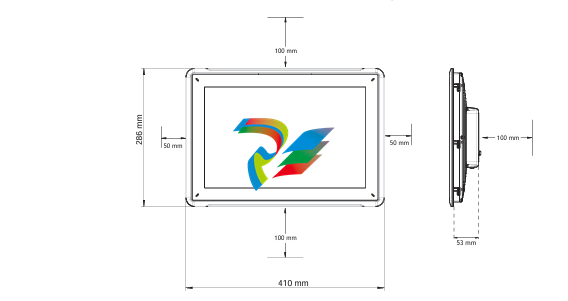
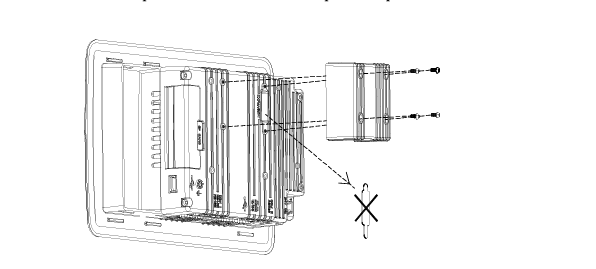
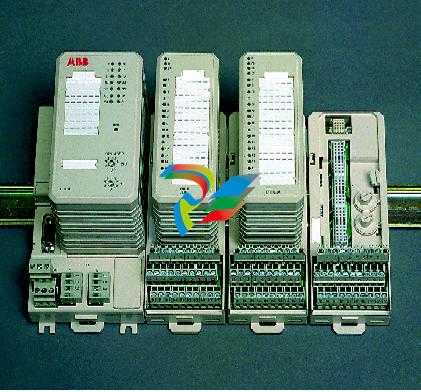
- Compact and Integrated Design: Dual Speed Modules typically have a relatively compact form factor, which allows for easy installation within the limited space available in many systems. They are often integrated with other components, such as motors, gearboxes, or control circuits, to form a cohesive unit. The outer casing is usually made from durable materials like high-strength plastics or metal alloys to protect the internal components from environmental factors like dust, moisture, vibration, and temperature variations.
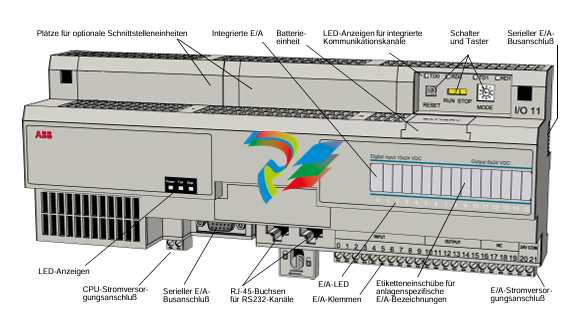
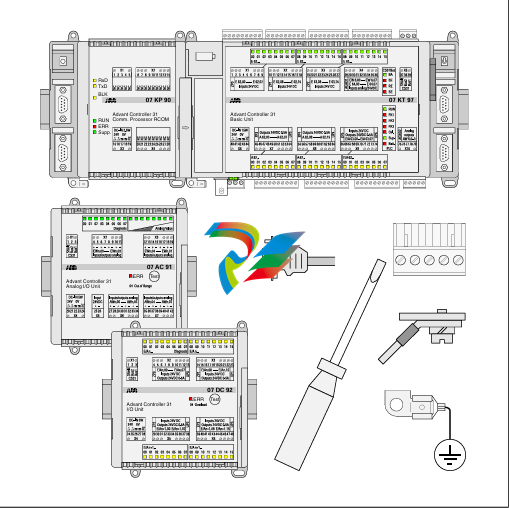
- Internal Circuitry: Inside the module, there is sophisticated circuitry that controls the speed selection and operation. This circuitry may include power electronics components such as transistors, thyristors, or integrated circuits that manage the flow of electrical current to achieve the two different speed levels. There are also often control interfaces and logic components that receive input signals from external sources (like switches or control systems) to determine which speed mode to activate.

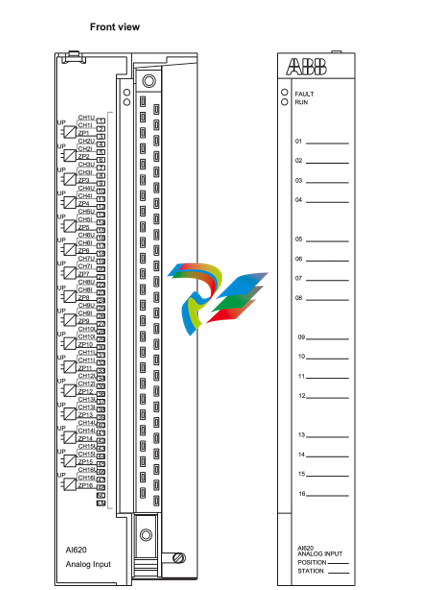
- Connection Points: The modules are equipped with various connection points for power input, connection to the driven device (such as a motor shaft), and interfaces for receiving control signals. The power input connections are designed to handle the appropriate voltage and current levels for the specific application, while the control signal interfaces can be compatible with different types of electrical signals, such as digital signals from a programmable logic controller (PLC) or analog signals from a potentiometer.
3. Speed Control Mechanism
- Two Distinct Speed Settings: As the name implies, Dual Speed Modules offer two predefined speed levels. These speed settings can be configured during the manufacturing process or adjusted within a certain range depending on the specific design and application requirements. For example, in an industrial fan application, one speed setting might be used for normal ventilation purposes, while the other higher speed setting can be activated during periods of increased heat or air circulation needs.
- Switching Mechanism: There are different ways to switch between the two speeds. In some modules, this can be achieved through a simple mechanical switch, where an operator manually toggles between the two options. In more automated systems, the switching is controlled electronically. For instance, a control signal from a central control system can trigger the module to change from one speed to the other. This electronic switching can be based on various conditions, such as time-based schedules, sensor inputs (like temperature or pressure sensors indicating a need for a speed change), or commands from an operator interface.
- Speed Regulation and Accuracy: The modules are engineered to provide accurate and consistent speed regulation at both speed settings. This is achieved through feedback control mechanisms that constantly monitor the actual speed of the driven device (usually with the help of speed sensors like tachometers) and make adjustments to the electrical power supplied to maintain the desired speed. The level of speed accuracy can vary depending on the application requirements but is typically within a small tolerance range to ensure reliable performance.
Purchase history
| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|
Total 0 Record
Customer Reviews
Satisfaction :
5 Stars
No evaluation information